Enterprise Resource Planning, or ERP, helps organizations manage their resources in one unified system. It connects departments, automates workflows, and improves decision-making through real-time data and analysis.
Using mind maps makes understanding ERP much easier. These diagrams show how finance, logistics, production, and sales connect within a business.
They help teams see how information flows and where each process fits in the larger system.
With Wondershare EdrawMind, ERP concepts become clearer through visuals. You can explore structure, implementation, and optimization mind maps that simplify complex systems.
These visuals make planning, managing, and improving enterprise operations faster and more efficient.
In this article
What Is ERP?
What is ERP? According to Wikipedia, ERP stands for enterprise resource planning.
It is also an integrated enterprise management software for material resource management (material flow), human resource management (human flow), financial resource management (financial flow), and information resource management (information flow).
So far, do you think this is software? That's true, but it is also a management tool, which is very useful for the ordinary management and operation of enterprises.
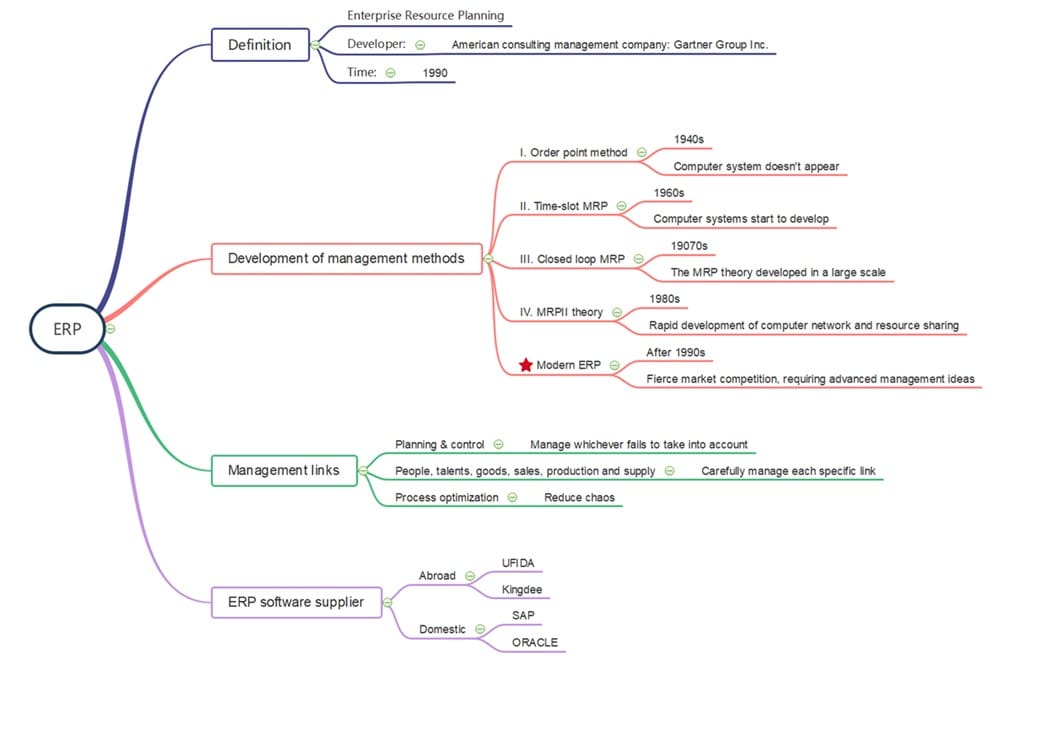
After reading the mind map above, I believe you have a specific understanding of ERP.
The ERP management project is a complex and colossal system engineering task, and it isn't just about money. It is more of an advanced management idea, a platform for enterprise management.
As an advanced modern enterprise management mode, the main object of ERP is the enterprise.
The purpose of ERP is to allocate resources (including human, financial, material, customer, production, supplier, selling, etc.) in all aspects of the enterprise reasonably, to maximize its efficiency.
