Mind mapping seemed simple—draw a few circles, connect ideas, and get organized. But some maps worked perfectly, while others left me feeling even more disorganized.
The problem? Each type of mind map serves a different role. Some fuel brainstorming, while others help structure complex information. Choosing the wrong format can slow you down.
So, in this write-up, I'll break down the different types of mind maps and how to choose the right one for you.
In this article
What is a Mind Map?
A mind map works as a blueprint for my thoughts. It organizes ideas when projects become detailed or information appears scattered.
I begin with a central idea and let branches extend to related thoughts, facts, or tasks. Each branch grows into smaller segments, forming a simple yet adaptable design.
The process remains simple. I place my main topic at the center of a blank page or digital screen (my preferred choice). Then, I draw lines to key ideas and extend branches to add details. It gives the flexibility to customize connections, mark key points, or add visuals.
I use them when I need to sort my thoughts for various tasks. I plan projects, summarize books, prepare presentations, and organize personal goals. The visual structure helps me identify patterns and link ideas.
Common Types of Mind Maps
Over time, I have tried many mind map types. Each form meets different needs. Below is a detailed look.
Basic Mind Map
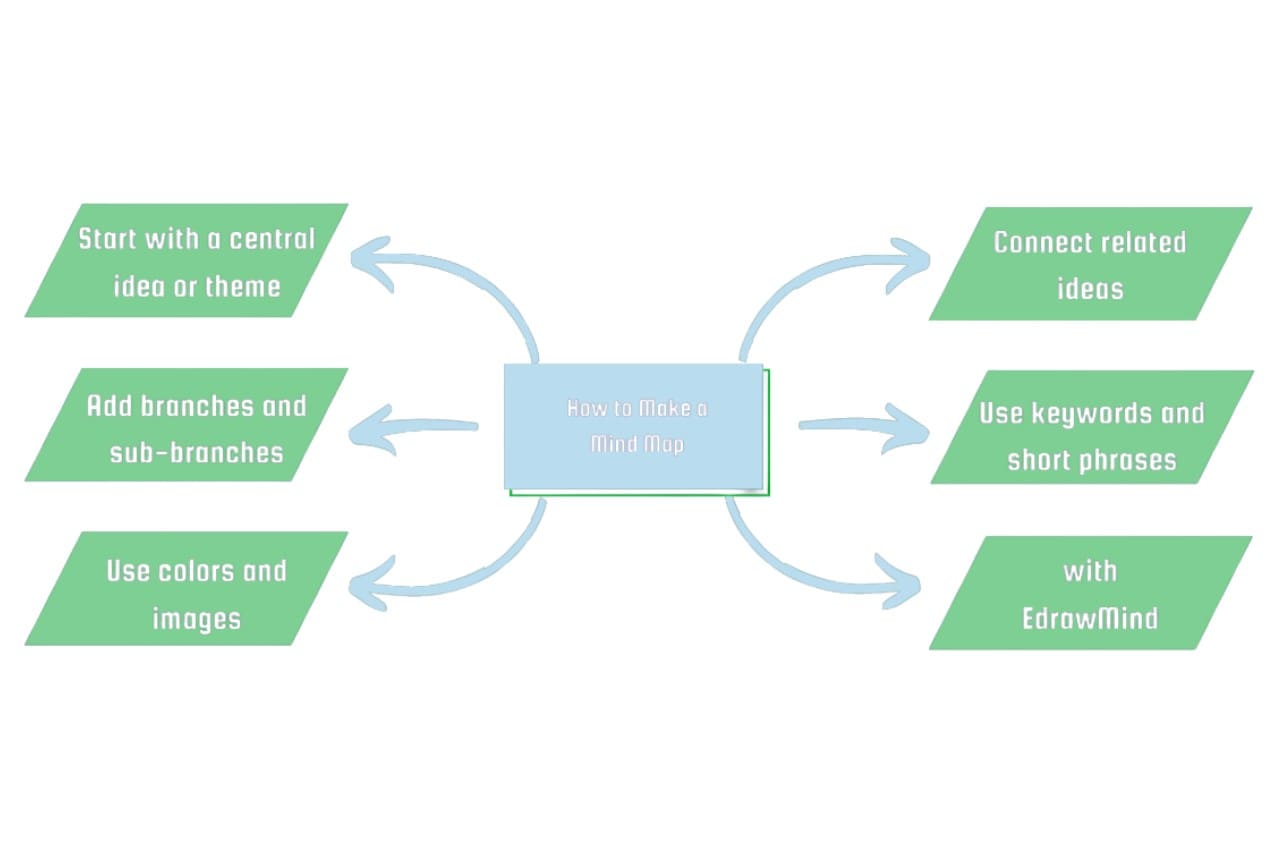
How It's Built?
