About this English literature history template
This comprehensive template provides a visual timeline of English literary history. It highlights major periods, key authors, and significant works. It is perfect for students and educators looking to understand how literature evolved from the Old English era to the present day.
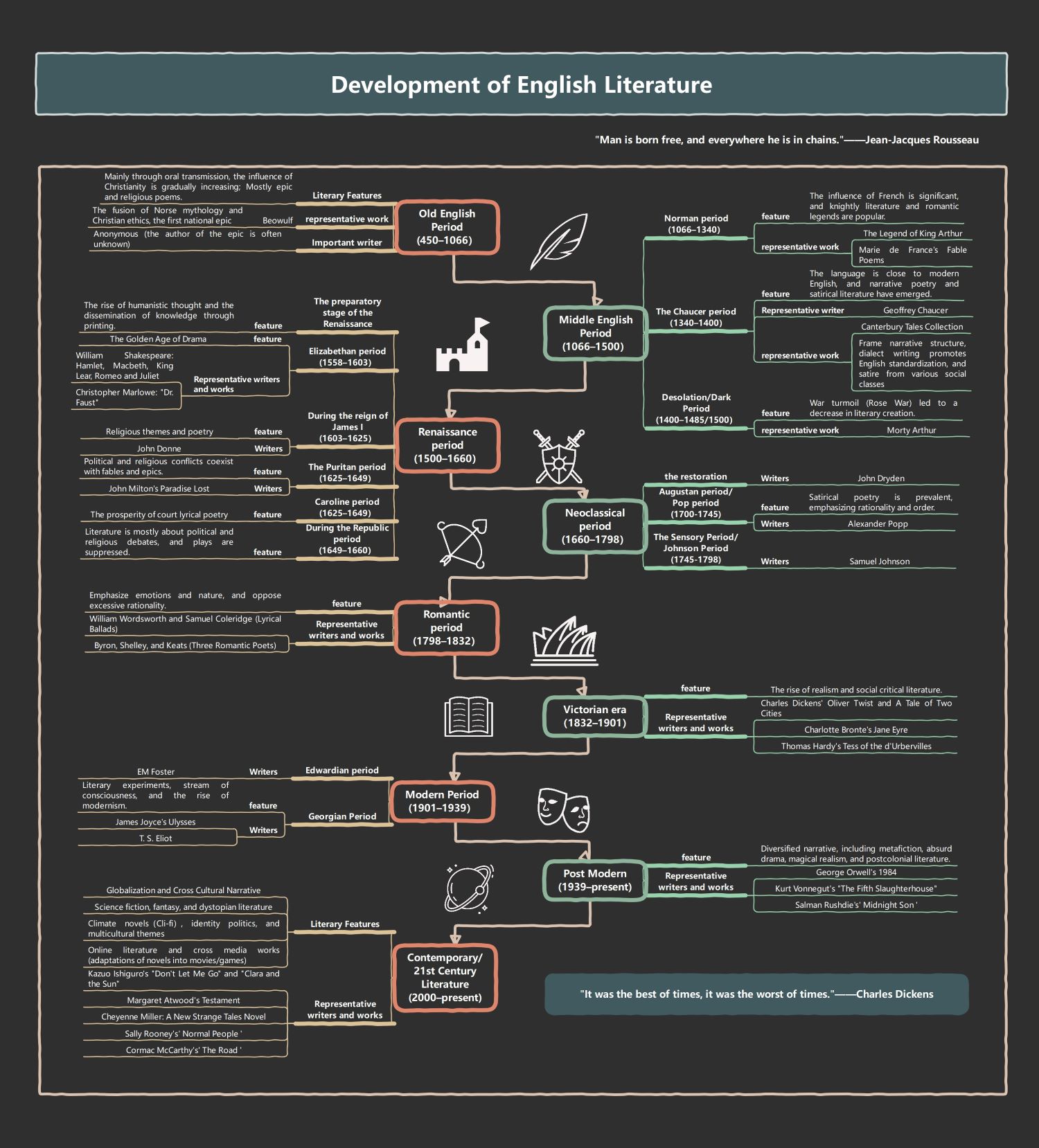
Old English Period (450-1066)
This foundational era features literature primarily shared through oral tradition. It blends Norse mythology with early Christian ethics, creating unique cultural narratives. Writers often remained anonymous while producing heroic epics that celebrated the first national identity of England.
