Creating a decision tree involves a structured approach, much like concept mapping but simpler. Instead of a central concept, you start with a critical decision and outline factors branching out. Unlike concept maps, decision trees lack crosslinks and represent data straightforwardly.
The main question is, How do you make a decision tree? Because, crafting one manually requires skill and resources, but time constraints often pose challenges. This is where advanced decision tree tools like EdrawMInd become invaluable. Whether constructing a tree manually or using a tool, the emphasis remains on practical and efficient decision-making. Let’s take look at making a decision tree as soon as possible.
In this article
What is a Decision Tree
A decision tree is a hierarchical model used for decision support, which presents decisions and their potential outcomes in a tree-like structure. It incorporates chance events, resource costs, and utility to comprehensively analyze. This is a method of presenting an algorithm that solely consists of conditional control statements.
Decision trees are widely utilized in the field of operations research, particularly in decision analysis. It assists in determining the most effective strategy for achieving a desired outcome. Additionally, they are highly favored in the realm of machine learning as a valuable tool.
How to Create a Decision Tree in General
Whether using a digital platform or traditional paper, creating a decision tree involves a structured series of steps. Here's a breakdown of the process:
Step 1: Define the Root Decision
Start by identifying the main decision or objective. This becomes the root of your decision tree. For example, "Choosing a Career Path."
Step 2: Branching Options and Risk Assessment
Draw arrows or branches from the root to represent various decision options. Attach notes to each branch detailing associated costs and risks. Example options: "Software Development," "Data Science," "Marketing."
Step 3: Attach Leaves for Expected Outcomes
At the end of each branch, add square leaf nodes to represent expected results or subsequent decisions. Use circles for uncertain outcomes. Example outcomes: "Job Satisfaction," "Career Growth," "Exploration Period."
Step 4: Determine Probability of Success
Research and assess the probability of success for each decision option. Utilize data, industry trends, and personal experiences to estimate success rates. Example: High success probability for "Software Development" based on market demand.
Step 5: Evaluate Risk Vs Reward to Make Decision
Calculate the risk vs reward for each option by considering potential gains and losses. Use this analysis to inform your final decision. Example: "Software Development" has high reward potential but moderate risk due to evolving technologies.
