About this Financial Mathematics Formulas template
This template provides a comprehensive map of essential financial equations. It covers everything from basic interest calculations to complex derivative pricing. It is a perfect quick-reference guide for students and professionals in the finance industry who need to verify calculations quickly.
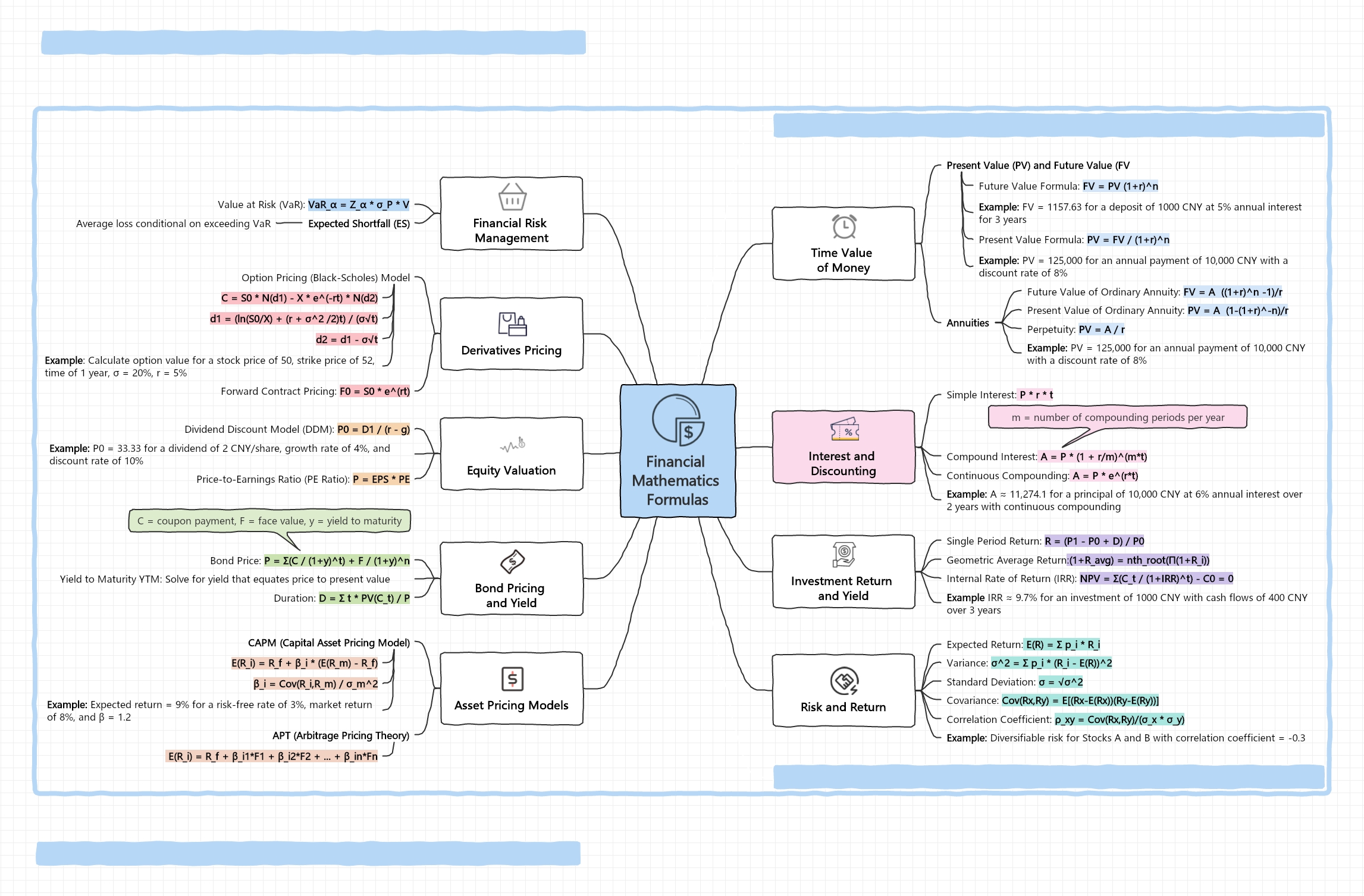
Time Value of Money
The time value of money is a core financial concept. It explains how the value of money changes over time due to interest. Understanding this helps in evaluating the growth of savings and investments efficiently.
