Covering the widest time frame of the three prehistoric eras, the Stone Age is often confused with the use of stone tools by archaic humans. For instance, the present-day Ethiopia traces back the Homo habilis, the early members of the Homo Genus, back to 2.6 million years ago. Yet, the evidence of hominids using stone tools goes back to 3.3 million years ago.
But worry not! Let’s break this huge amount of time with an easy-to-follow Stone Age timeline, so you know better what the 3 Stone Ages and their respective eras are.
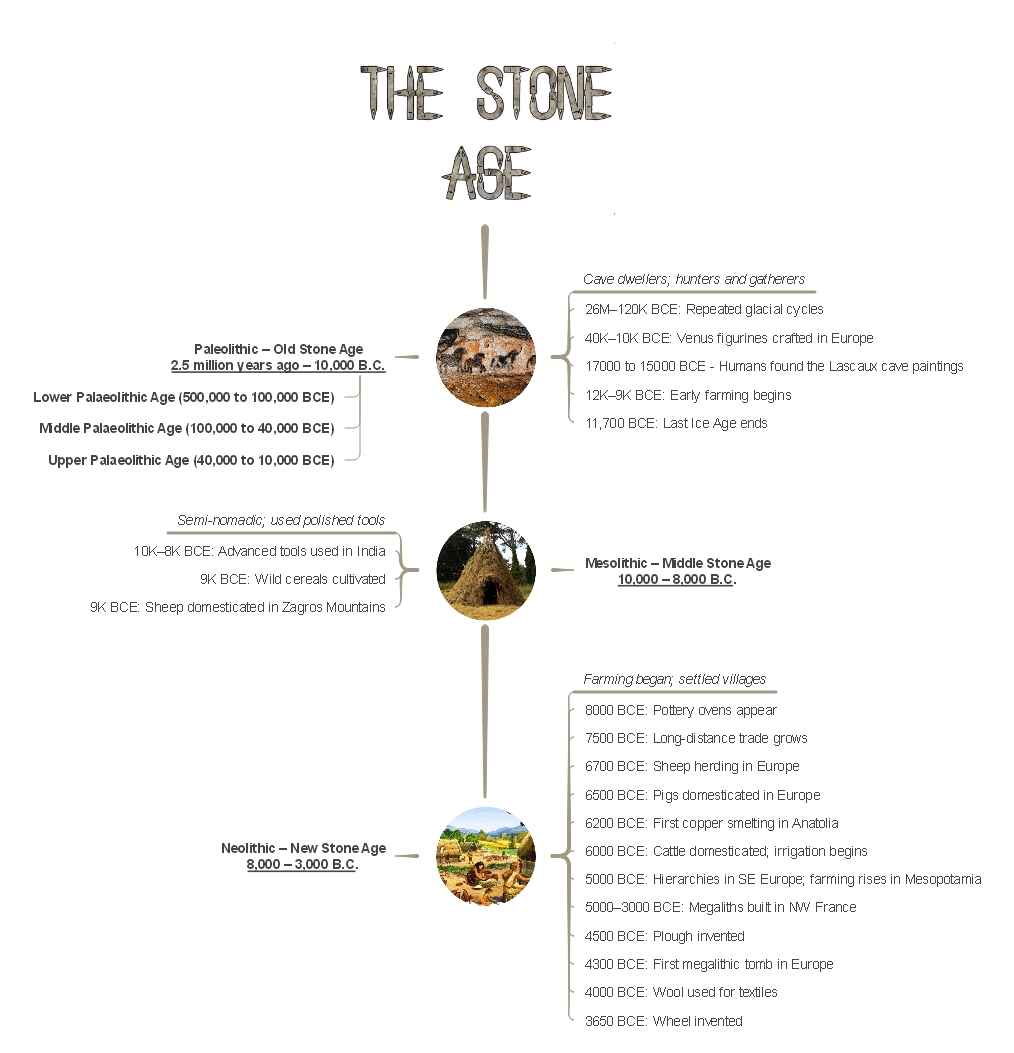
Stone Age Timeline Explained
The Stone Age, a prehistoric era, precedes the Bronze and Iron ages. Further divided into Old Stone Age, Middle Stone Age, and New Stone Age, this era is marked by the early human ancestors. What started as a hunter-gatherer society evolved into farming and food production by the end of the Neolithic period, also known as the New Stone Age.
