Involving more than 50 states across regions, the Second World War was undoubtedly the bloodiest war the system has witnessed. The world has yet to recover from the atomic bombing that ended this war. Throughout the war years, naval, infantry, and aerial confrontations between the Allies and Axis kept the world thinking about the fate of the Earth.
Let’s revisit the horrors of this lengthy confrontation with the World War II timeline. Make use of it to understand the importance of strategy and pragmatic foreign policy in a war scenario.
In this article
Part 1: World War II Timeline Explained | 1939 to 1945
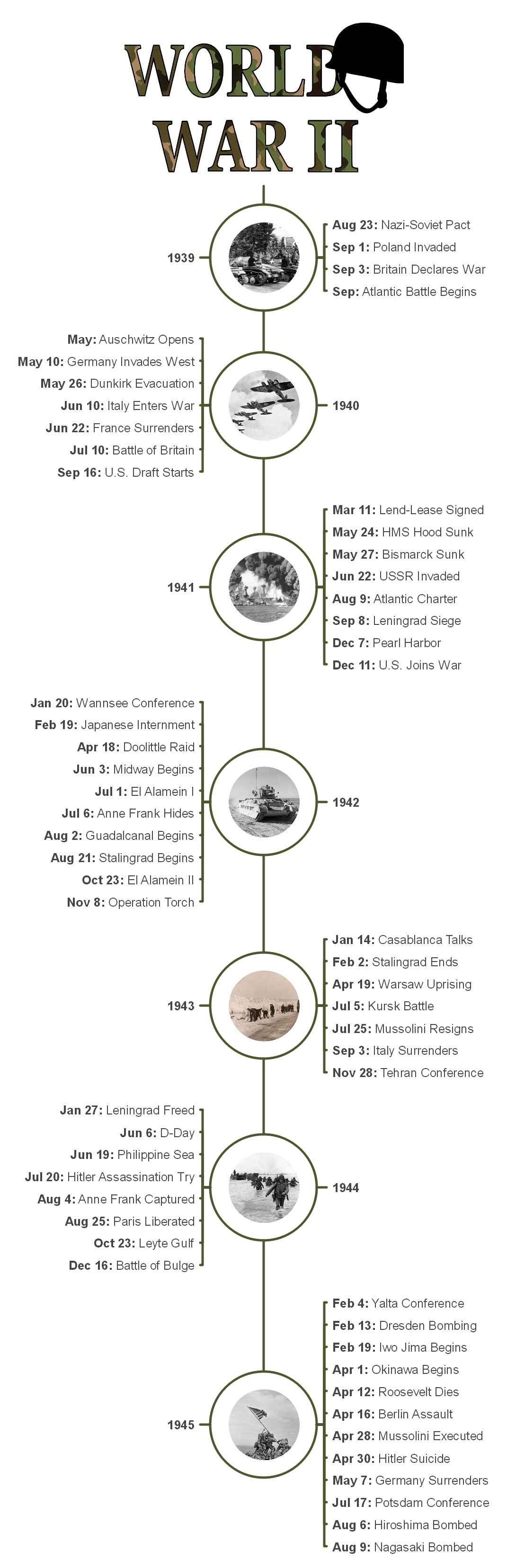
1939
Many believe that September 1 of 1939, marks the official start of World War II, when Hitler invaded Poland. However, it didn't start in a vacuum.
Events such as the Japanese invasion of China, tensions in Europe due to the rise of Hitler, and the German annexation of Austria triggered the episode. Meanwhile, Germany violated the Munich Pact by invading Poland. Other parties in Europe felt threatened.
- August 23 - USSR (Soviet) and Germany sign the Nazi-Soviet Non-Aggression Pact. This pact declared the USSR's military support for its German ally.
- September 1 - Hitler invaded Poland on September 1, which caused great distress in Britain and France.
- September 3 - Paris and London declared war on Germany.
- Late September - The Battle of the Atlantic started with naval campaigns between Britain and Germany. Meanwhile, the Soviet Union invaded East Poland. Consequently, the Polish government fled to France and later Britain. The Polish territory was divided between the USSR and Germany.
1940
The following year witnessed Germany invading its neighbors: Denmark, Norway, the Netherlands, France, and Luxembourg. Faced with a security dilemma, the Royal Air Force undertook nighttime raids in Germany.