Start with a central idea in the middle. Branches extend outward. Each branch holds a key theme with further sub-branches.
Where does it work best?
This format suits brainstorming, note-taking, and general organization. It also works for planning travel and outlining writing.
Who Finds This Most Useful?
It is helpful for students, professionals, creatives, and those planning simple tasks.
Why Choose This Approach?
It supports non-linear thought. It is quick and flexible.
Pro Tips for Getting Started
Mark themes with colors or icons. Keep branches brief. Start wide and then add detail.
Radial Map
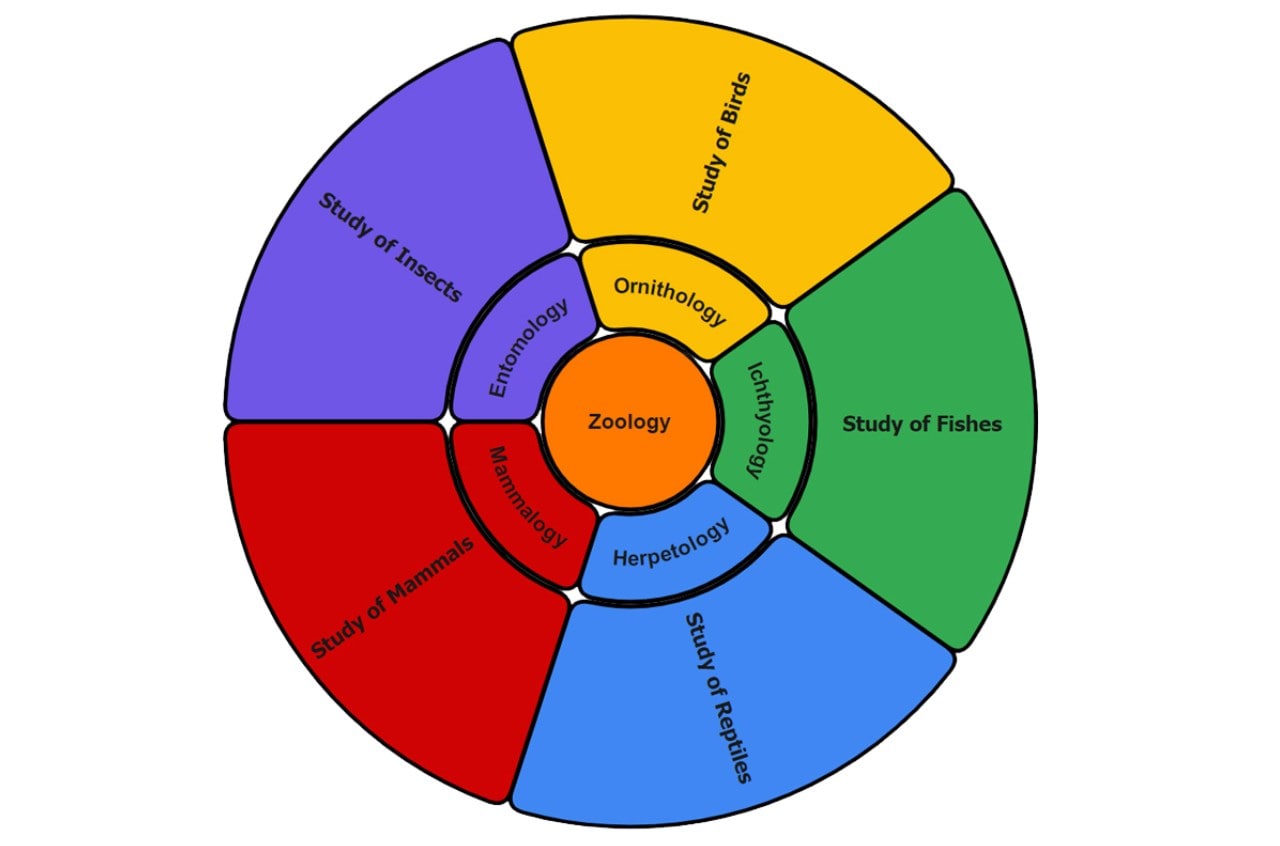
How It's Built?
This map shows ideas in a circular, balanced layout. Ideas radiate out in even layers.
Where does it Work Best?
It is effective for breaking down hierarchical data, such as company goals or course syllabi. Also, it helps plan product roadmaps.
Who Finds This Most Useful?
It suits teams and individuals looking for a balanced view.
Why Choose This Approach?
It gives a balanced overview. It keeps relationships clear and suits long-term planning.
