For every academic institute or student, effective learning is considered the cornerstone. Over several years, note-taking has played an important part in this process. However, with the advancement in education and refinement in teaching methods, most teachers have recommended mind mapping note taking techniques.

As the name suggests, mind mapping visualizes different ideas and information, typically designed around a central topic. For note-taking, we always start with it and add different subtopics as per the gravity of the topic. This way, it facilitates a more holistic view of the entire subject.
This EdrawMind guide will explore the benefits of mind-mapping note-taking methods and offer practical guidance on using them to ace tests and exams.
In this article
What is the Mapping Method for Note Taking
The mind mapping method for note-taking is a dynamic technique that lets the students create visually rich mind maps representing the information as a whole. Mind maps are graphical tools that usually start with an idea and branch out to topics. Through this process, students can create a web of interconnected information.
Some notable benefits of using mind mapping for note-taking are:
- Enhanced Comprehension: Mind maps provide a deeper understanding of any complex topic by helping the students visualize different relationships between sub-topics or ideas.
- Improved Retention: Students who create mind maps and color code different branches tend to retain the information longer.
- Improved Organization: Mind mapping for note-taking lets the students organize complex topics into smaller parts.
- Creative Expression: Students become more creative when making mind maps for note-taking.
- Problem-Solving: With mind maps, one can easily brainstorm to identify the actual cause of any problem.
When students start making mind maps, they often wonder how this visualization differs from traditional methods. In short, note-taking is a linear form of summarizing important information. In contrast, mind maps follow a more nonlinear process.
The difference between mind-mapping note-taking and over the traditional method is explained below:
| Sr. No. | Mind Maps | Traditional Note-Taking |
| 1. | Mind maps use a radial structure, like a spider or Fishbone diagram. | Traditional note-taking is linear and follows a straight hierarchy. |
| 2. | They are visually engaging. | Traditional notes rely on texts. |
| 3. | They emphasize more on connections between different ideas. | It is very hard to make any connections because of its linear form. |
| 4. | The topic's summary can easily be understood. | You need to go through the entire content to find the summary. |
As you saw, mind mapping has an edge over the traditional note-taking method. There are several scenarios where one can use the mind-mapping note-taking method, like:
- The student needs to capture key points and find relevant connections in lectures and classes.
- During group sessions, when the student needs to generate new ideas or review the notes from the textbooks.
- When you need to tackle a complex problem.
Why is Mind Mapping Note Taking Helpful and Effective for Students
When teachers incorporate mind mapping into their curriculum, they ensure students grasp complex subjects easily. With a well-defined mind mapping, students can retain the information longer and streamline their entire syllabus.
Some of the most important reasons why the mind mapping note-taking method is helpful for students are:
- Memory Retention: In mind mapping, students add visual elements, like cliparts, icons, and images. This makes the diagram's content more memorable to the students at the time of tests.
- Organization: When making a mind map, students can organize their thoughts and topics in an organized manner. This way, they can even identify any hidden connection between subtopics, which might have been left untouched if they had gone through the traditional note-taking method.
- Time Efficiency: Mind maps let students break down different topics into manageable subtopics. So, at the time of tests, the student won't have to go through the textbooks again. They can simply check these mind-mapping notes and revise the important chapters accordingly.
How to Use a Mapping Method for Note Taking
Creating a mind-mapping note-taking method may sound like a daunting task, but if you go ahead with a mind-mapping software like EdrawMind, you will realize how effective and easy the entire process is.
Check out the following steps to use mind mapping for note-taking methods:
Step 1: Identify a Central Theme
The first step in creating a mind mapping for note-taking is brainstorming on the central theme. This main topic will be the point of reference on which the entire mind map will be based.