- Future Value (FV): PV (1+r)^n
- Present Value (PV): FV / (1+r)^n
- Annuities (Ordinary and Perpetuity)
- Perpetuity: PV = A / r
Interest and Discounting
Interest calculations determine how much an investment grows or how much debt costs. These formulas account for different compounding frequencies. These frequencies significantly impact the final amount earned or owed over any specific time period.
- Simple Interest: P * r * t
- Compound Interest: A = P * (1 + r/m)^(m*t)
- Continuous Compounding: A = P * e^(r*t)
Investment Return and Yield
Measuring investment performance is crucial for portfolio management. These formulas help investors calculate returns over single or multiple periods. They also determine the internal rate of return, which is vital for comparing different business projects.
- Single Period Return: R = (P1 - P0 + D) / P0
- Geometric Average Return: nth_root(Π(1+R_i))
- Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
Risk and Return
Risk management involves measuring the volatility and relationship between different assets. These statistical formulas allow investors to quantify uncertainty. By calculating variance and correlation, professionals can build more stable and diversified investment portfolios easily.
- Expected Return: E(R) = Σ p_i * R_i
- Variance and Standard Deviation
- Covariance and Correlation Coefficient
Asset Pricing Models
Asset pricing models estimate the required return on an investment based on its risk level. These frameworks are essential for valuing securities. They help in understanding how market factors influence individual asset prices within a portfolio.
- Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM)
- Arbitrage Pricing Theory (APT)
- Beta Calculation: Cov(R_i, R_m) / σ_m^2
Bond Pricing and Yield
Bond valuation formulas determine the fair price of fixed-income securities. By calculating the present value of future coupon payments, investors can assess value. This ensures they know whether a bond is a good buy today.
- Bond Price: P = Σ(C / (1+y)^t) + F / (1+y)^n
- Yield to Maturity (YTM)
- Duration: D = Σ t * PV(C_t) / P
Equity Valuation
Valuing a company stock requires looking at dividends and earnings. These formulas help investors estimate a stock intrinsic value. This allows for better decision-making when choosing between undervalued or overvalued stocks in the open market.
- Dividend Discount Model (DDM): P0 = D1 / (r - g)
- Price-to-Earnings Ratio (PE Ratio): P = EPS * PE
Derivatives Pricing
Derivatives are complex financial instruments that derive value from underlying assets. These mathematical models help traders calculate the fair price of options. They consider factors like time and volatility to ensure accurate market pricing.
- Black-Scholes Option Pricing Model
- Forward Contract Pricing: F0 = S0 * e^(rt)
Financial Risk Management
Managing financial risk is about predicting potential losses in a portfolio. These metrics help institutions set capital requirements and prepare for market events. They provide a clear picture of the maximum expected loss during volatility.
- Value at Risk (VaR)
- Expected Shortfall (ES)
FAQs about this Template
-
What is the Time Value of Money and why does it matter?
The Time Value of Money (TVM) is a foundational concept stating that money available now is worth more than the same amount in the future. This is because current money can earn interest through investment. TVM formulas help people calculate interest, plan for retirement, and determine the present value of future cash flows.
-
Why is the CAPM formula important for investors?
The Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) is vital for calculating the expected return of an asset based on its systematic risk. It helps investors understand the relationship between risk and reward. By using Beta, investors can determine if a stock is more or less volatile than the overall market, aiding in portfolio diversification.
-
How does compound interest differ from simple interest?
Simple interest is calculated only on the principal amount of a loan or deposit. Compound interest is calculated on the principal plus any accumulated interest from previous periods. This means that compound interest grows much faster over time. It is a powerful tool for long-term wealth building, but increases debt costs significantly for borrowers.