Pro Tips for Getting Started
Ensure symmetry to show a clear hierarchy. Use color coding for groups. Avoid too many layers.
Bubble Map
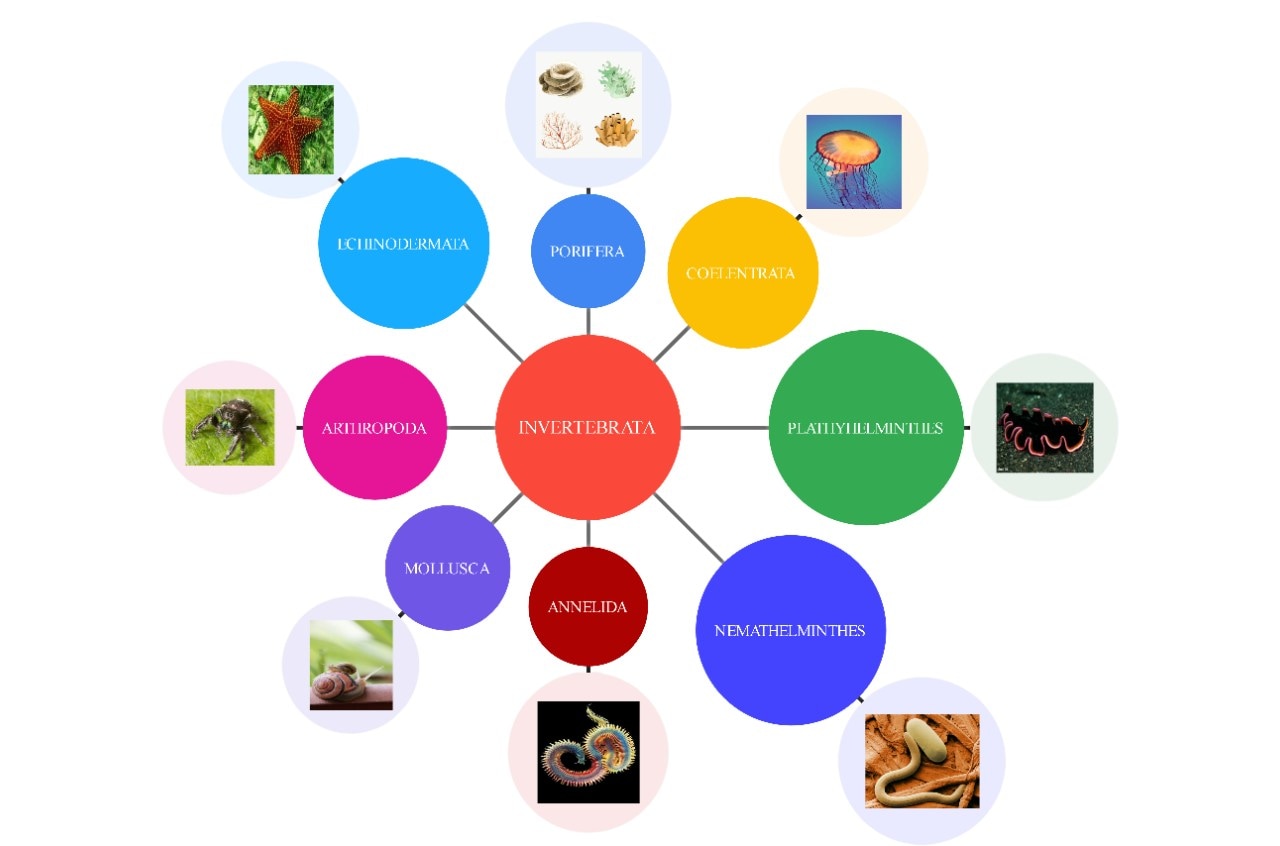
How It's Built?
This map is like a web of circles. Each bubble encloses a concept. Lines connect bubbles in multiple directions.
Where does it Work Best?
It is ideal for descriptive brainstorming, character analysis, and exploring idea links. Writers and marketers use it often.
Who Finds This Most Useful?
It works for writers, teachers, and professionals with interconnected ideas.
Why Choose This Approach?
It shows how ideas relate. It offers flexibility without a strict order.
Pro Tips for Getting Started
Vary bubble sizes to show significance. Connect ideas freely. Add colors for clarity.