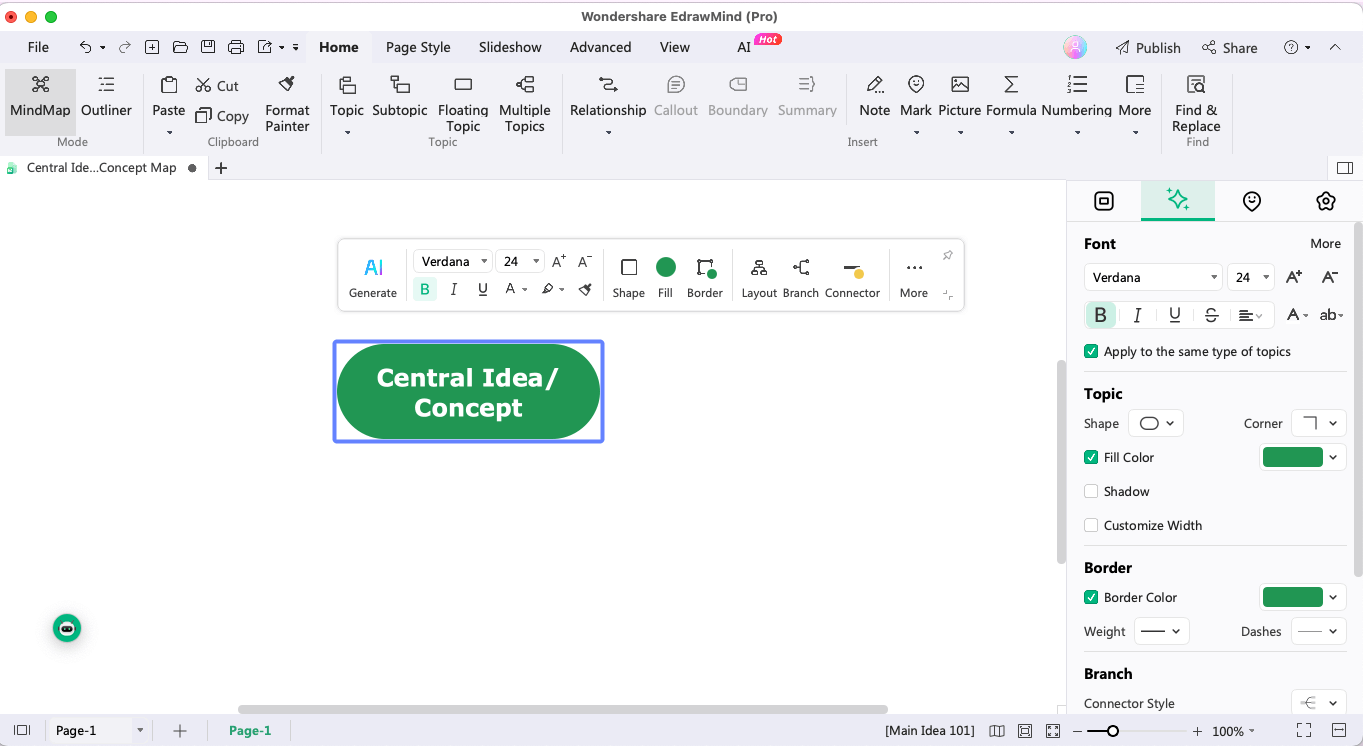
Step 2: Create the Central Node
Once you have finalized the central theme, head to a mind mapping tool and replace the Main Theme with the finalized topic. This way, you will have a proper understanding of how you would like to proceed with your mind mapping.