Let's track these three eras in detail with a Stone Age timeline in order.
Palaeolithic - Old Stone Age (2.5 Million Years Ago to 10,000 BC)
Palaeolithic people were our human ancestors, also known as cavemen. As nomads, they primarily gathered food, shelter, tools, and other essential items from their surroundings.
Ancient humans in the Palaeolithic Stone Age mostly hunted animals such as red deer, wild cattle, wild horses, and red foxes. One example of their genius is that they would use every part of their prey for living - meat for food, fur for clothing, and marrow for glue.
These Palaeolithic humans were also the first to leave their mark on the art of the ages to come. They used a mixture of minerals, burnt bone meal, water, animal fat, and blood to engrave humans, signs, and animals.
The last ice age marks the end of the Old Stone Age. Climate change led to the extinction of large mammals and rising sea levels, forcing humans to migrate.
Being the longest time in the Stone Age timeline, the Palaeolithic age is further divided into three ages.
- Lower Palaeolithic Age (500,000 to 100,000 BCE): It is divided into the Oldowan and Acheulean Stages. During the first stage, people witnessed the development of chopping tools, also known as pebbles. As humans transitioned to the second stage, they used sophisticated hand axes.
- Middle Palaeolithic Age (100,000 to 40,000 BCE): This age was characterised by the widespread use of fire. The tools from the previous age evolved into flake tools, made from stones, which had sharp edges.
- Upper Palaeolithic Age (40,000 to 10,000 BCE): This age was the latest stage of the Palaeolithic period. It mostly witnessed the use of sophisticated tools and the introduction of agricultural activities near the water bodies.
Some notable events that occurred during the Palaeolithic Stone Age included:
- 26,000,000 to 120,000 BCE - The world experienced repeated cycles of glacial and interglacial activity.
- 40000 to 10000 BCE - People in Europe produced the infamous Venus figurines.
- 17000 to 15000 BCE - Humans found the Lascaux cave paintings.
- 12000 to 9000 BCE - Small-scale agricultural practices initiated.
- 11700 BCE - The Ice Age officially came to an end. The world experienced the most recent glacial episode.
Mesolithic - Middle Stone Age (10,000 to 8,000 BC)
The Middle Stone Age is commonly referred to as the Mesolithic era. Humans in this era lived nomadically in camps and simple huts near water sources. Given the advantages of rivers, these people began agriculture and established permanent settlements in the countryside.
They also used stone tools, but now polished. Most of these tools were also crafted with points and attached to bones and antlers, acting as arrows and spears. The Mesolithic humans always hunted animals in groups of 10-40 people.
Some worthy events that occurred during the Mesolithic Stone Age are as follows.
- 10000 to 8000 BCE - Tools, such as backed blades, crescents, spearheads, knives, and daggers, became common in India.
- 9000 BCE - Cultivation of wild cereals became common.
- 9000 BCE - People started domesticating wild sheep in the Zagros Mountains.
Neolithic - New Stone Age (8,000 to 3,000 BC)
Following the permanent settlements of the Mesolithic age, the Neolithic people stopped moving and began to cultivate a true agricultural culture. They started farming crops such as wheat and spelt while domesticating animals. The Neolithic humans also used polished tools, such as hand axes and adzes, for farming activities, like tilling the land and ploughing.
The advancements made by Neolithic people were not limited to farming and construction, but also included art. They learnt pottery, sewing, and weaving.
Some notable events during the Neolithic Stone Age worldwide are as follows.
- 8000 BCE - Ovens were established for pottery production.
- 7500 BCE - Long-distance trade gained momentum across the world.
- 6700 BCE - Europeans domesticated sheep in herds.
- 6500 BCE - Europeans started domesticating pigs.
- 6200 BCE - The First ever copper smelting was found in Anatolia.