Tree Map
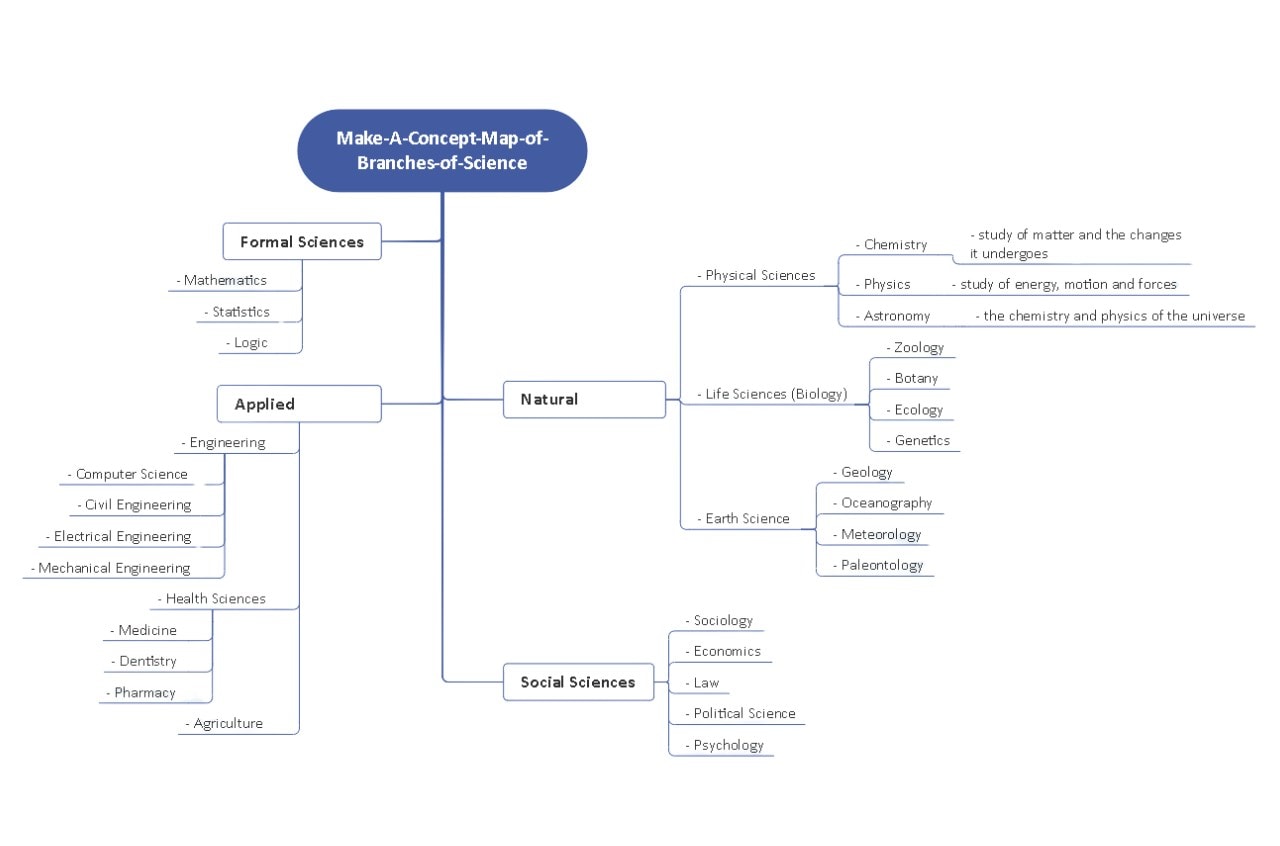
How It's Built?
This diagram works top-down. A central idea sits at the top, and branches spread downward.
Where does it Work Best?
It helps classify information and break down complex subjects. It is common in business, legal, and educational settings.
Who Finds This Most Useful?
It suits business professionals, teachers, and analysts.
Why Choose This Approach?
It organizes information into precise levels and helps make rational decisions.
Pro Tips for Getting Started
Keep main branches broad and details focused. Avoid too many nested levels. Use indentations or numbers as needed.