In 1940, the Axis powers - Germany, Italy, and Japan - also entered into a joint military and economic agreement. As a result, Italy invaded Egypt, which the British mainly controlled.
Concerned with the security situation in Europe, the US abandoned its stance of neutrality and introduced the Lend-Lease Act. Under this act, the United States would provide its allies with material aid in exchange for leases on military bases abroad.
- May - the Auschwitz Nazi camps were established.
- May 10 - Hitler invaded Belgium, the Netherlands, and France.
- May 26 - The trapped British Expeditionary Forces succeeded in evacuating from Dunkirk to England.
- June 10 - Italy declared war on France and Britain by signing the Pact of Steel with Germany.
- June 22 - France surrendered to Germany.
- July 10 - The Battle of Britain started. The Royal Air Force defeated Germany in the Blitz. Meanwhile, Britain also received significant US aid under the Lend-Lease Act.
1941
1941 marks some of the biggest escalations during World War II. Germany broke its pact with Russia and invaded neighboring countries. Hence, the Soviet Union joins the Allied bloc. Meanwhile, Japan's misadventure at Pearl Harbor officially counted the US in the war.
- March 11 - US President Franklin Roosevelt signed the Lend-Lease bill.
- May 24 - The German battleship Bismarck sank the British ship HMS Hood, the pride of the Royal Navy.
- May 27 - The Royal Navy sank the German battleship Bismarck.
- June 22 - Operation Barbarossa began with Germany's attack on Russia. The Germans were able to advance 200 miles into Moscow, mainly due to the inadequate Russian Aviation technology.
- August 9 - The Atlantic Conference began. The two leaders, US President Roosevelt and UK Prime Minister Churchill, formally met to propose a joint declaration.
- September 8 - The Axis powers besieged Leningrad, in the Soviet Union. The military blockade cut the land off from the rest of the country.
- December 7 - Approximately 360 Japanese aircraft launched a surprise attack on Pearl Harbor. It was a US naval base in Hawaii.
- December 11 - Following the Congress declaration of war on Japan, the Axis powers announced war against the US. America also declared war on Italy and Germany.
1942
1942 started with Japan capturing significant lands in the Pacific. However, the Battle of Midway turned the momentum in favor of the Allies by mid-1942. By the end, the Allies also started making gains in Africa.
- January 20 - The Wannsee Conference was held to answer the question of jews in Europe.
- February 19 - US President Roosevelt issued Executive Order 9066. This order called for the internment of Japanese Americans.
- April 18 - The US launched the Doolittle air raid on major cities in Japan.
- June 3 - The Battle of Midway began. The US Navy defeated the Japanese by sinking four of their aircraft carriers.
- July 1 - The First Battle of El Alamein began. The Axis and Allied forces had a lengthy confrontation in Egypt.
- July 6 - Anne Frank, the infamous German-born Jewish girl, went into hiding with her family.
- August 2 - The Guadalcanal campaign started. It consisted of major naval and land battles up until 1943.
- August 21 - The Battle of Stalingrad began. The Axis powers and the Soviet Union fought for control of the city of Stalingrad in the USSR.
- October 23 - The second Battle of El Alamein began. The Axis forces of Italy and Germany suffered a massive defeat at the hands of the British.
1943
The Soviet Union achieved significant advances in the Stalingrad, turning it into Germany’s major defeat. The tide started to shift in the Allies’ favor, and by the fall, Italy surrendered to the Allied powers. Meanwhile, the US also gained territories in the Pacific.
- January 14 - The Casablanca Conference started to finalize the Allies’ strategic plan against the Axis.
- February 2 - The Germans finally surrendered in Stalingrad, USSR.
- April 19 - The Warsaw Ghetto uprising began. It was a symbol of Jewish resistance in German-occupied Poland.
- July 5 - The Nazi Germany and USSR had one of the major confrontations in Kursk, Soviet Union. The Battle of Kursk ended with a Soviet victory.
- July 25 - The Fascist Grand Council declared the overthrow of Mussolini.
- September 3 - Italy surrendered immediately after the establishment of the new government led by Pietro Badoglio. German forces in the country took control of the Northern territories.
- November 28 - The Tehran Conference started with the Allies finalizing their plan against the Axis powers.
1944
American troops launched surprise attacks against the Germans. Italy was liberated while the USSR counterattacks pushed the Germans back to Warsaw. However, the Battle of the Bulge delayed the Allied plan to advance into Germany.