Tip: Go back to the decision tree often and make changes as needed as things change or new information comes in. This looping process makes sure that the decision tree stays useful and useful.
How to Make a Decision Tree in EdrawMind
It could take a lot of time to build a decision from scratch. However, software like EdrawMind has made mind mapping easier and faster. Now that we have this tool, let's create a decision tree and see whether it helps.
First, download EdrawMind on your computer. You can access your ID by logging in with your social media accounts. Or, you can create a new wondershare account in a few minutes.
Method 1: Creating a Decision Tree from Templates
Step 1:Choose a Template
From the main page, go to the Mind Map Gallery. A lot of different thought maps will be shown. Scroll down until you find the right Decision Tree or mind map. When you're done, click Duplicate.
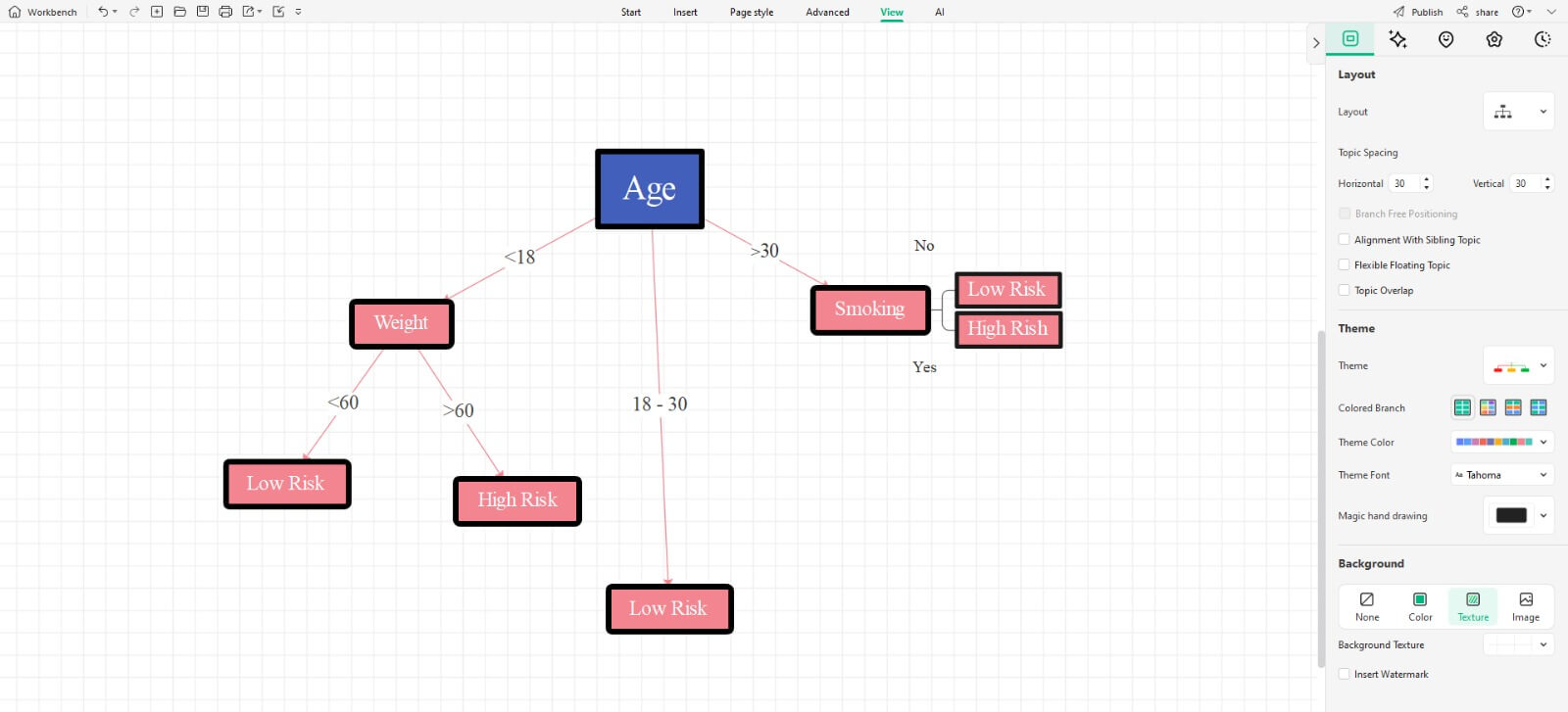
Step 2:Customize your Template
You can alter the layout by adding or removing topics and subtopics from the homepage. Update the information and make the decision tree's theme fit your needs. Now the decision tree is complete.
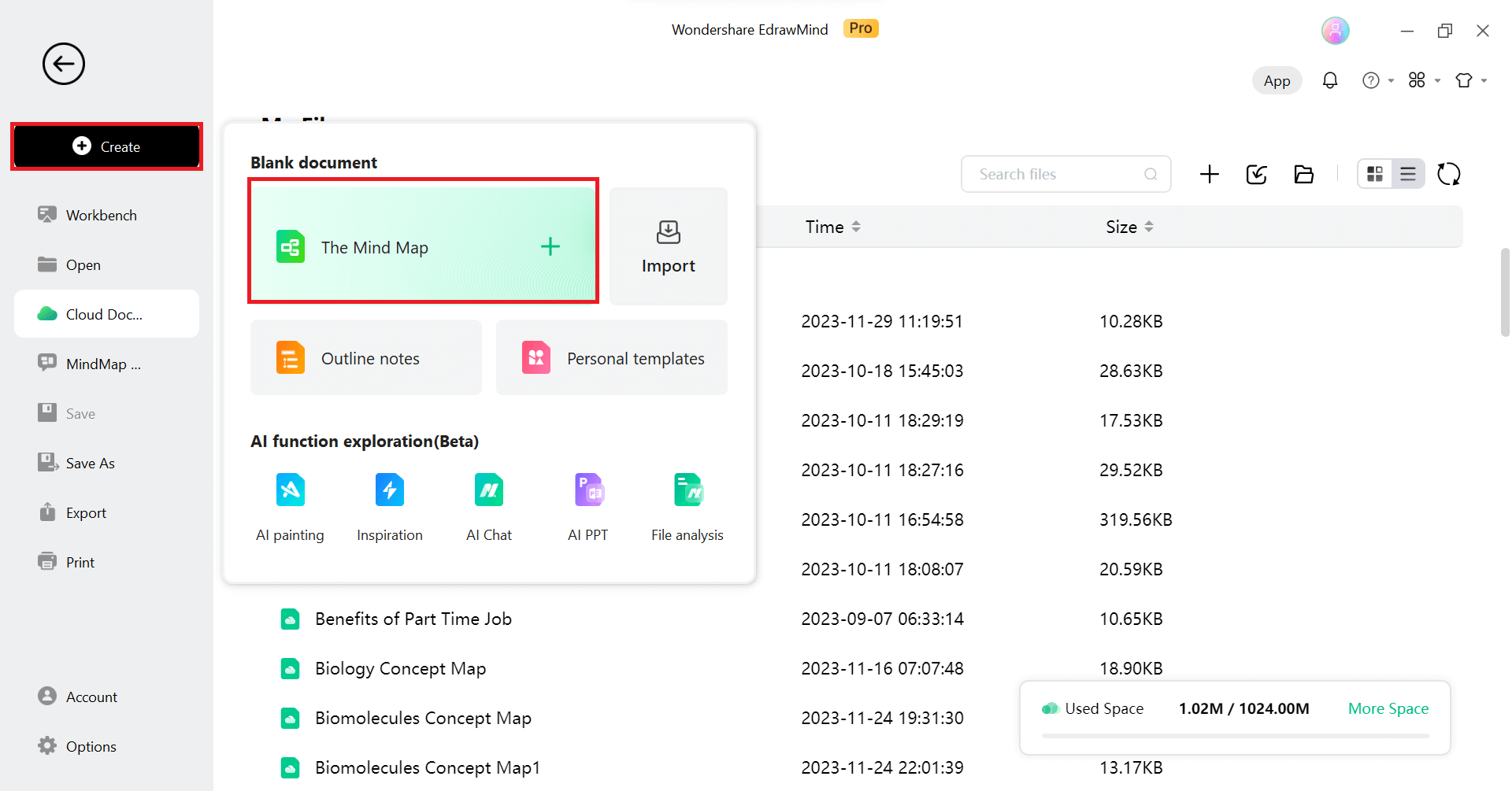
Method 2: Creating a Decision Tree from Basic
Step 1:From Scratch
Suppose you have a preference for creating a mind map from scratch instead of using pre-made templates and have the time to do so. To access the editing panel, simply click Create and then select The Mind Map.