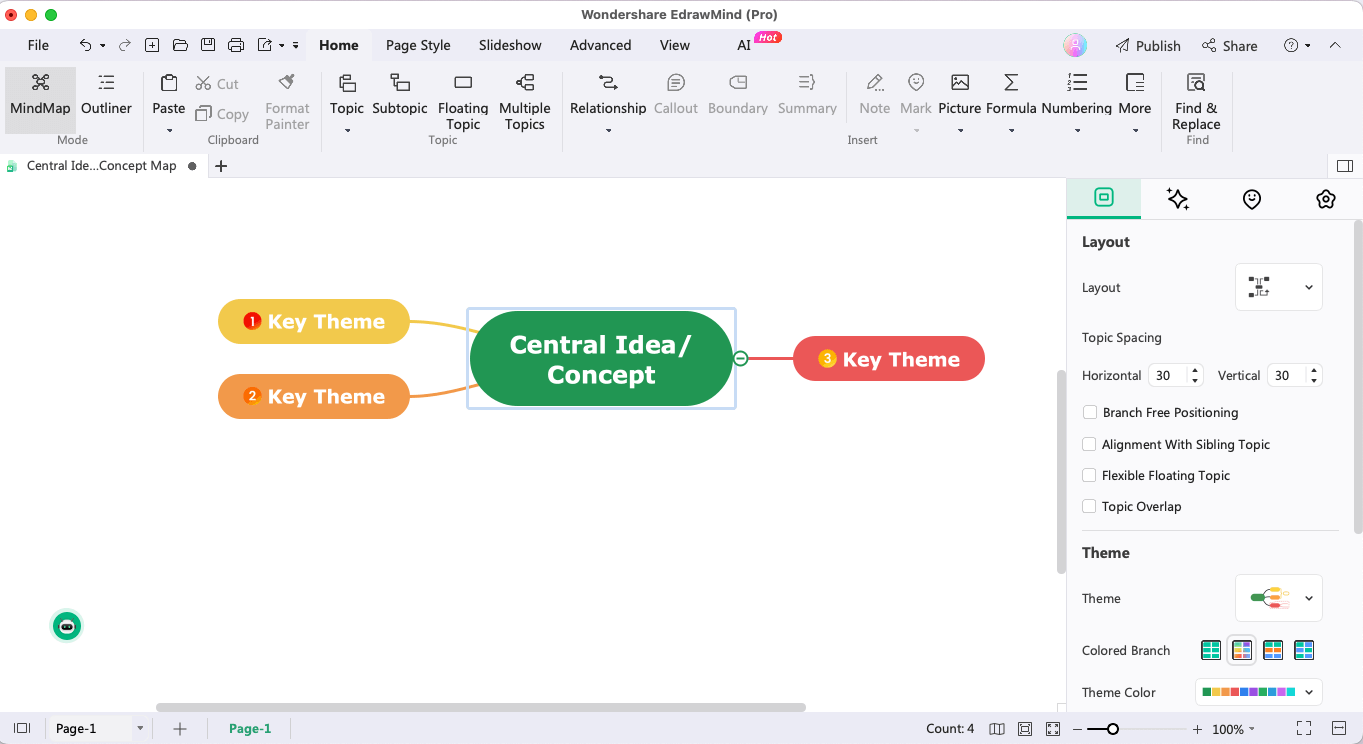
Step 3: Identify Subtopics
Start adding primary and secondary subtopics from the main theme. Based on your tool, you can add subtopics and customize them using different colors and fonts.
Step 4: Add Keywords
Keywords and phrases are very important when it comes to mind mapping, as they help the reader understand more about the central theme. Try adding concise keywords to your secondary subtopics that would resonate with the overall theme.