- 6000 BCE - People domesticated cattle. The first irrigation system was also established during this time.
- 5000 BCE - Hierarchical societies emerged in Europe, particularly in the Southeastern Regions. Meanwhile, the agricultural practices also gained momentum in Mesopotamia.
- 5000 to 3000 BCE - The Megaliths were created at the Neolithic site in North-West France.
- 4500 BCE - Invention of the plough.
- 4300 BCE - The first Megalithic tomb was created in Europe.
- 4000 BCE - People used wool for textiles.
- 3650 BCE -The wheel was invented.
How to Make a Similar Timeline Using EdrawMind?
Timelines are an excellent way to make sense of historical events. The prehistoric Stone Age timeline gives you a visual glimpse of this era's chronology. You can also make similar infographics to graphically explain any complex or basic historical event.
Good news - It's no work with EdrawMind's preset timeline structures and resourceful editing kit. Let's see how you can plot the three stone ages in minutes.
Step 1: Access the Blank Canvas
- Download and install the EdrawMind desktop version. Or you can just try EdrawMind online in your browser.
- Register your email on EdrawMind if it is your first time. Or, log in to your Wondershare account.
- Once on the dashboard, click Create > Local Mind Map from the top-left corner.
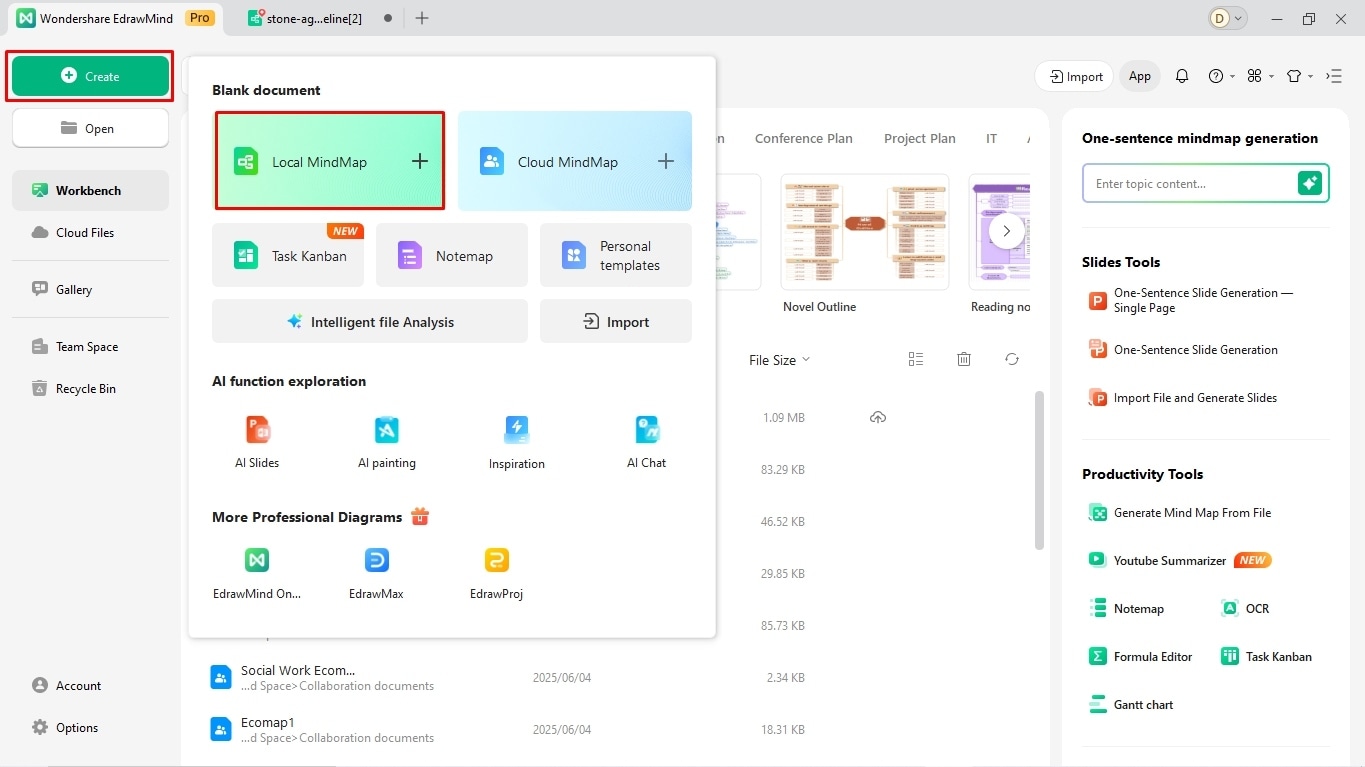
Step 2: Adjust the Layout
Let's start with the timeline structure. The default canvas layout is set to mind map; therefore, you need to change it to timeline.