Organizational Chart
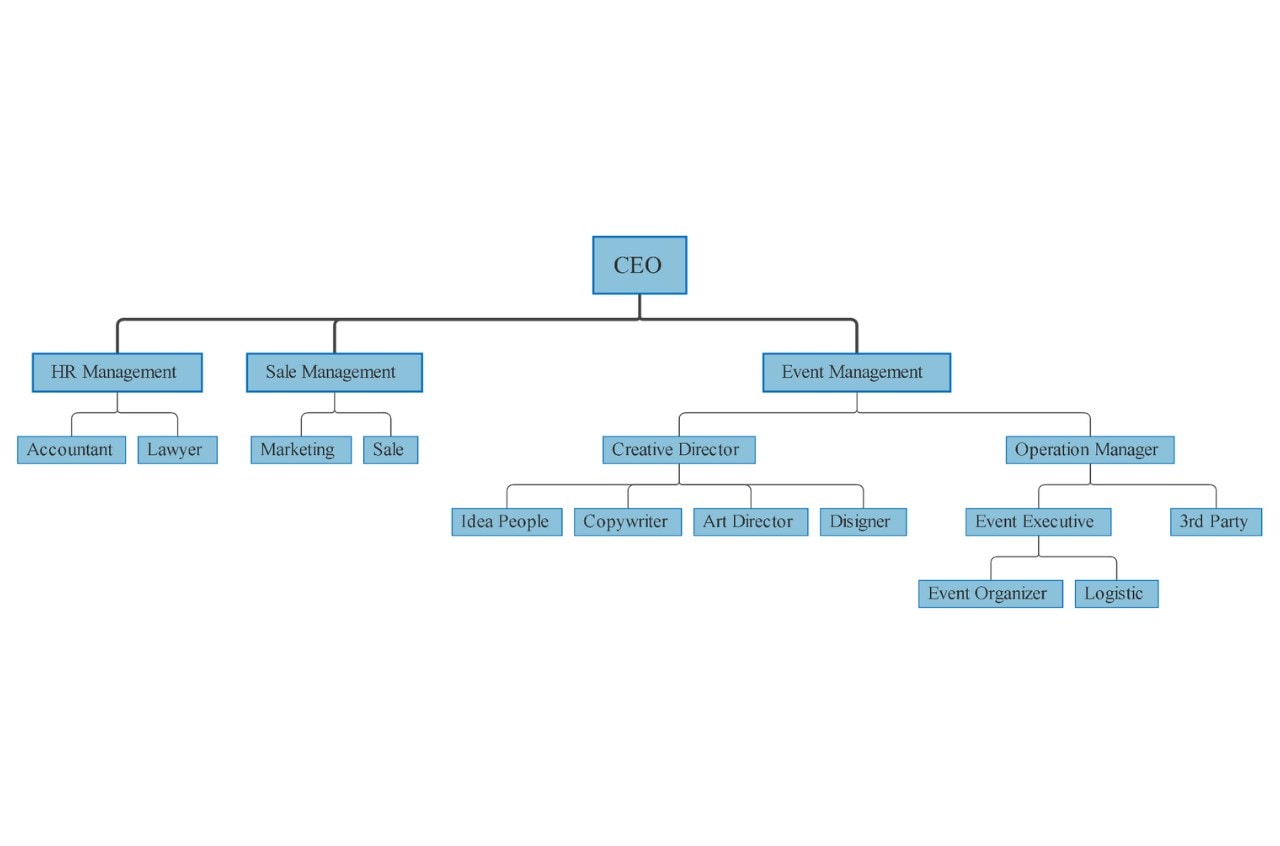
How It's Built?
This chart shows a strict hierarchy. Entities are arranged in specific levels, either top-down or left-to-right.
Where It Works Best?
It is used to show team structures, reporting relationships, or department divisions.
Who Finds This Most Useful?
It fits HR staff, managers, and company leaders.
Why Choose This Approach?
It defines roles and reporting lines clearly. It helps visualize team structure.
Pro Tips for Getting Started
Use different shapes to mark different roles.
Maintain an even hierarchy.
Highlight reporting lines.