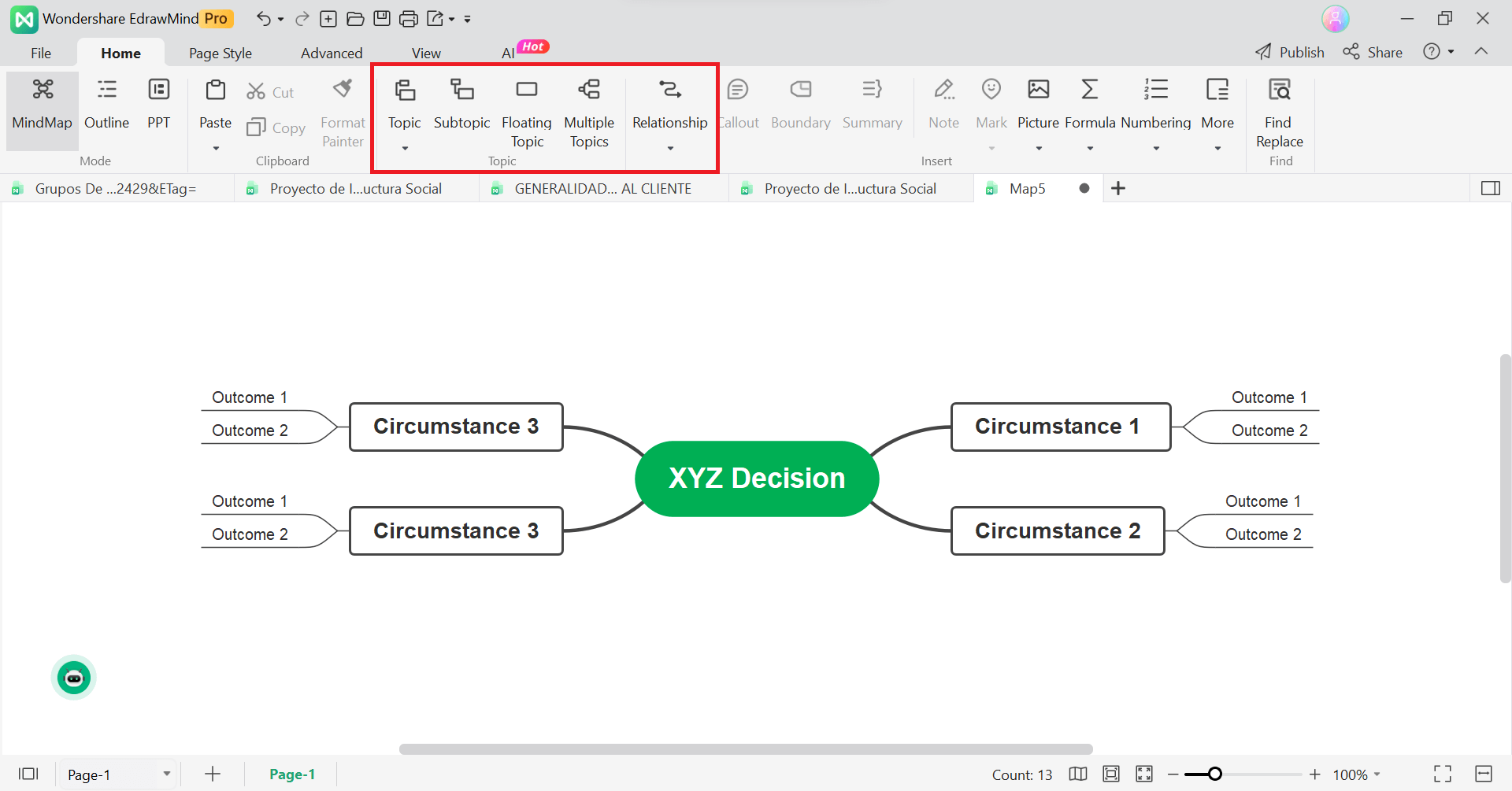
Step 2:Add information
There is a mind map layout on the EdrawMind editing canvas. This is how it works:
- Use the top menu to expand the branches. You can add themes and subtopics.
- Once you're satisfied with the plan, fill in the boxes with information.
- Use the floating topics to add facts that back up your claims.
- To connect circumstances and outcomes, use arrows.
Step 3:Change the format and customize it
Once you're done rewriting and organizing your decision tree, it's time to make it look appealing by adding your own touches. To change the fonts, colors, styles, and shapes, click the Page Style tab.
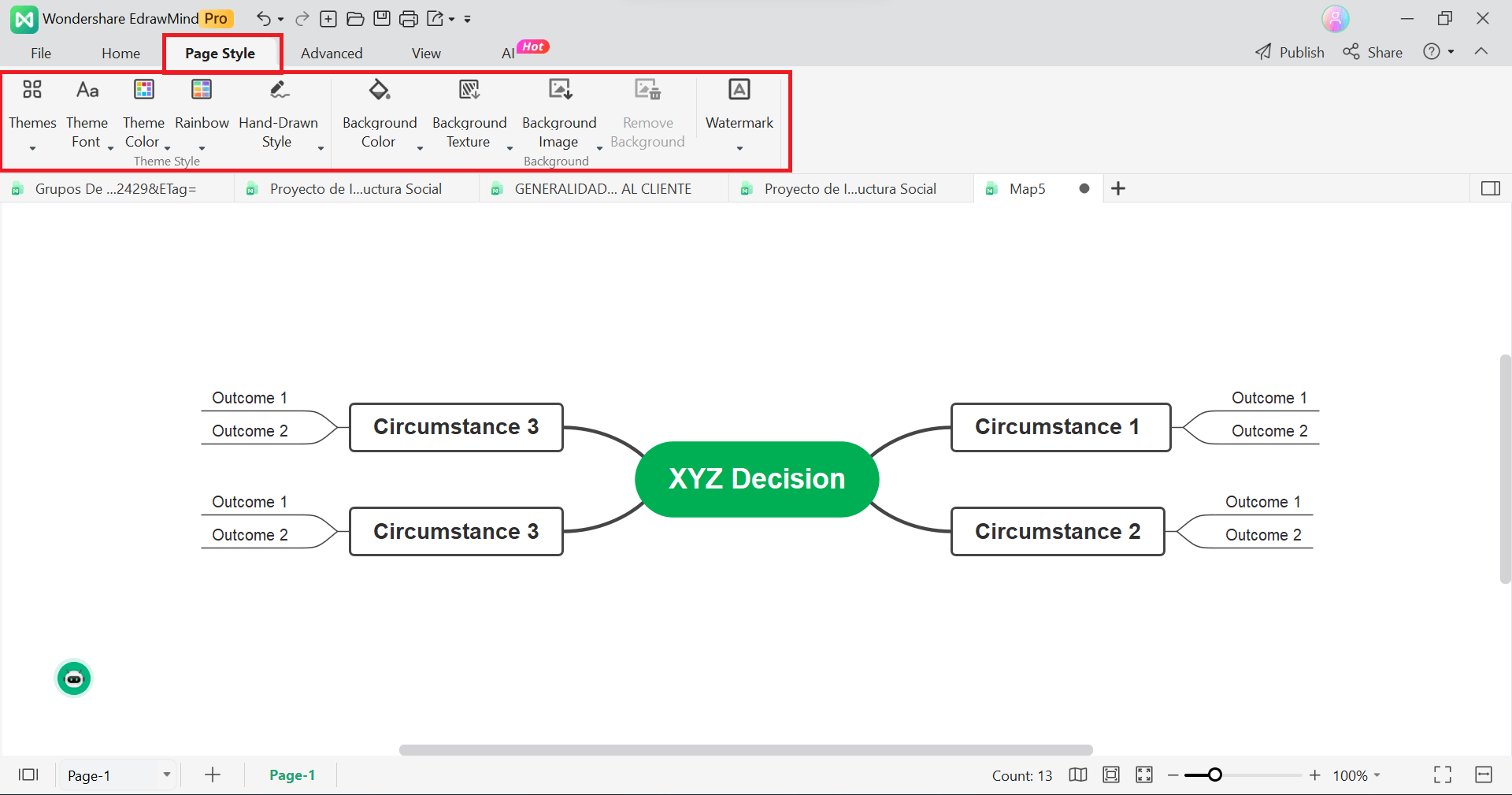
Step 4:Save and Share
It is time to save your decision tree on your computer once you are happy with how it looks. Just go to the File menu, click Save as, and pick the way you want to save the file. You can also use the Share button in the top right corner to send your design to other people.
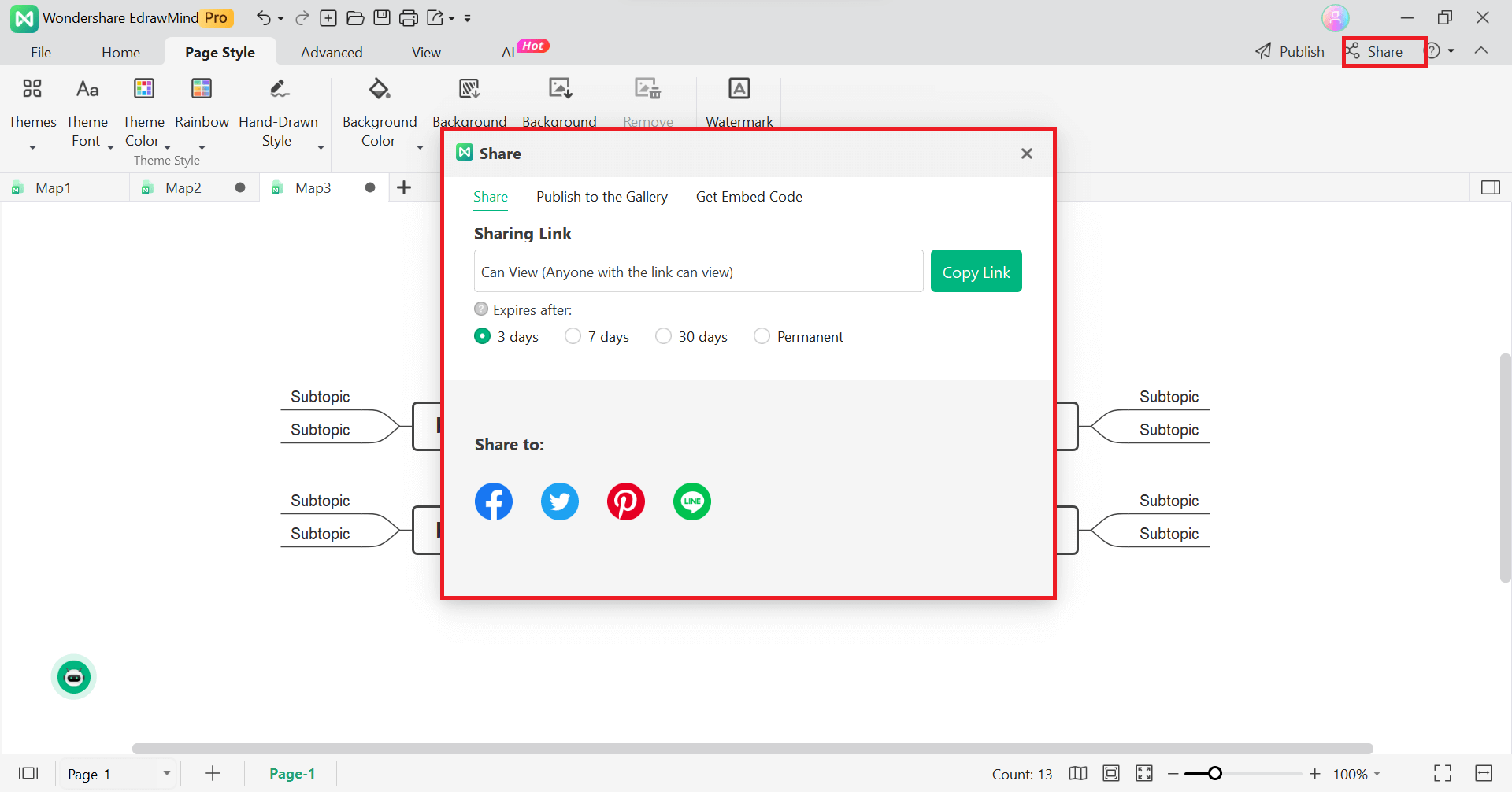
So, this is how you can make a decision tree. You can change it to fit your needs and wants by using templates or starting from scratch.
Free Decision Tree Maker
EdrawMind is one of the best mind-mapping programs because it has all the features that users of all skill levels need. The paid features of this tool give you even more advanced features than the free version, making it the best choice for mind mapping.