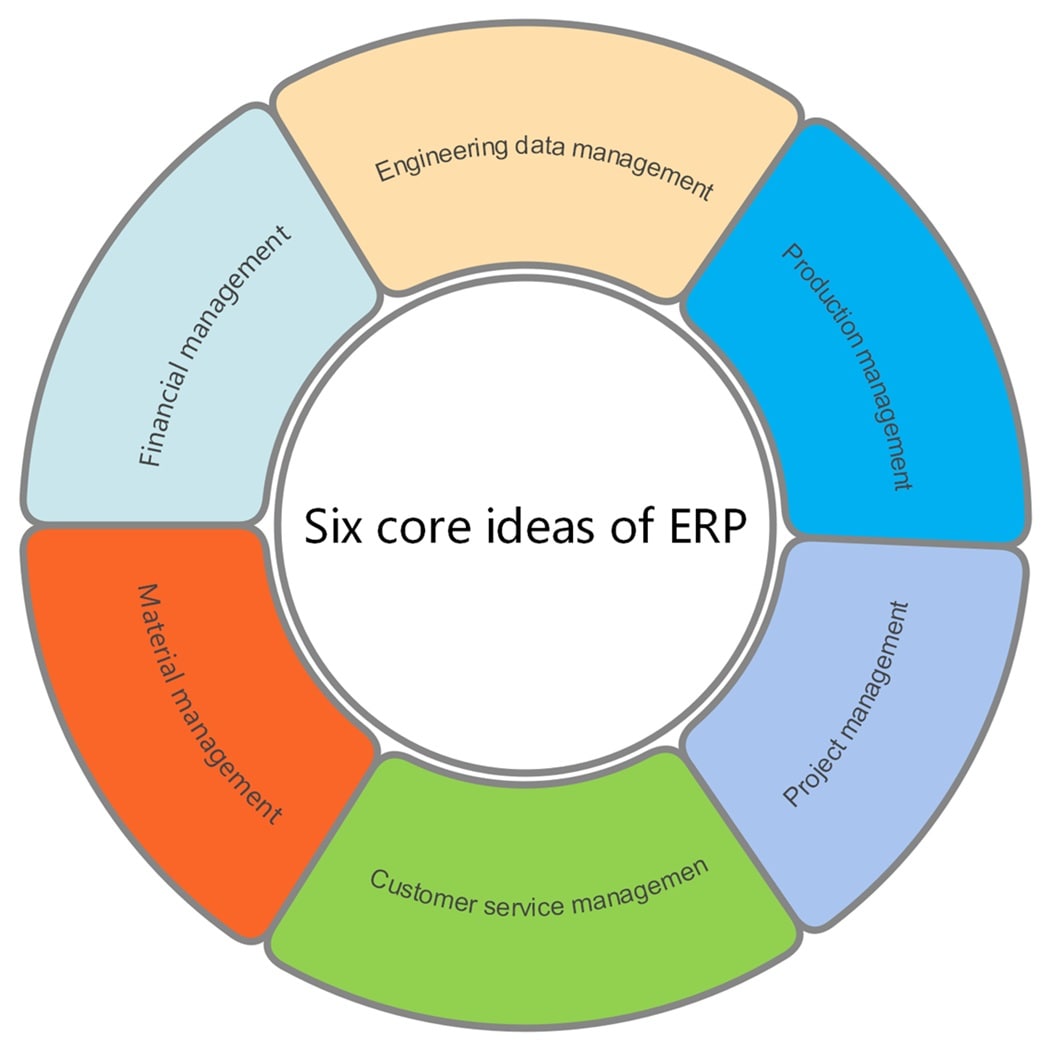
So, the enterprise can secure a favourable position in the competitive market and achieve its goal of maximizing profits. So, what is the core idea of ERP? See the picture below.
Is ERP Omnipotent?
The above explains what ERP is, and also outlines its advantages and core ideas. However, ERP involves a wide range of resources, has a long implementation cycle, can be difficult, and carries certain risks.
Hence, not all enterprises are suitable to use ERP software to manage their operations, especially small and medium-sized enterprises. Why? You can figure it out through a mind map.