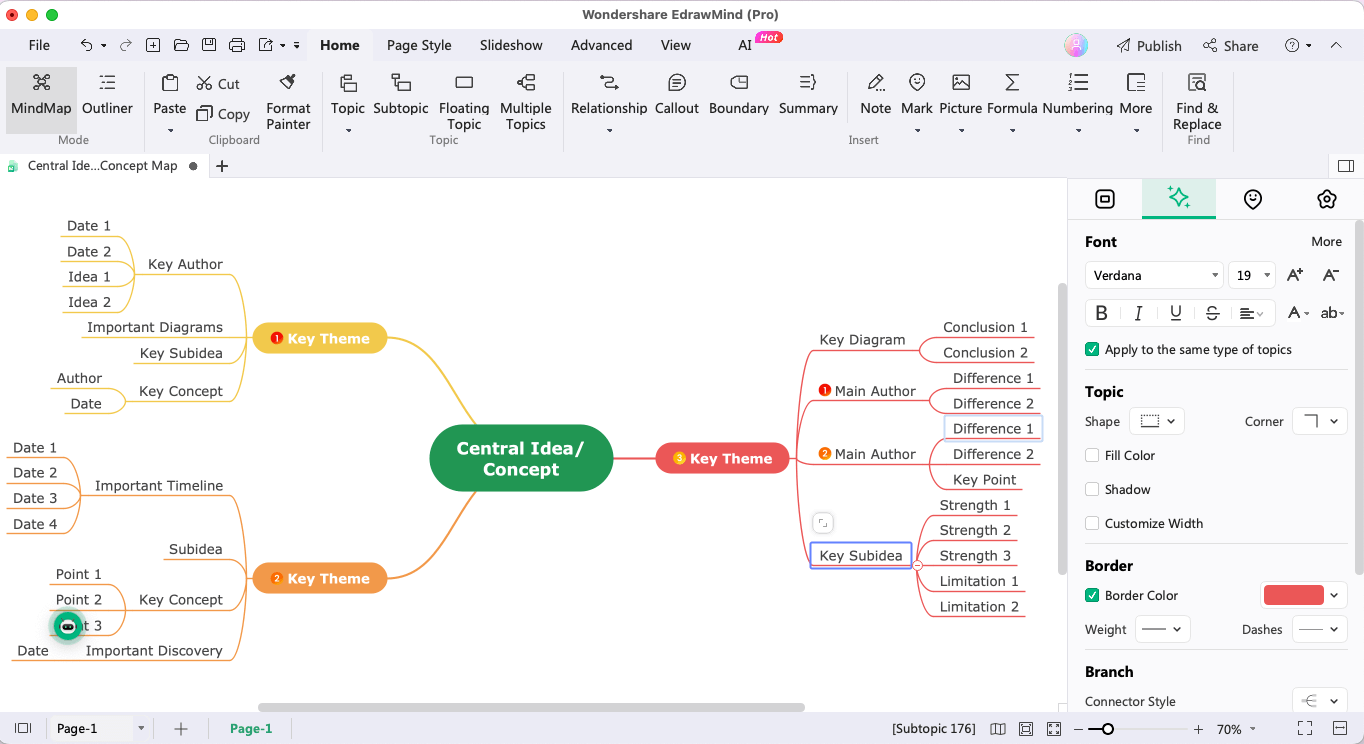
Step 5: Add Connection
Connecting different subtopics is the most important part of any mind map. Once you have added all the relevant keywords or phrases, find the connections between them. Try to customize different connectors based on their relationship.