- January 27 - The Siege of Leningrad finally ended after 900 days.
- June 6 - Allied powers advanced into Normandy, France, marking D-Day.
- June 19 - The Battle of the Philippine Sea started between the US and Japanese fleets. It ended with a US victory.
- July 20 - “The 20 July Plot”, the assassination attempt on Hitler failed.
- August 4 - Anne Frank was arrested with her family.
- August 25 - The Allied forces successfully liberated Paris.
- October 23 - The Battle of Leyte Gulf started. It was the largest naval battle between Japan and the Allies, mainly the US.
- December 16 - Germany started the Battle of the Bulge to push the American and British forces out of the country. It marks the last offence by Hitler during World War II.
1945
Most of Europe is now liberated from the World War II theatre. However, the war in the Pacific continues. Soon after the atomic bombings by the US, Japan surrendered.
- February 4 - The Yalta Conference was held. The leaders of the UK, the USA, and the USSR meet to define the postwar power organization of Europe and Germany.
- February 13 - The Allied powers started bombing the German city of Dresden.
- February 19 - The US Army and Navy captured the Iwo Jima islands from the Japanese Imperialist Army. This episode is titled 'The Battle of Iwo Jima.'
- April 1 - The Japanese Imperial Army and the US Army fought the Battle of Okinawa in the Pacific.
- April 12 - President Frank Roosevelt dies of declining health.
- April 16 - The Battle of Berlin started. The Soviet Union blocked the city militarily, taking revenge on the Soviets since 1941.
- April 28 - The Italian partisans assassinated Mussolini.
- April 30 - Hitler committed suicide.
- May 7 - Finally, Germany surrendered unconditionally.
- July 17 - President Truman, Prime Minister Churchill, and Leader Stalin gather in the Potsdam Conference to discuss the war with Japan. They also distributed the German land into four occupation zones.
- August 6 - The US dropped the second atomic bomb, named Little Boy, on the Japanese city of Hiroshima.
- August 9 - America dropped the second atomic bomb, named Fat Man, on the Japanese city of Nagasaki.
- September - US General Douglas accepted Japan’s surrender. This ended the Second World War.
Part 2: How to Make a Similar Timeline Using EdrawMind?
Capturing an extensive and detailed chronology of events, such as World War II, in a timeline is always an excellent idea. It gives your audience a quick glimpse of the event in a brief moment, without requiring them to read lengthy documents.
If you are currently covering such a topic, definitely consider a timeline. EdrawMind made it simpler with its preset structure, expandable branches, and design assistance. Let’s see how we can replicate a similar timeline infographic using this tool.
Step 1: Open the EdrawMind Canvas
Download and install the EdrawMind desktop version.
Or, try EdrawMind online.
Log in to your Wondershare account or register your email if it is your first time.
Step 2: Plot the Structure
Select the Main Idea box, click Layout, and choose Vertical, Horizontal, or Snake structure.
Count the number of events and dedicate a topic box for each year.
Step 3: Add Text Labels
Double-click any box and start typing.
Change the font details (size, style, color, etc) from the on-screen prompt.
Step 4: Insert Descriptions
Click the sub-topic boxes and start typing descriptions.
Modify the font size, color, and style from the on-screen prompt.