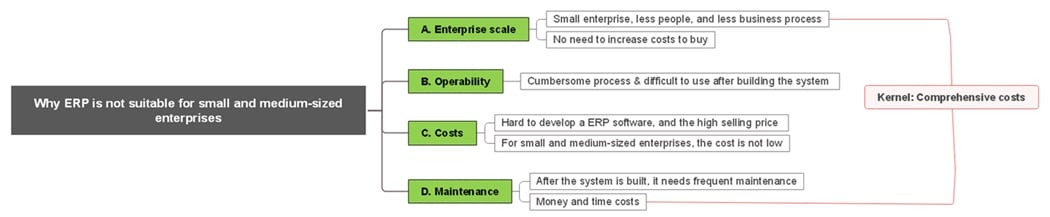
Generally speaking, for small & medium-sized enterprises, the ERP system is not the best choice. After all, for them, survival and development are the most important considerations at this stage.
When they reach a specific scale and stage, ERP can be considered to assist them in enterprise management.
Now, do you have a clear understanding of ERP? However, ERP is a systematic and sophisticated software that needs to be explored in practical applications. Making good use of this management tool is a massive benefit for enterprise management.
At the same time, when managers encounter management problems in running enterprises, they can also spread their thinking and analyze the nature of the issues through EdrawMind, as I did, which is more conducive to solving problems.
Mind Map Examples for ERP
Mind map examples from Wondershare EdrawMind’s Gallery help you understand ERP. These visual diagrams show how resources, workflows, and business processes connect. These mind maps make it easier to analyze, manage, and improve enterprise operations effectively.
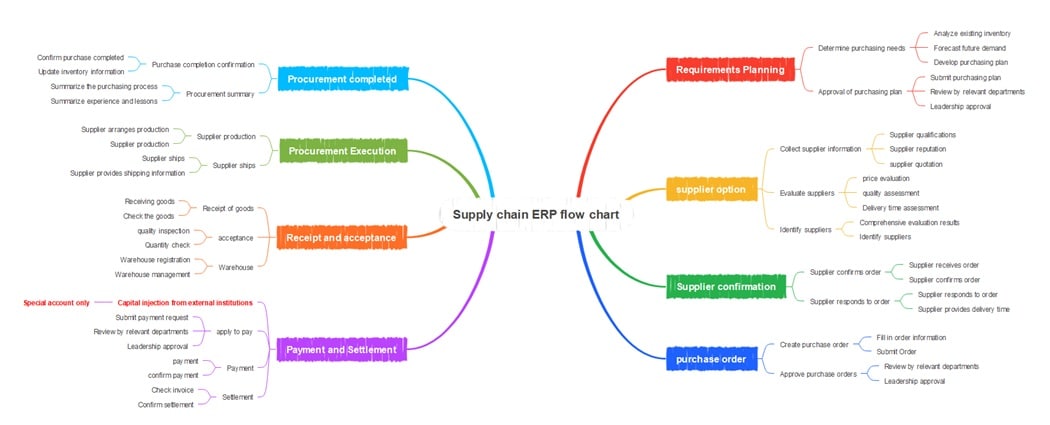
Supply Chain ERP Flowchart
The Supply Chain ERP flow chart starts with Requirements Planning, where teams check inventory, forecast demand, and submit purchasing plans for approval. This step ensures accurate budgeting and alignment with business needs.
Next is Supplier Evaluation, where supplier data such as pricing, quality, and reputation is reviewed. Approved suppliers confirm orders, provide delivery details, and begin production. Purchase orders are then issued and verified by management.
In Procurement and Settlement, payments are processed, invoices checked, and goods inspected. After quality and quantity checks, items are stored in the warehouse. This system keeps the supply chain efficient and transparent.