Flow Map
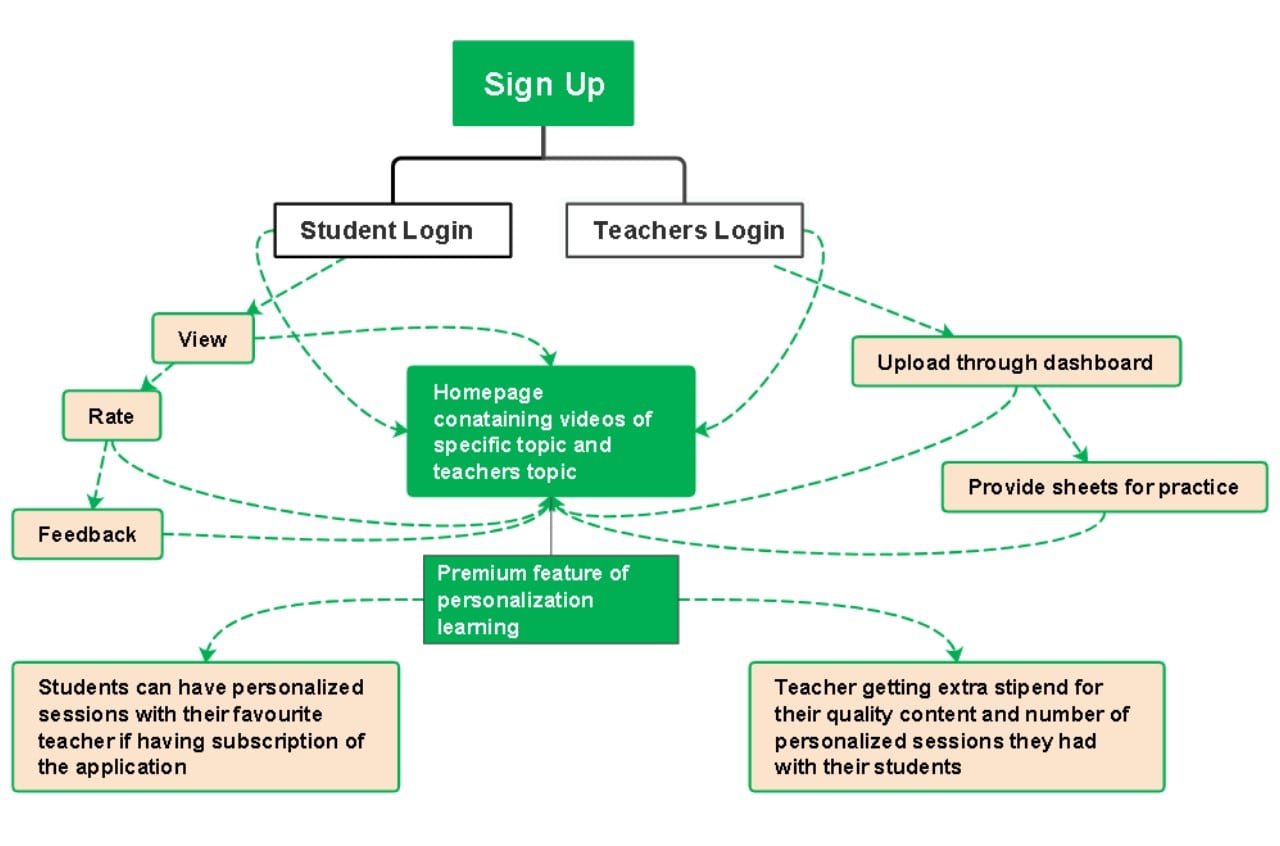
How It's Built?
This diagram follows a step-by-step format. Stages connect with arrows.
Where does it Work Best?
It is common for process mapping, workflow analysis, and creating guides. Project managers, engineers, and teachers use it.
Who Finds This Most Useful?
It works for process-focused professionals and teams.
Why Choose This Approach?
It breaks complex processes into clear steps. It shows the order and dependencies.
Pro Tips for Getting Started
Use arrows to show the flow. Keep each step short. Use colors to mark decision points.
Concept Map
