About this Types of Nouns template
This template provides a comprehensive visual guide to the various categories of nouns in English. It simplifies complex grammar rules into easy-to-understand branches. Use this tool to master parts of speech and enhance your linguistic skills effectively.
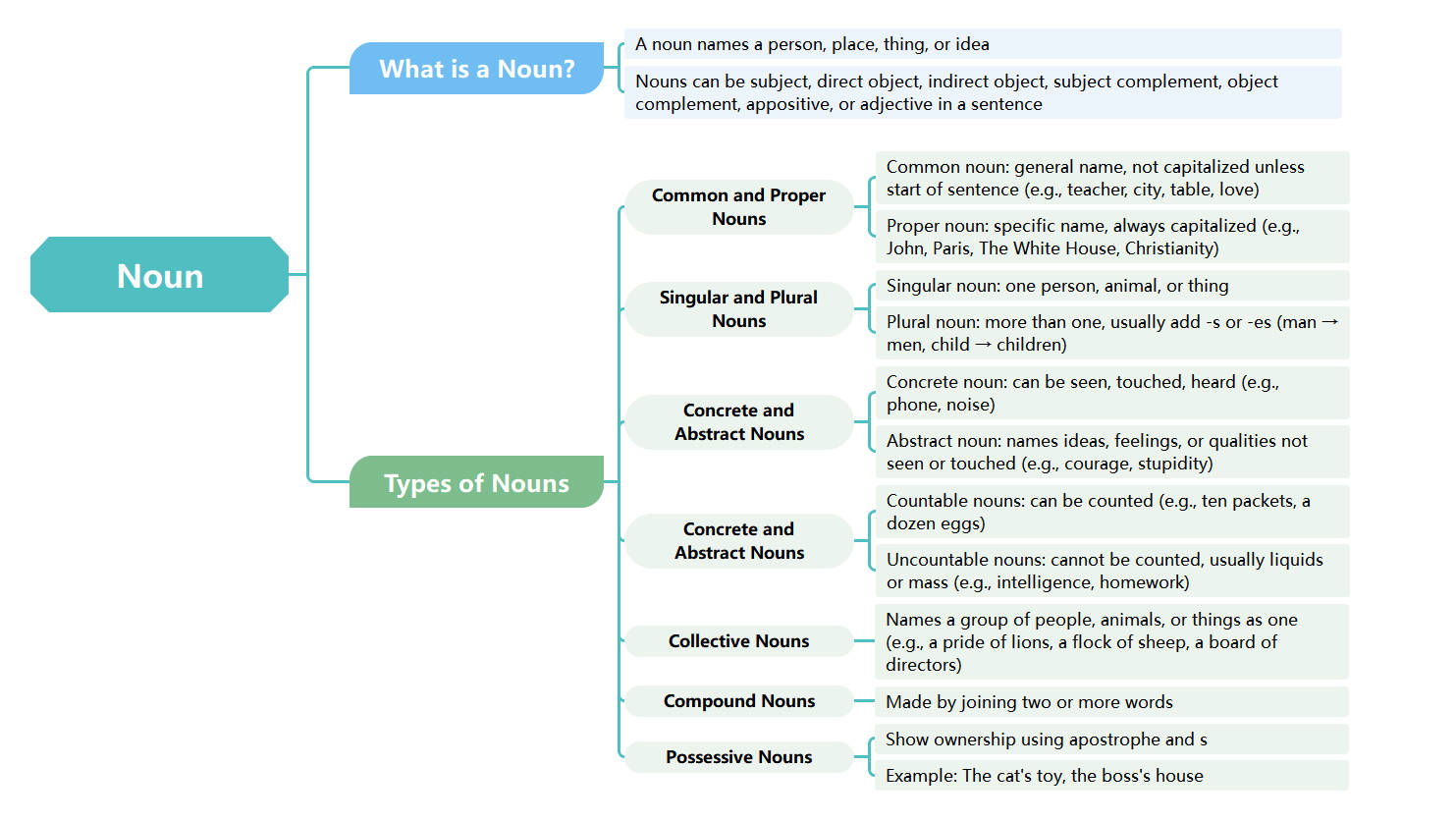
What is a Noun?
A noun serves as a label for people, places, things, or abstract ideas within a sentence. They function in various roles, such as subjects or objects, to provide essential structure and meaning to our daily communication.
- A noun names a person, place, thing, or idea
- Nouns can be subjects, direct objects, or indirect objects
- They can also function as subject complements or object complements
- Nouns may act as appositives or adjectives in sentences
Common and Proper Nouns
Common nouns refer to general items and are not capitalized unless starting a sentence. In contrast, proper nouns identify specific names and always require capitalization to distinguish unique people, places, or organizations from general categories.
- Common noun: general name (e.g., teacher, city, table)
- Proper noun: specific name (e.g., John, Paris, Christianity)
- Proper nouns are always capitalized
- Common nouns are only capitalized at the start of sentences
Singular and Plural Nouns
Singular nouns represent a single person, animal, or object. Plural nouns describe more than one entity, usually formed by adding suffixes like -s or -es. Some nouns have irregular plural forms that require specific memorization for correct usage.
- Singular noun: one person, animal, or thing
- Plural noun: more than one entity
- Usually add -s or -es to form plurals
- Irregular examples include man to men and child to children
Concrete and Abstract Nouns
Concrete nouns are physical things you can experience through the five senses, like sight or touch. Abstract nouns refer to intangible concepts, such as emotions, qualities, or ideas, which cannot be physically perceived or held by anyone.
- Concrete noun: can be seen, touched, or heard
- Examples: phone, noise, table
- Abstract noun: names ideas, feelings, or qualities
- Examples: courage, stupidity, love, happiness
Countable and Uncountable Nouns
Countable nouns represent items that can be quantified with numbers. Uncountable nouns refer to substances, liquids, or mass concepts that cannot be counted individually. These nouns often require specific quantifiers like some or much to indicate their total amount.
- Countable nouns: can be counted (e.g., ten packets)
- Uncountable nouns: cannot be counted (e.g., liquids, mass)
- Examples of uncountable: intelligence, homework, water
- Countable examples: a dozen eggs, five cars
Collective and Compound Nouns
Collective nouns name groups of people, animals, or objects as a single unit. Compound nouns are formed by joining two or more words together to create a new meaning. Both types help in making descriptions more concise.
- Collective nouns: names a group as one (e.g., a pride of lions)
- Examples: a flock of sheep, a board of directors
- Compound nouns: made by joining two or more words
- Common examples: keyboard, toothpaste, rainfall
FAQs about this Template
-
What is the difference between a common noun and a proper noun?
A common noun is a general name for a category of things, like city or dog, and it is not capitalized. A proper noun refers to a specific, unique entity, such as London or Rex. Proper nouns always begin with a capital letter, regardless of where they appear in a sentence, to signify their unique identity.
-
How do you identify an abstract noun in a sentence?
Abstract nouns identify things that do not have a physical presence. You cannot see, touch, hear, smell, or taste them. Instead, they represent ideas, qualities, or conditions, such as freedom, love, or patience. If a word describes a concept or a feeling rather than a physical object, it is likely an abstract noun.
-
What are collective nouns and how are they used?
Collective nouns are words used to describe a group of individuals or things as a single unit. Examples include team, family, or flock. In American English, they are usually treated as singular, requiring a singular verb. However, in British English, they can be treated as plural if the focus is on the individual members within the group.