- Click the Main Idea box and select Layout from the customization panel on the right side.
- Take the time to review the data.
- Decide whether the information requires a horizontal, vertical, or snake-like timeline structure.
- Once decided, apply the desired layout.
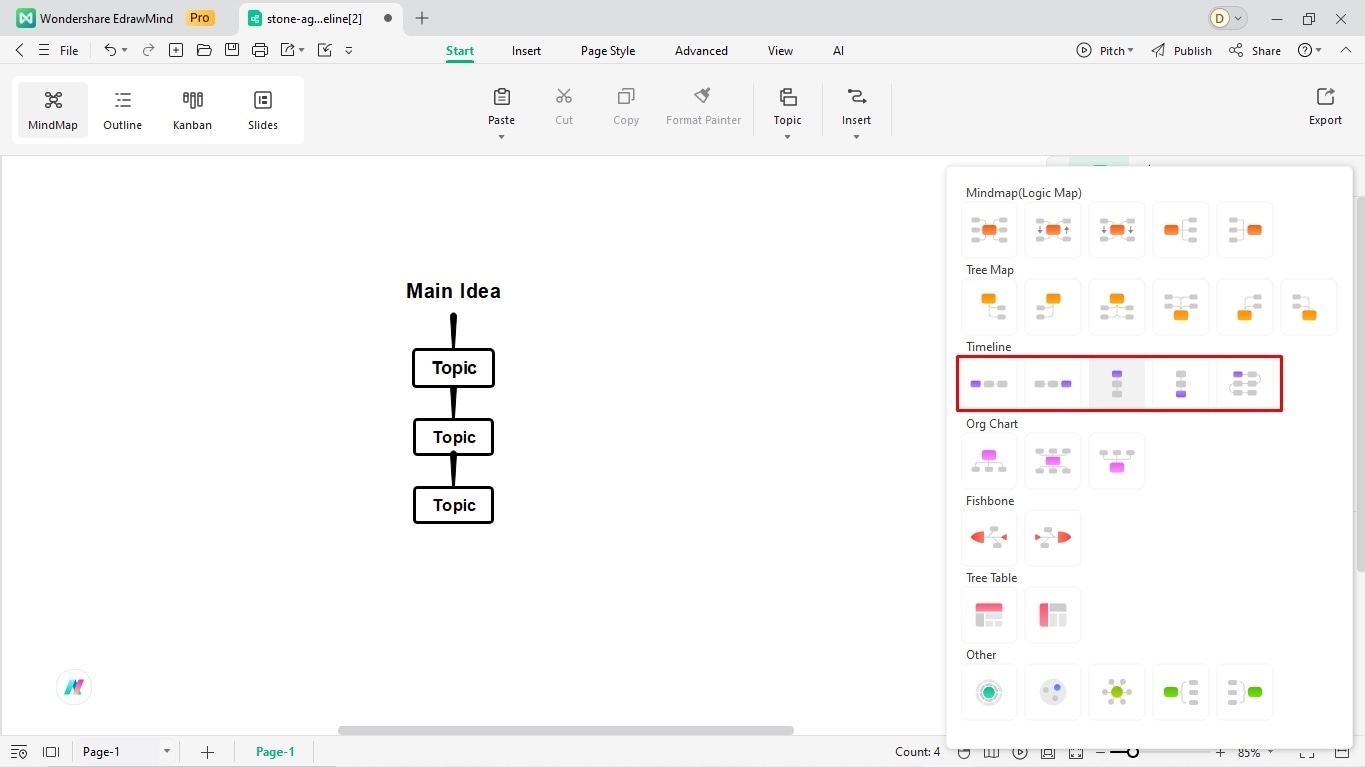
Step 3: Add or Remove Branches
The next step is plotting the structure. Review the data to see the number of milestones. Extend the branches accordingly. For this, you have two options.