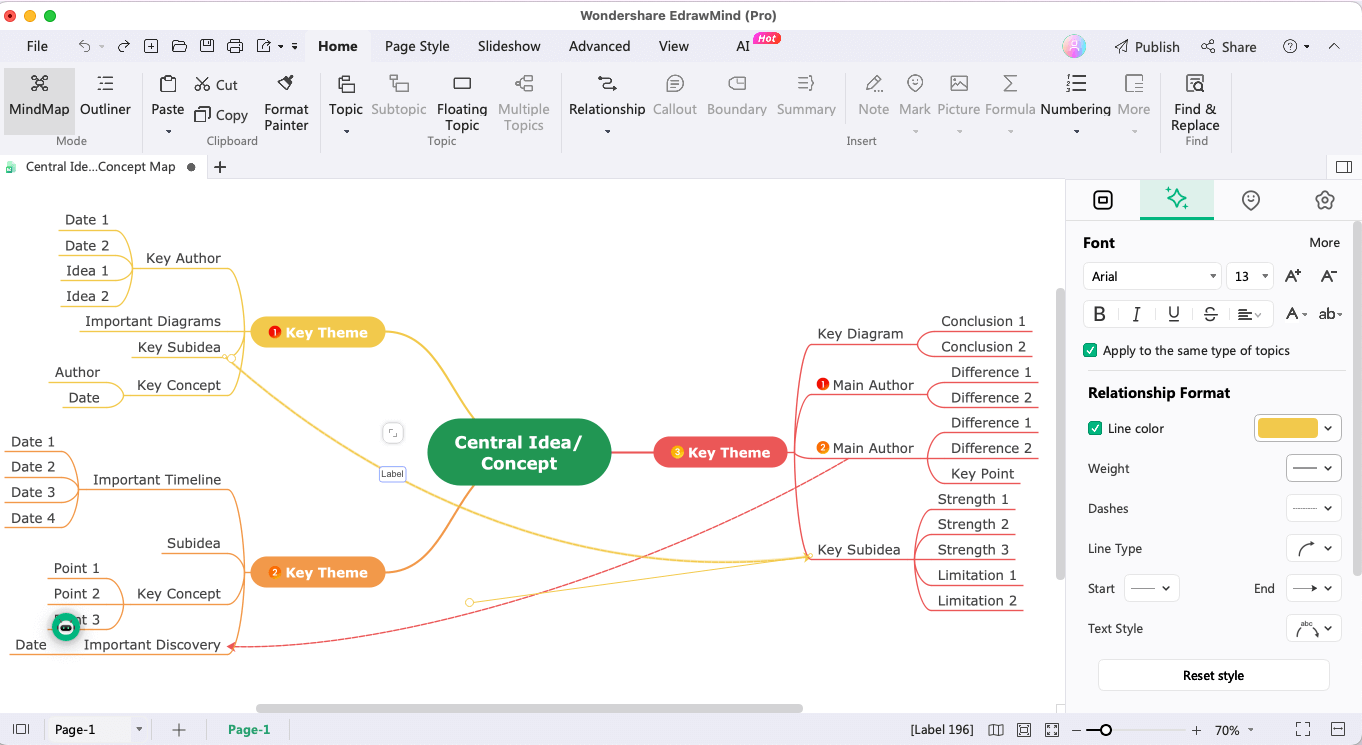
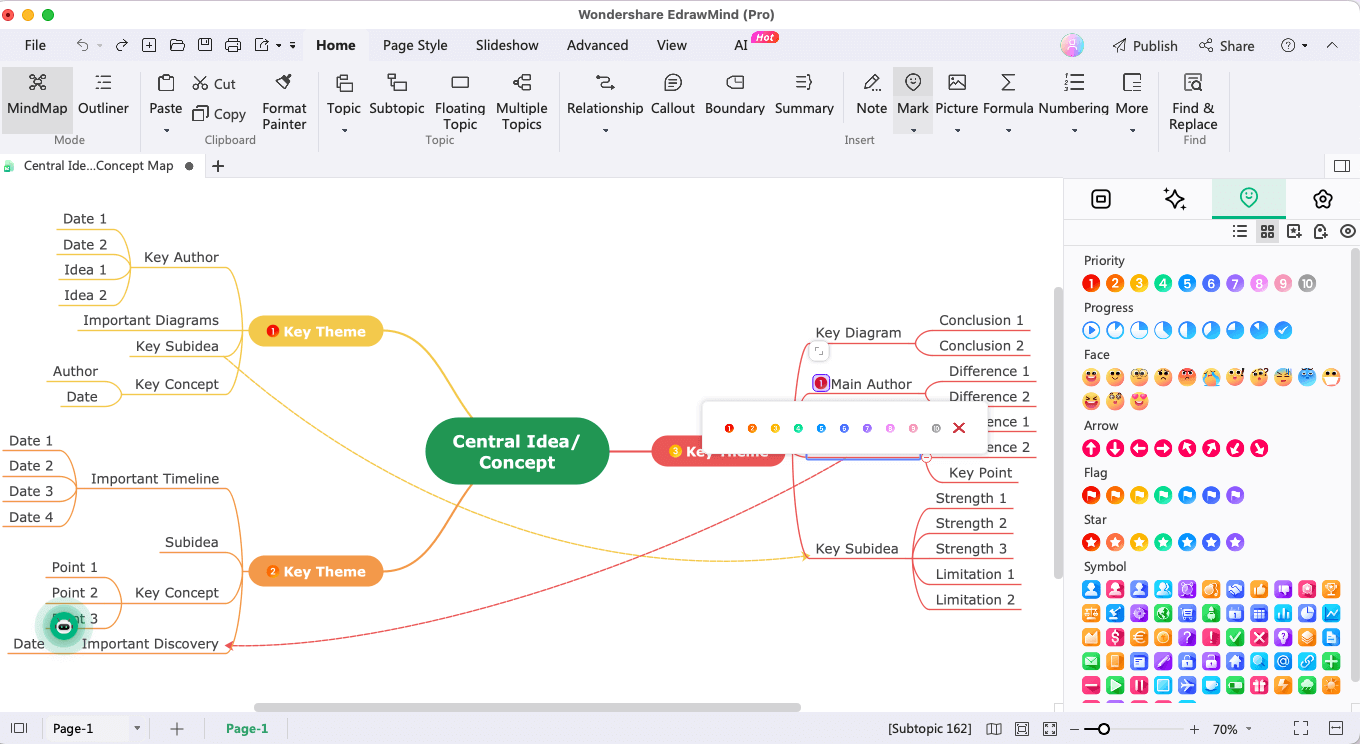
Step 6: Add Elements
It is always recommended to add different elements to your mind maps. You can import images, add cliparts, or even set priority numbers to your subtopics or keyphrases. Such elements will visually enhance your mind maps and help you retain the information.
Example for Mind Mapping Note-Taking
1. Note: Making/Taking
Here is a great example of a mind mapping note-taking method. As you can see in the following template, we have added practical usage of mind maps by adding different topics and sub-topics. Additionally, we have found the relevant connection between them. Such mind maps are a great example of how a student can take notes while ensuring that they make it more creative.
2.How to Take Notes
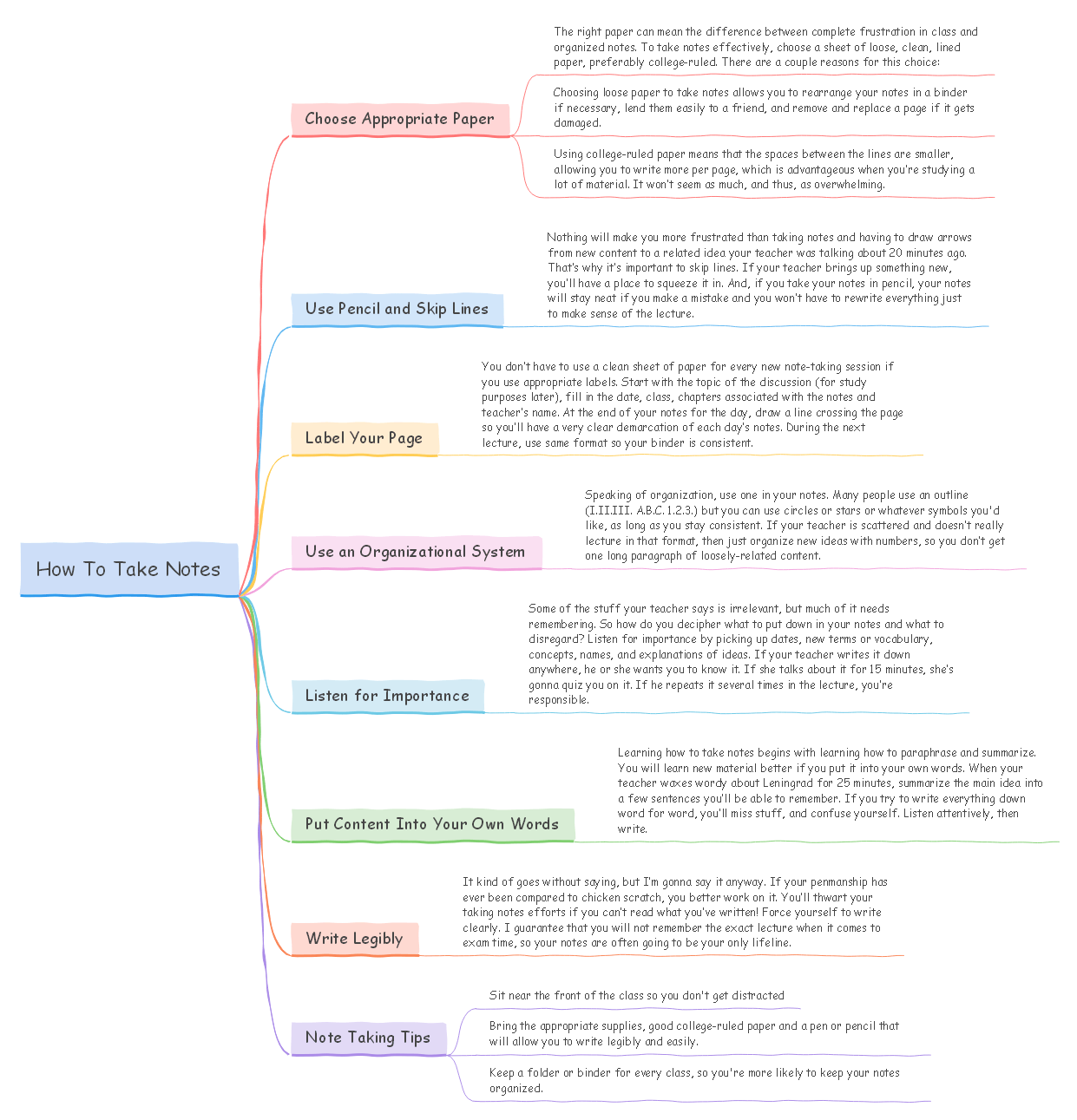