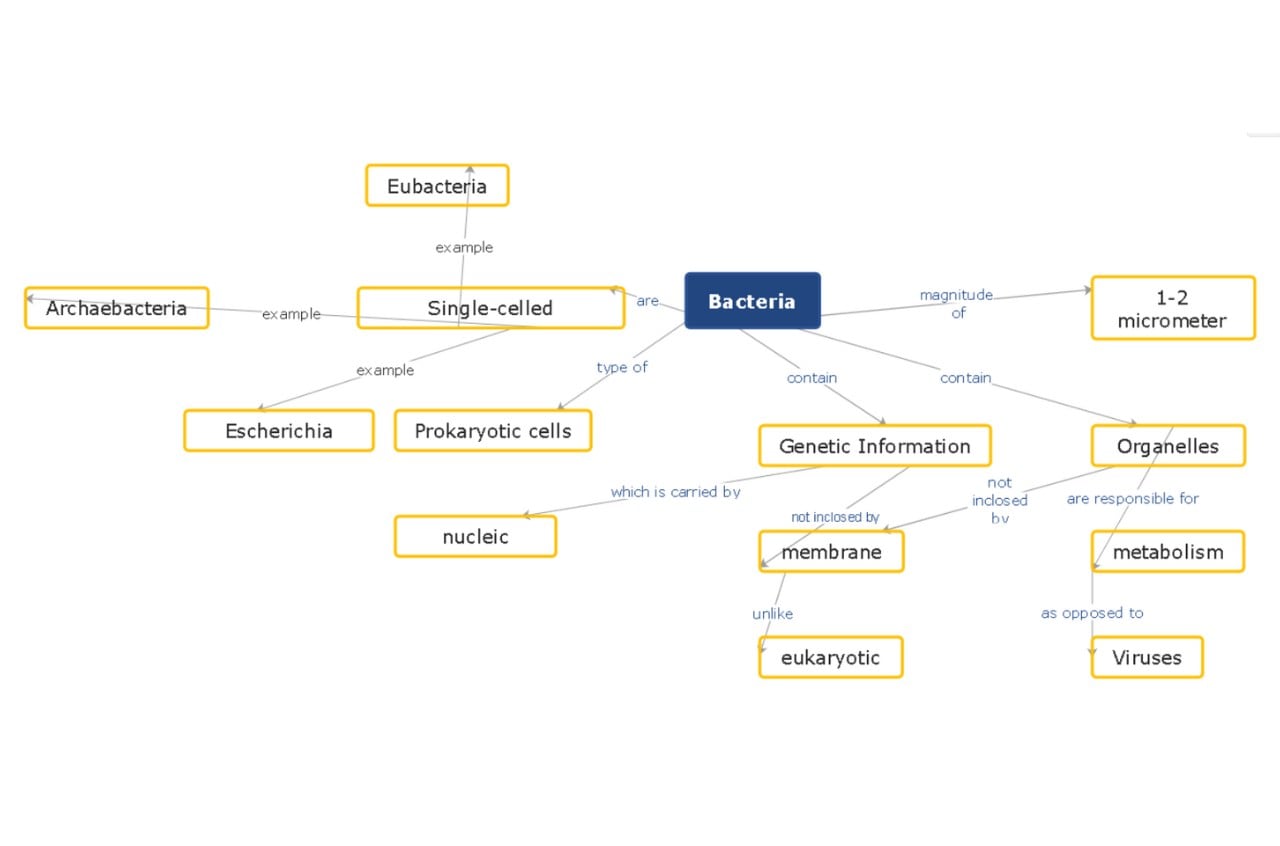
How It's Built?
This map connects ideas with labeled links. It shows how one idea leads to another.
Where It Works Best?
It is used in research, planning strategies, and managing knowledge.
Who Finds This Most Useful?
It fits researchers, planners, and educators.
Why Choose This Approach?
It shows complex relationships clearly. It encourages deeper analysis.
Pro Tips for Getting Started
Label each link to explain the connection. Use a hierarchical structure where needed. Keep links clear and direct.
Fishbone Diagram
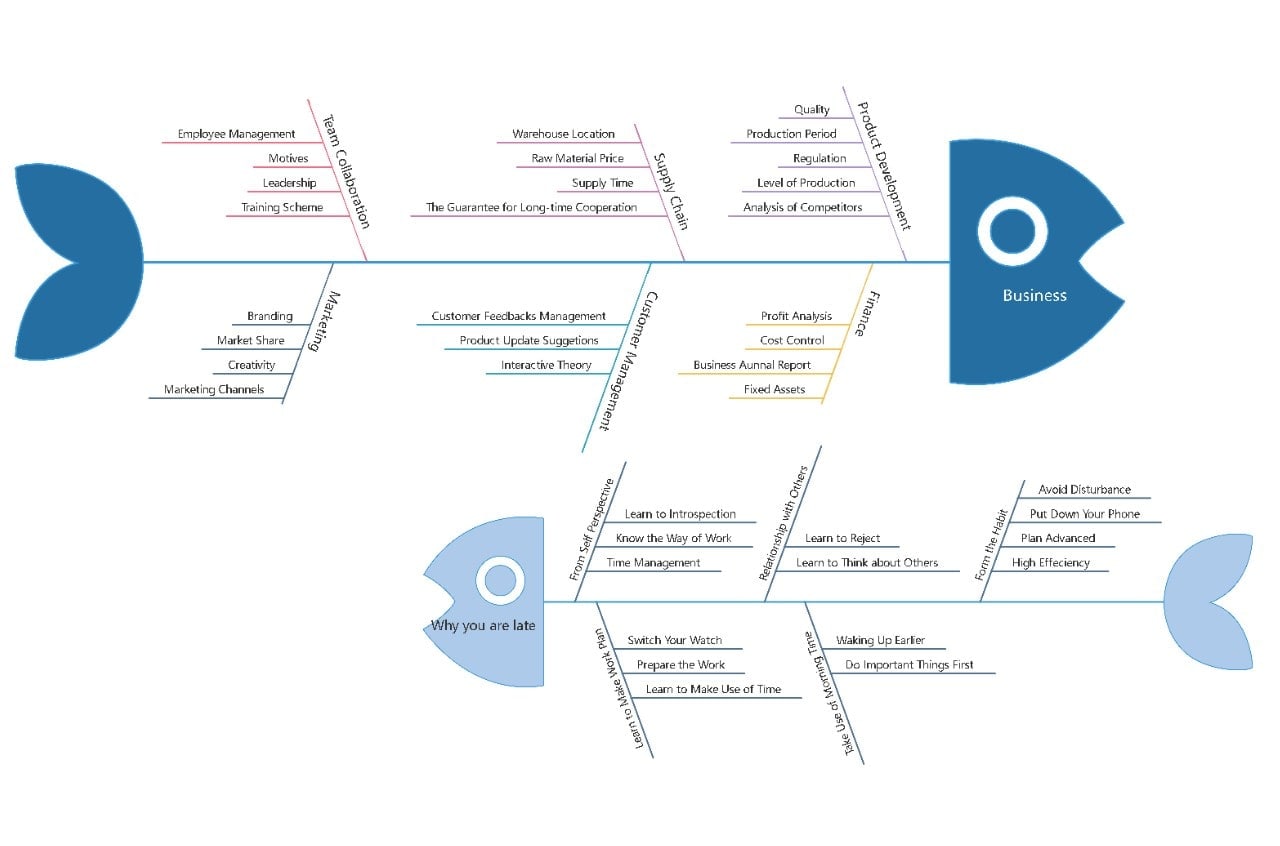
How It's Built?