- Select the Main Idea box and press Enter on your keyboard to add a new branch. Keep doing this for each milestone.
- Alternatively, you can right-click any box and click More > Desired Extending Branch.
- Don't rush and take a moment to build your structure, events, and sub-branches, as it will determine how your timeline will look.
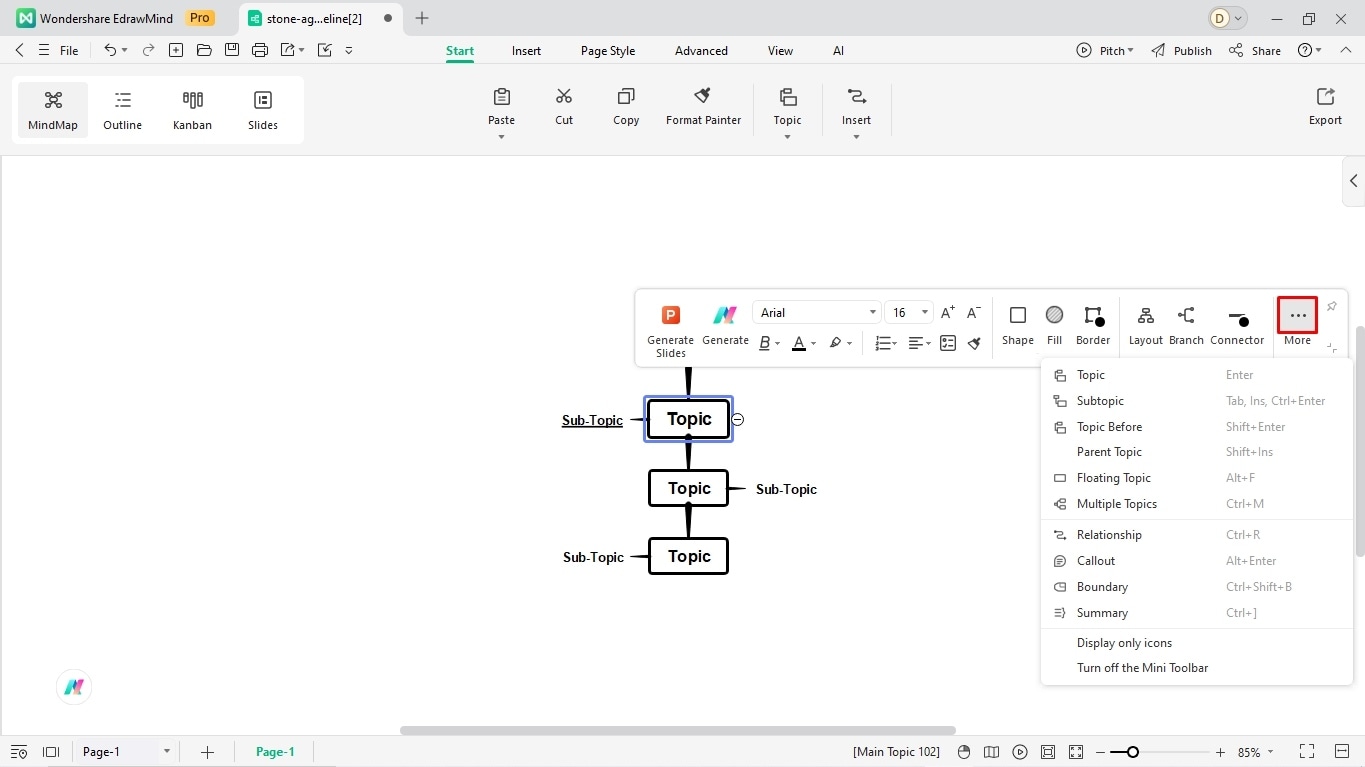
Step 4: It's Time to Label Milestones
Satisfied with the structure? Proceed and label the milestones. You can easily do it in the Outline Mode.