Here are some reasons why EdrawMind is the best program for making decision trees:
1. AI Integration
The latest update to EdrawMind adds AI technology, making mind mapping easier with one-click input hints. The AI programs do the summarizing for you, which saves you time. Edraw AI can be used to ask questions and solve problems. It is a complete and time-saving tool as it lets you easily make audio and video presentations that can be exported for added ease.
2. Personalization
The modification options in EdrawMind are extensive. There are many ways to change the layout of a mind map, such as changing the size, color, and style of each part. These tools help you get your thoughts and ideas across more clearly.
3. Several Templates
In EdrawMind's mind map gallery, you can find many handy templates for making diagrams fast. It makes it easier to make thought maps for many uses, like managing projects, coming up with new ideas, and teaching.
4. Different ways to export and share
Users of EdrawMind can easily send their mind maps to others by saving in multiple formats. You can export them as PDFs, Word documents, Excel spreadsheets, PowerPoint presentations, and more.
Tips for Creating a Decision Tree
The Decision tree crafting process can be a hard nut to crack for beginners. Let’s take a look at tips on how you can make an effective decision-making tree.
- Impartially and thoroughly, list all the options for each factor.
- To quantify the impact of each component in the decision-making process, assign weights or scores after evaluating their significance.
- Keeping in mind the weights and possibilities, methodically follow the branches. To make a data-driven choice, choose the one with the highest cumulative score.
- Highlight the most important aspects to keep the decision tree brief. Make careful use of color and line thickness to refine the layout for clarity.
Conclusion
Creating a decision tree involves illustrating ideas and concepts similar to how our minds work. Unlike mind maps, decision trees organize information with several parent and daughter nodes, making them excellent for structuring complex data. Today, decision trees find applications across various fields like healthcare, education, and business.
However, crafting a decision tree requires patience, practice, and resources – a challenging task for busy professionals. If you are in a similar situation, consider using advanced tools like EdrawMind for decision tree creation.
What distinguishes EdrawMind is its AI technology, which swiftly generates intricate decision trees using prompts. This saves professionals valuable time while ensuring a straightforward and efficient approach to complex decision-making.