- Oral transmission and religious poems
- Fusion of Norse mythology and Christian ethics
- Beowulf as the first national epic
- Mainly anonymous authors
Middle English Period (1066-1500)
Significant French influence defined this era following the Norman conquest. Literature shifted toward knightly adventures and romantic legends. This period also saw the standardization of the English language through narrative poetry and satirical works that examined different social classes.
- Norman period and knightly literature
- Popularity of King Arthur legends
- Geoffrey Chaucer and The Canterbury Tales
- Emergence of narrative poetry and satire
Renaissance Period (1500-1660)
This era represents a massive surge in humanistic thought and the dissemination of knowledge via printing. Often called the Golden Age of Drama, it produced world-renowned plays and poetry. Writers explored complex themes of religion, politics, and the human condition.
- The Golden Age of Drama
- William Shakespeare's iconic tragedies
- John Milton's Paradise Lost
- Humanistic thought and scientific discovery
Neoclassical Period (1660-1798)
Rationality and order dominated the Neoclassical era. Writers focused on social critiques and satirical poetry to address political issues. This period emphasizes classical structures and the use of wit to examine the sensory world and human nature through logic.
- The restoration and Augustan period
- Satirical poetry and social commentary
- John Dryden and Alexander Pope
- Emphasis on rationality and formal order
Romantic Period (1798-1832)
Romanticism emerged as a reaction against excessive rationality and the Industrial Revolution. It prioritized deep emotions, the beauty of nature, and individual imagination. Poets focused on the sublime experience and often opposed the rigid structures of the previous age.
- Focus on emotions and the natural world
- William Wordsworth and Samuel Coleridge
- The Three Romantic Poets: Byron, Shelley, and Keats
- Opposition to industrial rationality
Victorian Era (1832-1901)
This period saw the rise of realism and social critical literature. Authors used novels to address the hardships of industrial life and class inequality. It was a time of significant social change reflected through detailed, character-driven narratives and moral questioning.
- The rise of realism in novels
- Charles Dickens and social critique
- Charlotte Bronte's Jane Eyre
- Thomas Hardy's exploration of fate
Modern Period (1901-1939)
Modernism introduced experimental techniques like stream of consciousness to reflect a fragmented world. Writers broke away from traditional storytelling to explore psychology and the inner lives of characters. This era was deeply influenced by global conflict and societal shifts.
- Literary experiments and stream of consciousness
- The rise of modernism in fiction
- James Joyce's Ulysses
- T. S. Eliot's influential poetry
Post Modern (1939-present)
Post-modern literature utilizes metafiction, absurd drama, and magical realism to challenge conventional reality. Narrative structures became more diversified and fragmented. Writers often explored themes of postcolonialism and the breakdown of traditional meaning in a complex, shifting world.
- Diversified narratives and metafiction
- George Orwell's political dystopian fiction
- Absurd drama and magical realism
- Salman Rushdie and postcolonial literature
Contemporary/21st Century Literature (2000-present)
Today's literature reflects globalization and cross-cultural narratives. It integrates diverse genres like climate fiction and dystopian themes with digital media influences. Contemporary writers address identity politics and multiculturalism, often adapting their stories for movies, games, and online platforms.
- Globalization and cross-cultural narratives
- Climate fiction and identity politics
- Margaret Atwood and Kazuo Ishiguro
- Adaptations across digital and print media
FAQs about this Template
-
Why is the Renaissance period significant in English literature?
The Renaissance period marked a massive shift toward humanistic thought and the dissemination of knowledge through the printing press. This Golden Age of Drama featured iconic writers like William Shakespeare and Christopher Marlowe. Their works explored complex human emotions and political power, fundamentally shaping the English language and establishing literary standards that continue to influence writers today.
-
What are the main characteristics of Romantic period literature?
Romanticism emerged as a powerful reaction against the excessive rationality of the Neoclassical age. It prioritized deep emotions, the beauty of nature, and individual imagination over scientific logic. Famous poets like Wordsworth, Keats, and Shelley focused on the sublime experience of the natural world, forever changing how people perceive the connection between the human spirit and the environment.
-
How does Contemporary literature differ from the Post-Modern era?
While Post-Modernism focused on metafiction and the absurd, Contemporary literature reflects a globalized society with cross-cultural narratives. It often explores climate fiction, identity politics, and multicultural themes through various media platforms. This era includes diverse voices like Kazuo Ishiguro and Margaret Atwood, addressing modern challenges such as technology, globalization, and social justice in an increasingly connected digital world.