This diagram type resembles a fish skeleton. The main issue appears at the head, and contributing causes branch off from the spine.
Where It Works Best?
It is used for root cause analysis in quality control and problem-solving.
Who Finds This Most Useful?
It serves business analysts, engineers, and problem-solving teams.
Why Choose This Approach?
It identifies root causes clearly. It organizes factors systematically.
Pro Tips for Getting Started
Group factors into logical categories like People, Process, or Equipment. Follow a step-by-step approach. Keep branches uncluttered.
Each mind map type has its own use. With the formats reviewed, here’s how to decide on the mind map type that fits your tasks.
How to Choose the Right Mind Map Type for Your Needs?
When choosing the mind map type, I begin by considering some notable factors. These factors help organize thoughts and keep the plan actionable.
- I assess the information's complexity and the required level of detail.
- Then, I note if the map is meant for personal use or a team effort.
- Next, I check the ease of updating the map.
- Finally, I also consider the need for clear visuals and details like color coding or a hierarchy.
Now, here's how I choose them for various needs:
For Studying and Note-Taking
I use a basic mind map for lectures or chapter summaries. Its open design lets me write ideas quickly. I can group related concepts with ease. Its simplicity speeds up the review.
For Business Strategy and Planning
I choose a radial or concept map for planning. The radial layout spreads ideas evenly. A concept map helps me connect business goals with trends and challenges. These maps make strategies clear.
For Project Management
I favor a flow map or tree map for projects. A flow map outlines each step and shows task dependencies. A tree map breaks a project into small parts. Deadlines and roles are easy to spot.
For Creative Brainstorming
I prefer a bubble map for creative sessions. It lets ideas associate freely. This map encourages unique connections and new views.
For Personal Goal Setting
An organizational chart fits my goal setting. It visualizes long-term aims and the steps needed, showing supporting roles and resources. The clear structure keeps me on track.
Matching the mind map style to your task helps organize thoughts and guide action. Once you select the right mind map style, use EdrawMind to bring your insights to life.
Start Mind Mapping Now for Free with EdrawMind
When ideas are scattered or planning feels heavy, the right mind-mapping tool matters. I have tested several mind-mapping tools, but EdrawMind has worked best for me. It suits both solo and team brainstorming and turns thoughts into structured visuals.
User-Friendly Interface with Huge Templates
Starting is simple. EdrawMind provides over 6,000 ready-made templates, covering everything from simple brainstorming to detailed business plans. I select a template, make minor adjustments, and then focus on the content.
Advanced AI-Powered Features
I value the AI structuring feature. It organizes thoughts without extra effort. You only need to input your ideas and let the tool shape them. This helps build maps quickly and clearly.

Live Collaboration Tools
Mind mapping can be a team activity. EdrawMind supports real-time collaboration. I have used it with remote colleagues to refine project plans. Everyone sees updates immediately.
Seamless Export and Integration Options
Once the map is complete, exporting is easy. The tool supports formats like PDF, Word, and PowerPoint, along with cloud services. I often integrate these maps with other tools in my work.
Whether you are studying, planning projects, designing strategies, or brainstorming creatively, EdrawMind offers a valuable space for your ideas. Start for free.
Generate a mind map with AI
Enter your prompts and let's generate a mind map now
Conclusion
My experience with mind maps explains that the right mind map type can shape scattered thoughts into structured plans.
Every type, from radial maps to fishbone diagrams, brings distinct advantages for study, strategy, or creative sessions.
I recommend trying various techniques to see which boosts your clarity and productivity. This practice helps you turn abstract ideas into clear actions.
EdrawMind remains my go-to tool for experimenting with different mind-mapping needs. You can give it a shot for free right now.