In the following mind map, we are discussing the most effective way to take notes. As you can see, there are large paragraphs that we have added to make our point. If we had gone traditionally, it would have become a more tedious diagram. Here, we have outlined different procedures to effectively take notes, and by following the process, a student can easily learn some of the best ways.
Conclusion
Mind mapping is a great tool for improving the learning habits of any student. When we use mind-mapping note-taking methods, we ensure that our topics are summarized so that we understand the different connections between them. This technique promotes active engagement, streamlines education, and encourages visual learning. When it comes to mind mapping, we recommend embracing EdrawMind. The free mind mapping tool has many free templates that help the students quickly take notes. Moreover, the outliner mode from the EdrawMind can easily transform your traditional notes into mind maps.
FAQ
-
1. Is mind mapping suitable for all subjects?
Mind mapping is a distinguished tool that can map out all subjects, including mathematics, language, science, personal hobbies, and more. -
2. Do I need to be artistic to create effective mind maps?
This is not necessary! What is more important in creating mind maps is how effectively you find the connections between subtopics. Once that is done, you can use EdrawMind's built-in features to customize the mind maps to make them more creative. -
3. Are there any mind-mapping techniques for problem-solving?
Yes, there are several important mind-mapping techniques for problem-solving, like Fishbone Diagram, SCAMPER, Six Thinking Hats, SWOT Analysis, Force Field Analysis, Pareto Analysis, and Mind Map Decision Trees, to name a few.