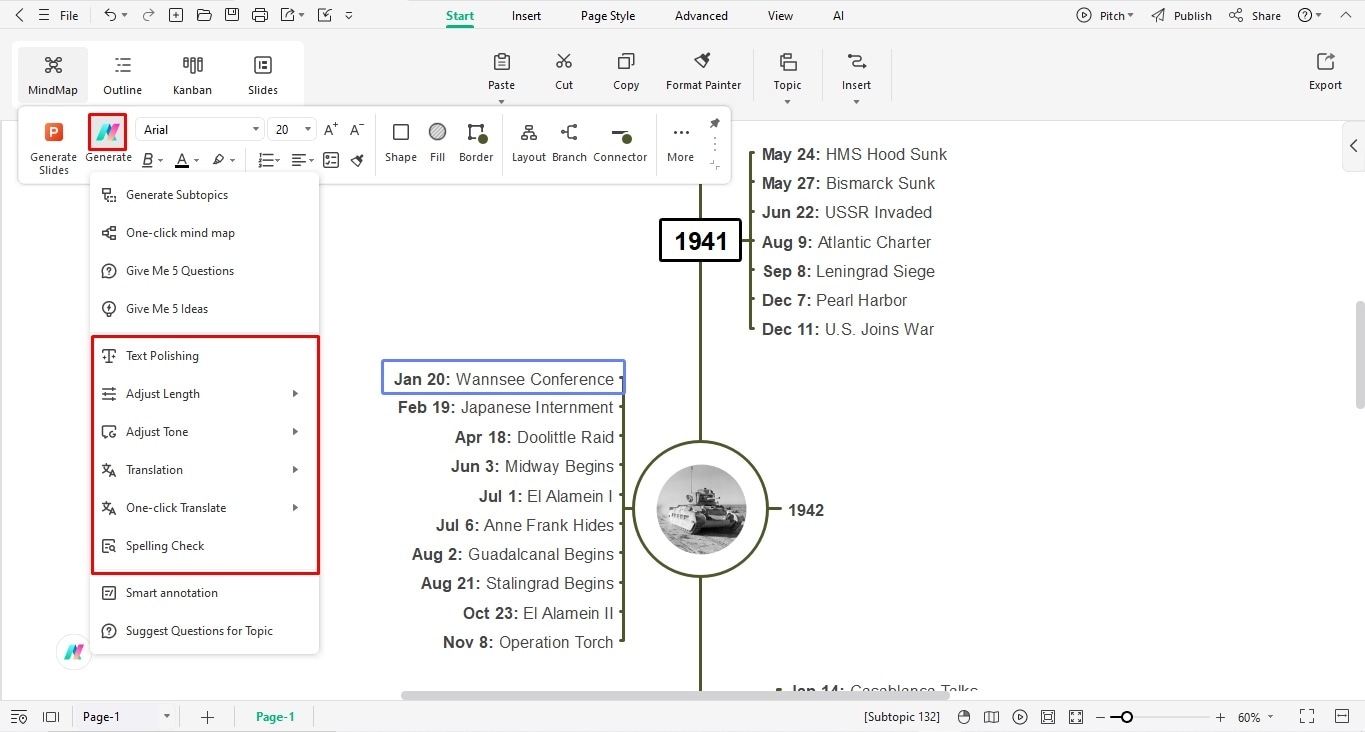
Bonus Step: Use Edraw AI to Generate Sub-Topics
Select the relative topic box and click Generate from the on-screen prompt.
Choose Generate Sub-Topic and leave the rest to the software.
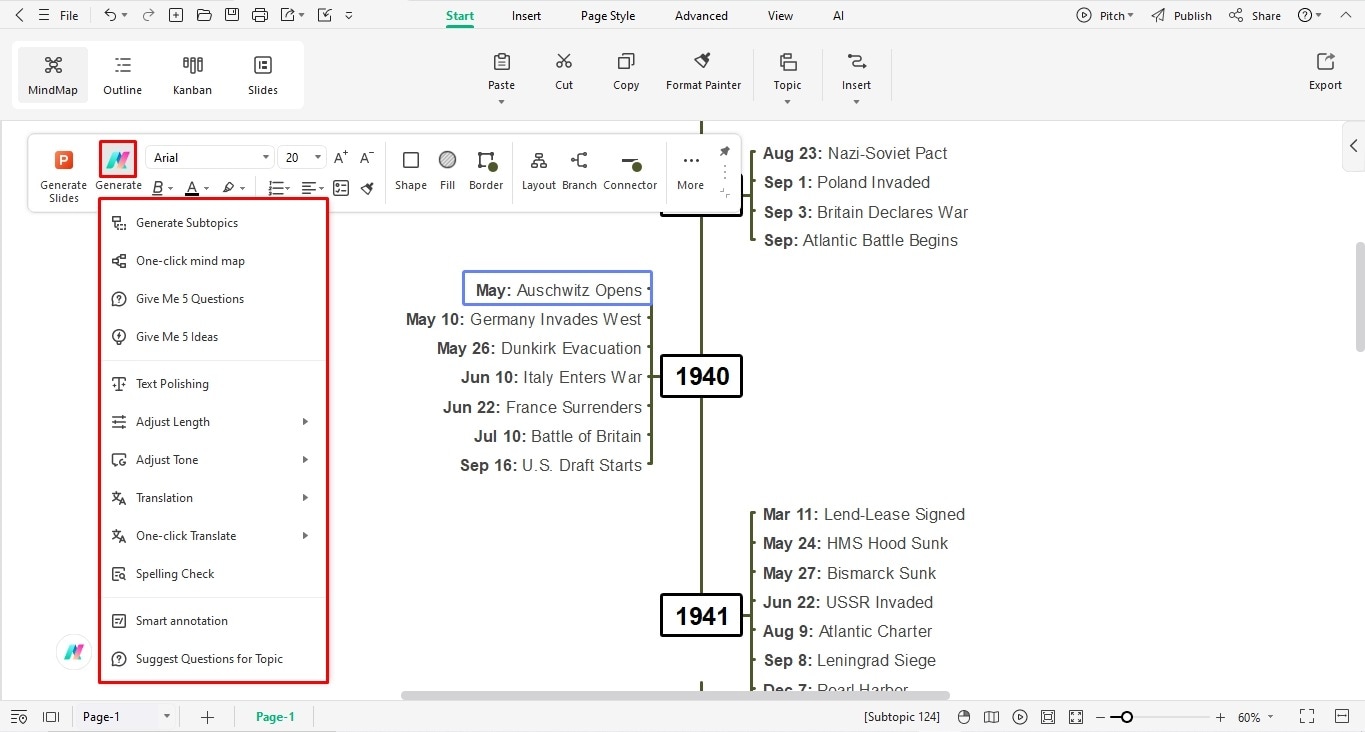
Step 5: Insert Visual Cues
Copy and paste the desired picture on the EdrawMind canvas.
Rotate, crop, and fine-tune them from the on-screen prompt.