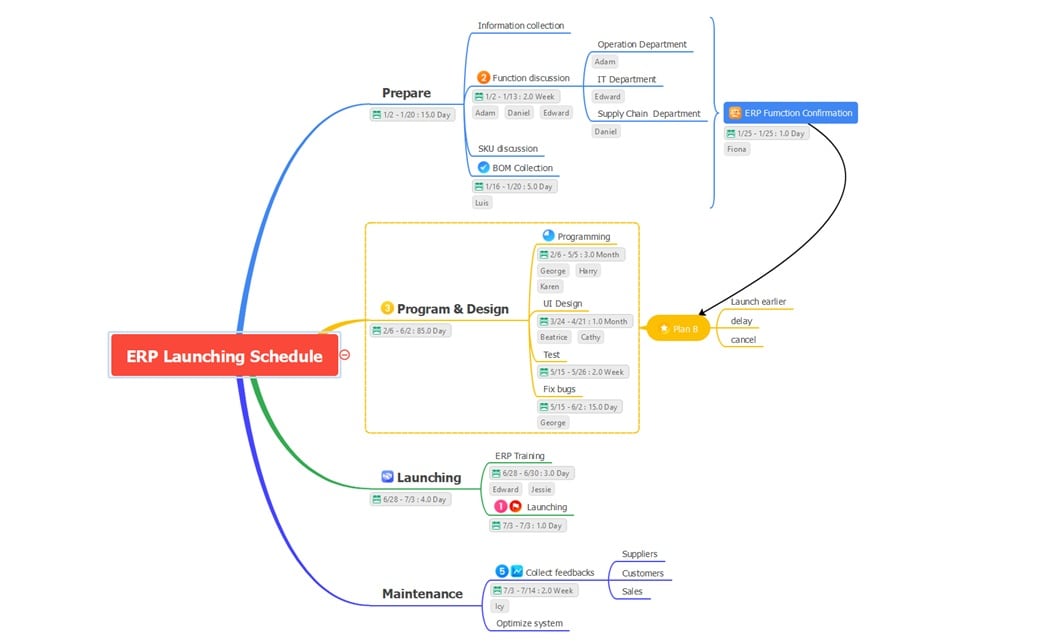
ERP Launching Schedule
The ERP Launching Schedule starts with the Preparation phase, where teams gather data, discuss functions, and confirm ERP features. Departments like IT, Operations, and Supply Chain collaborate to finalize SKUs and Bill of Materials for accurate setup.
In the Program and Design phase, developers handle programming, UI design, and testing. Any bugs are fixed before final approval. Teams also prepare a Plan B to manage early launches, delays, or cancellations as needed.
The Launching and Maintenance phase covers ERP training, feedback collection, and optimization. Input from suppliers, customers, and sales helps improve performance and system efficiency.
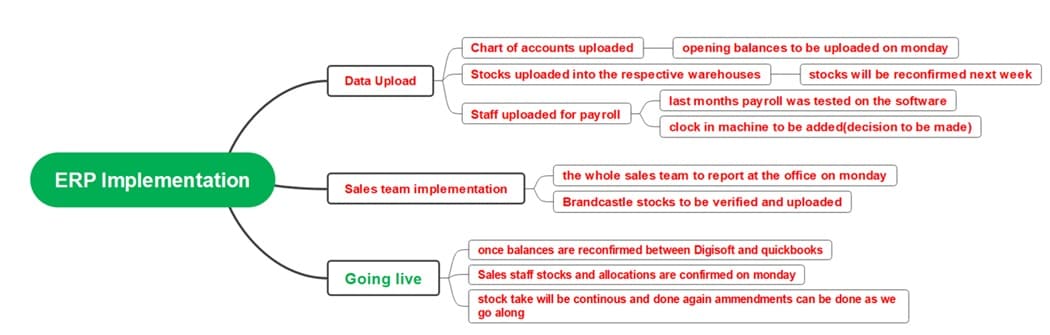
ERP Implementation
The ERP Implementation process begins with Data Upload, where financial and operational data are entered into the system. This includes uploading the chart of accounts, warehouse stocks, and staff payroll details for testing and verification.
The Sales Team Implementation follows, requiring all team members to report to the office for setup and validation. Brandcastle stocks are reviewed and uploaded, ensuring accuracy before the system becomes active.