- Switch to the Outline Mode from the top right of the canvas. It represents the timeline data in a linear view to aid your understanding.
- Double-click any box and start typing.
- Keep the milestone labels simple. Include basic information, such as the event title and date.
- Adjust the font size, style, and shape from the on-screen prompt.
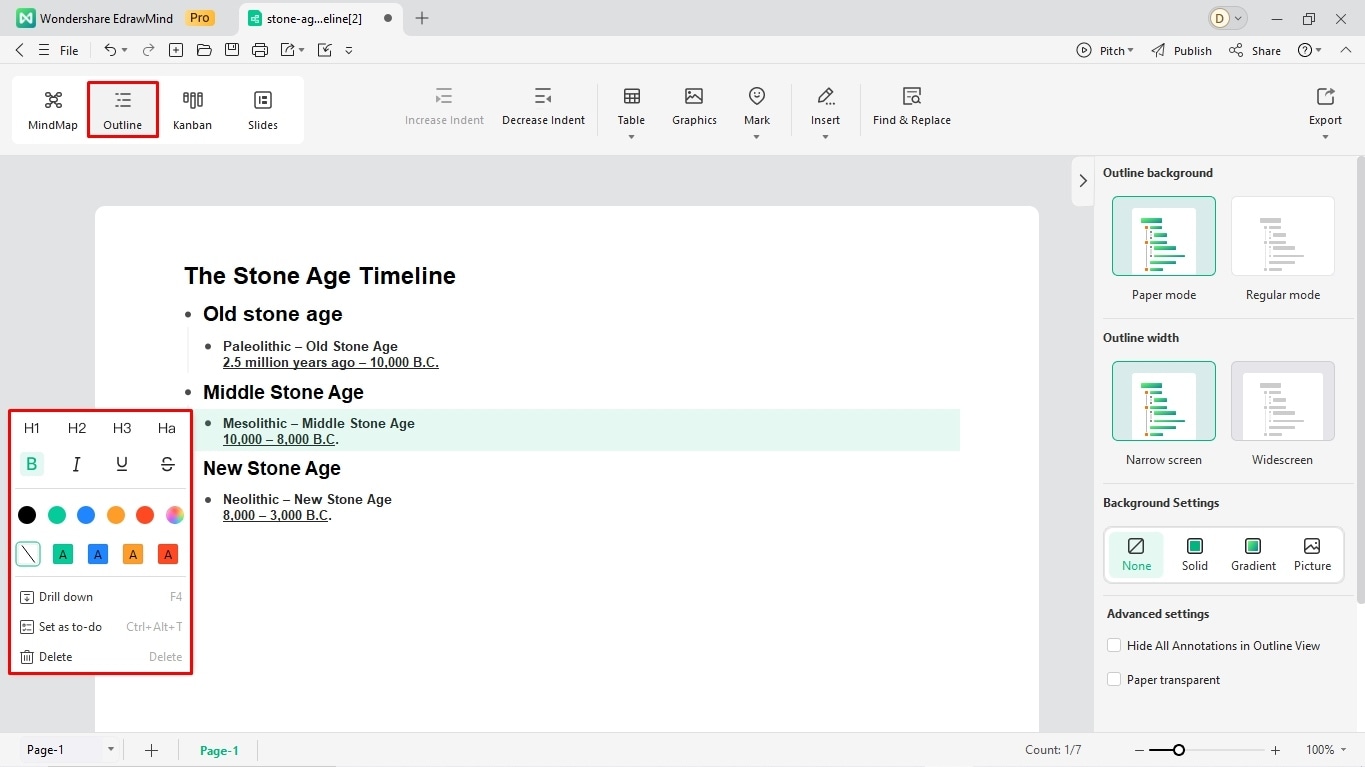
Step 5: Insert Descriptions for Milestones
It's time to enhance your viewers' understanding of the milestones by providing descriptions.