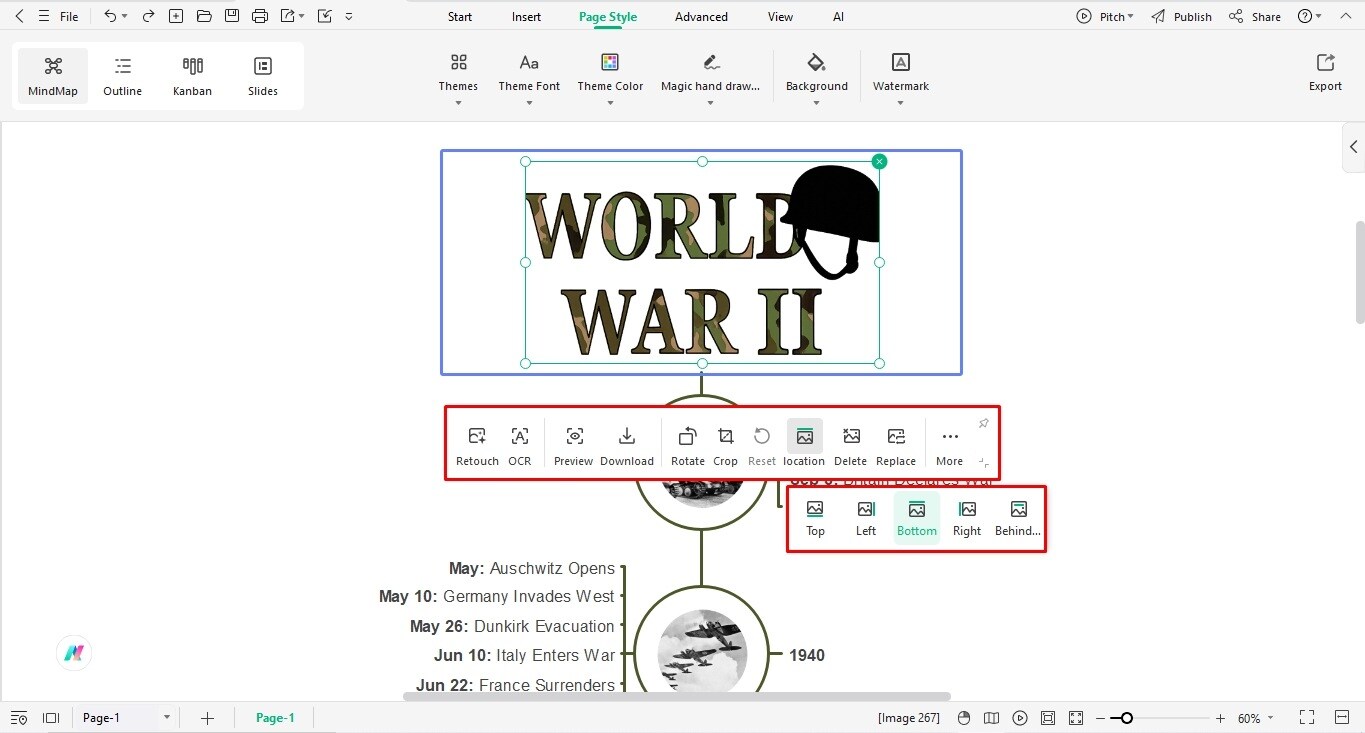
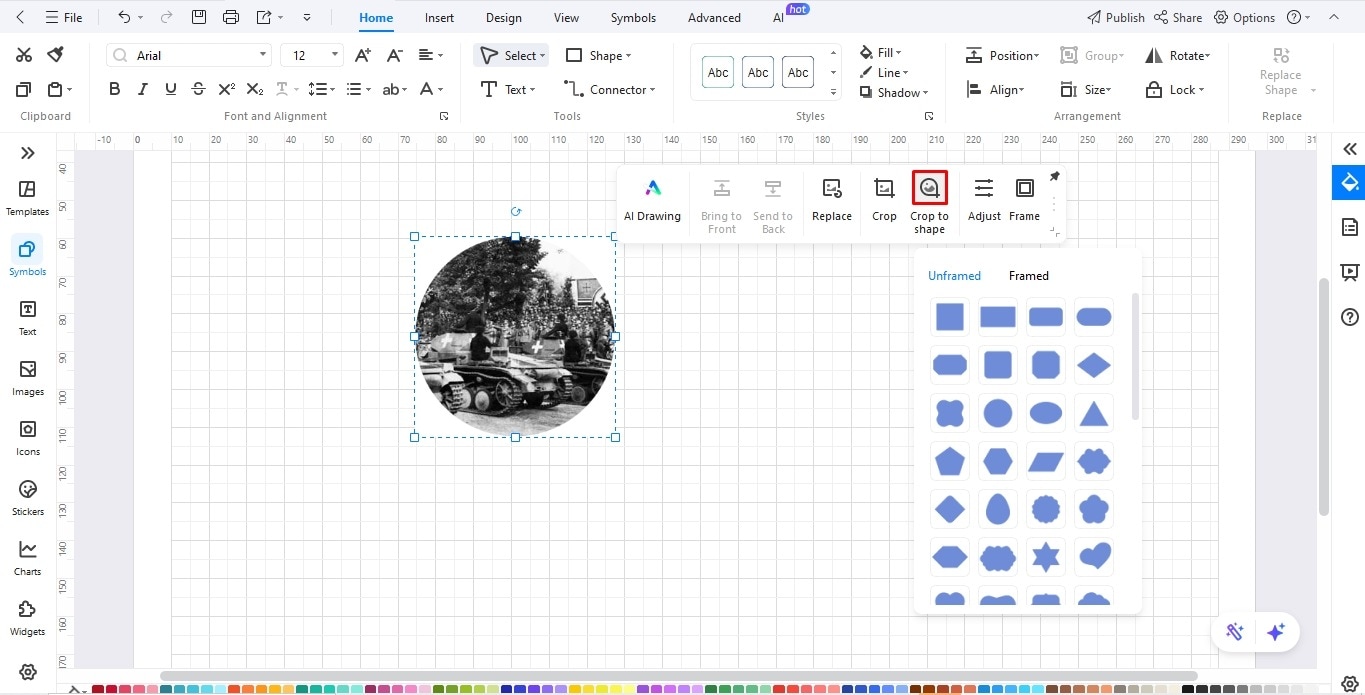
Bonus Step: Use EdrawMax to Adjust the Picture Frame
Copy and paste the required image on the EdrawMax blank canvas.
Locate the Crop to Shape button on the on-screen prompt.
Step 6: Modify the Design
Locate the Page Layout tab at the top.
Change the color scheme and theme of the infographic accordingly.
Step 7: Download the Timeline!
Visit the File menu from the top-left corner.
Click Save to save the diagram on your computer.
Conclusion
The World War II timeline is more than a chronology of events. It offers a detailed account of military miscalculations, the unavoidable consequences of economic depression, and never-ending political gains. You can also analyze similar events using timelines. Try EdrawMind to get started. It has a huge template gallery featuring numerous historical timelines.