The Going Live stage begins once the data between Digisoft and QuickBooks aligns. Continuous stock checks and real-time updates ensure that any discrepancies are corrected promptly for smooth daily operations.
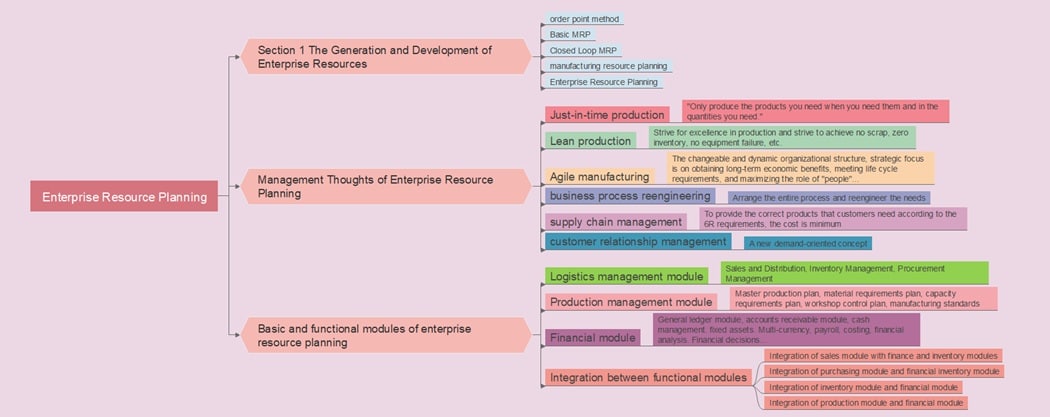
ERP Development Management
The Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) diagram explains how ERP systems evolved from early production planning to integrated enterprise management. It begins with methods like Order Point and Basic MRP to Manufacturing Resource Planning and ERP. It connects every business function.
The second part covers Management Thoughts that shape ERP philosophy. Concepts like Just-in-Time, Lean, Agile Manufacturing, Business Process Reengineering, Supply Chain Management, and Customer Relationship Management aim to increase efficiency, cut waste, and improve responsiveness to customer needs.
The final part details ERP Modules, including logistics, production, and finance. These modules work together, ensuring data consistency and seamless integration across all departments.
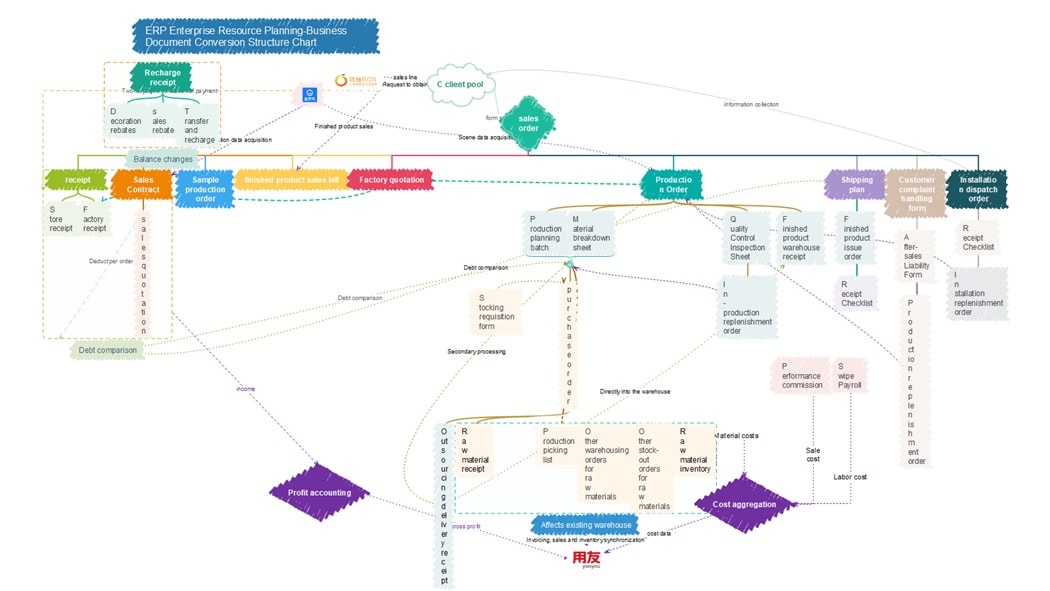
ERP Structure Chart
The Sales Order ERP Flow diagram shows how business transactions move through each stage of the sales and production process. It starts with receipts, contracts, quotations, and debt comparisons that form the foundation of order management.