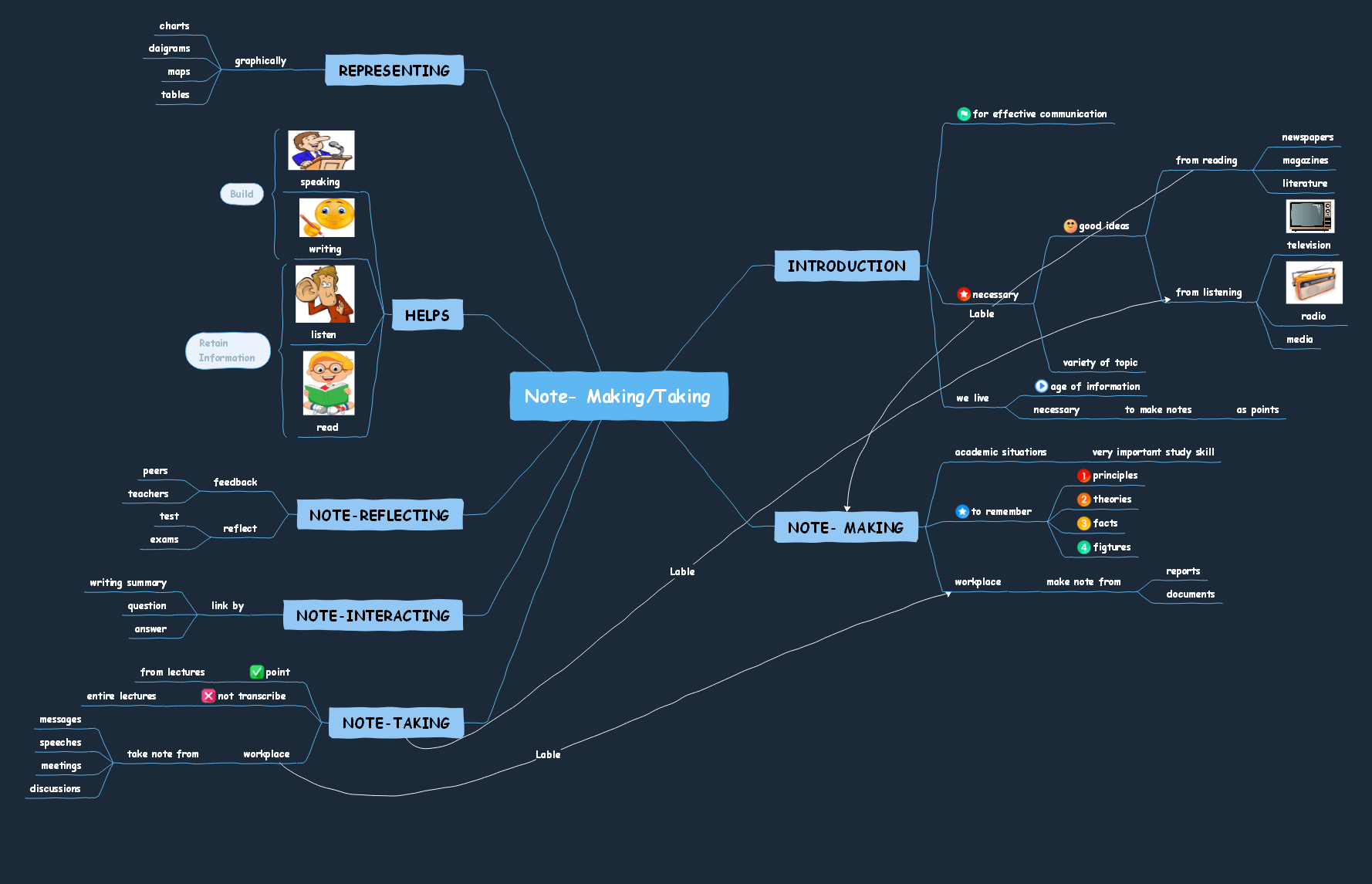
 below.
below.  below.
below.