The next part focuses on Production and Quality Control. It includes production orders, material breakdowns, raw material receipts, and warehouse updates. These steps ensure accurate inventory tracking and smooth production flow.
The last phase handles Post-Sales and Finance, including customer complaints, rebates, cost aggregation, profit accounting, and performance tracking. All processes are fully integrated within the ERP system.
Explore More Mind Maps or Make One for Free Now
EdrawMind makes ERP mind maps practical and easy to create. You can visualize workflows, manage resources, and plan system launches with clarity.
Explore templates from EdrawMind’s Gallery to find ERP structures for planning, operations, and system management. These predesigned templates help teams coordinate business processes effectively across departments.
Choose a layout that fits your ERP goal. Each template includes editable branches for modules like logistics, finance, and production.
Here’s how to create your ERP mind map using EdrawMind:
Step 1: Add Your Core Topic
Start with your main topic, such as “ERP Implementation,” “Supply Chain Planning,” or “System Integration.” This central node serves as your foundation for organizing processes and modules.
Step 2: Build Key Branches
Add branches for critical areas such as Finance, Procurement, Production, Sales, and HR. This structure helps teams see interconnections and improve coordination within the ERP framework.
Step 3: Customize With Visuals
Use colors, icons, and shapes to show dependencies and data flow. Highlight connections between modules to make complex ERP systems easier to understand and communicate.
Step 4: Improve With AI Assistance
With EdrawMind AI, you can summarize workflows, generate improvement ideas, or analyze process efficiency. It enhances planning accuracy and supports smarter ERP implementation.
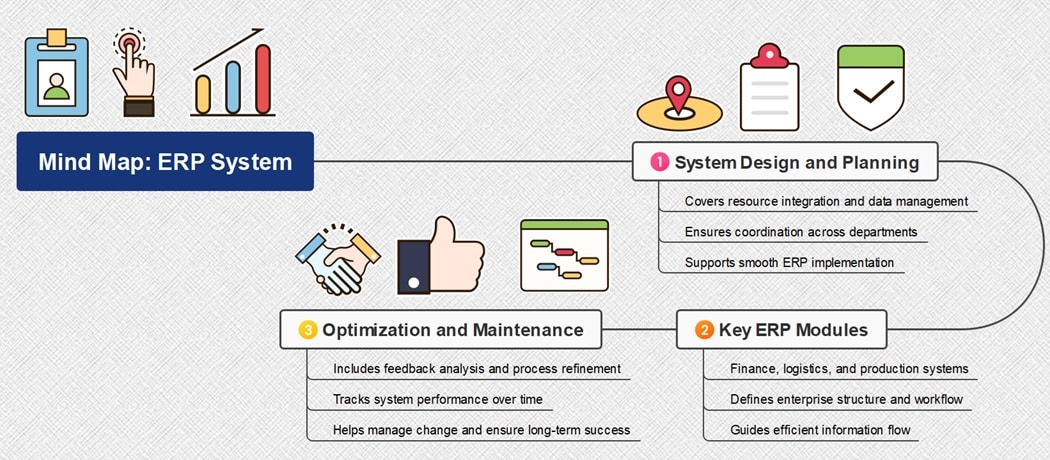
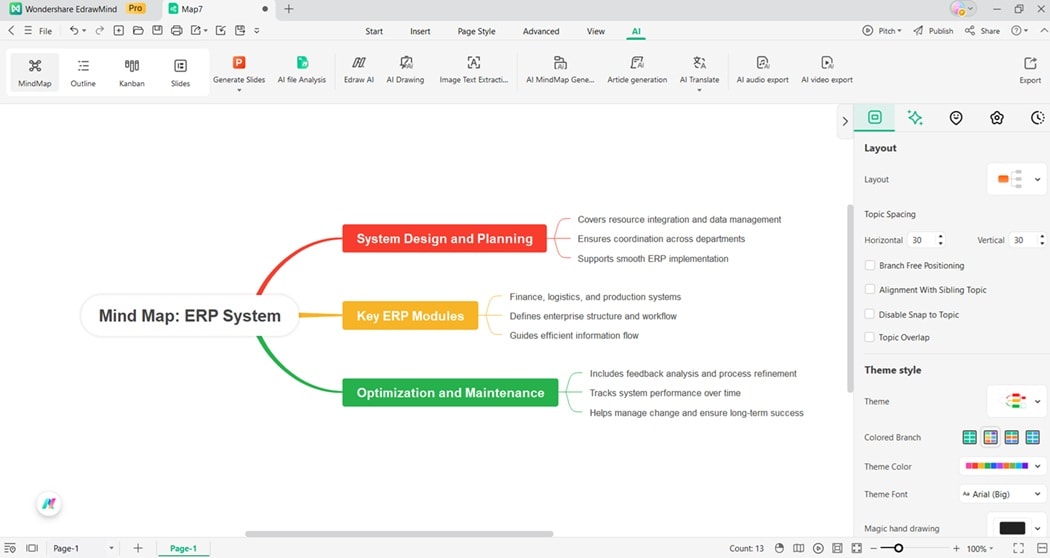
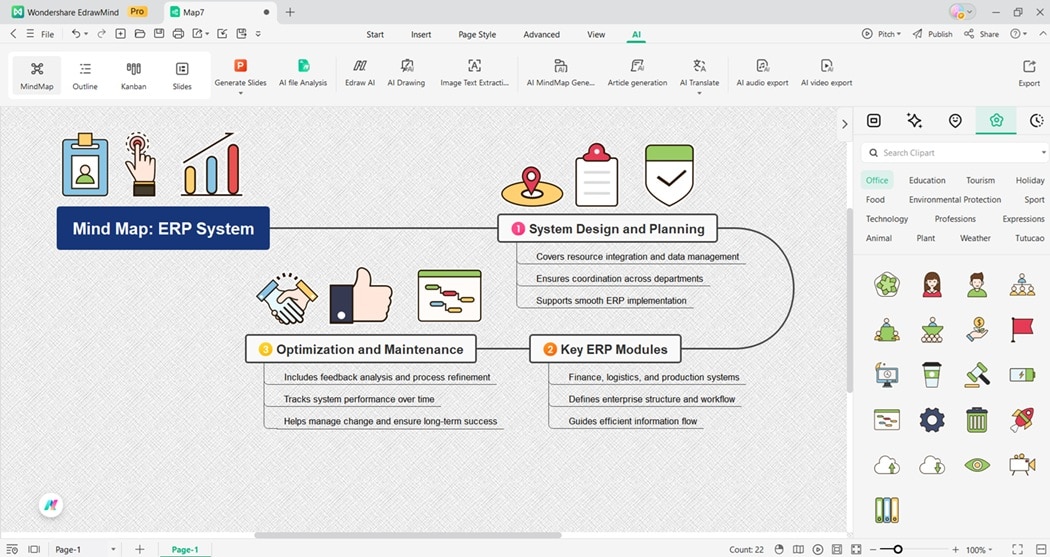
The ERP Mind Map begins with system design and planning. It covers resource integration, data management, and functional coordination to ensure smooth implementation across departments.
The next part focuses on key ERP modules, including finance, logistics, and production. These modules define the structure of enterprise systems and guide efficient information flow.
The last part emphasizes optimization and maintenance. It includes feedback analysis, process refinement, and performance tracking. The map helps organizations manage change and achieve long-term operational success.