- Double-click any sub-branch and type your milestone's description.
- Modify font details (size, color, shape, style, etc) from the on-screen prompt.
- However, descriptions can get wordy, and you should use Edraw AI to avoid this. This smart text assistance helps you adjust the text tone, shorten the length, and translate it into another language.
- Select any description box in the diagram and click Generate.
- Select your desired operation from the menu and let Edraw AI handle the rest.
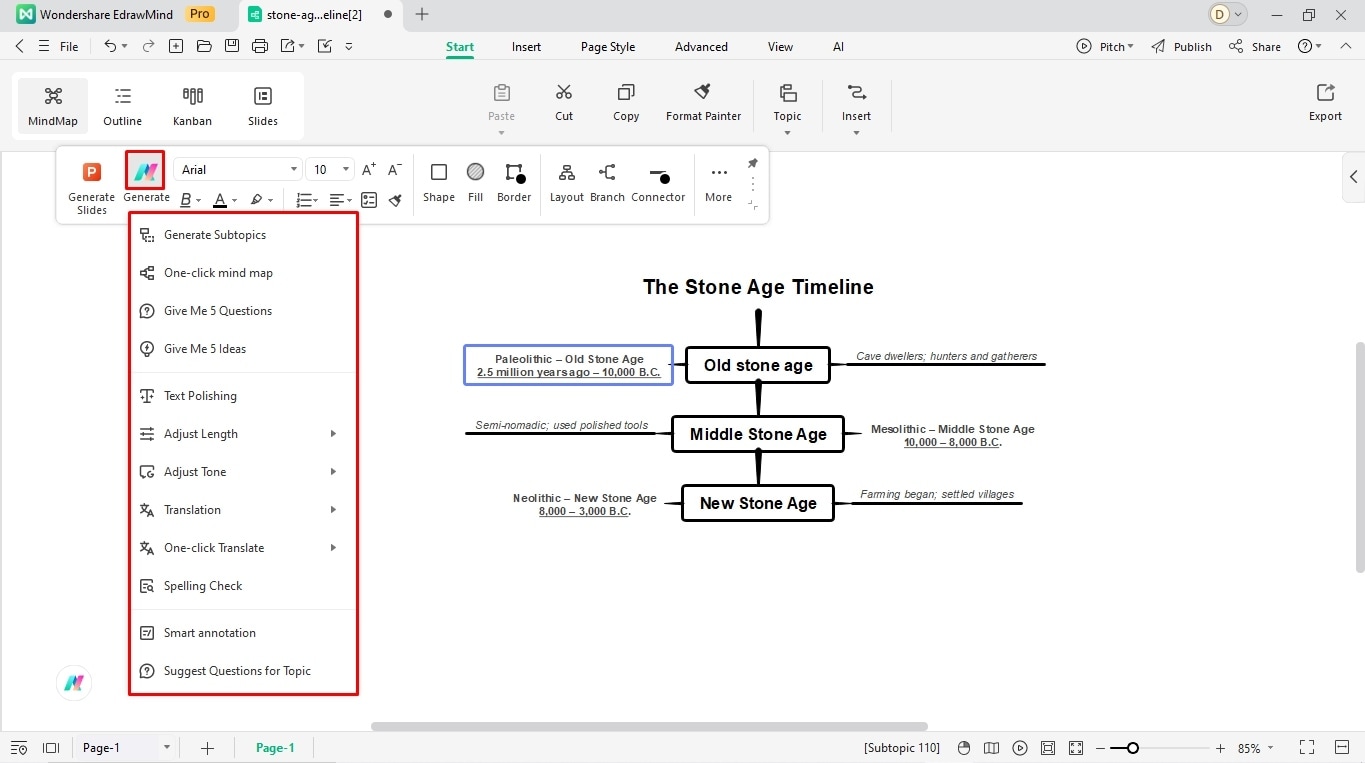
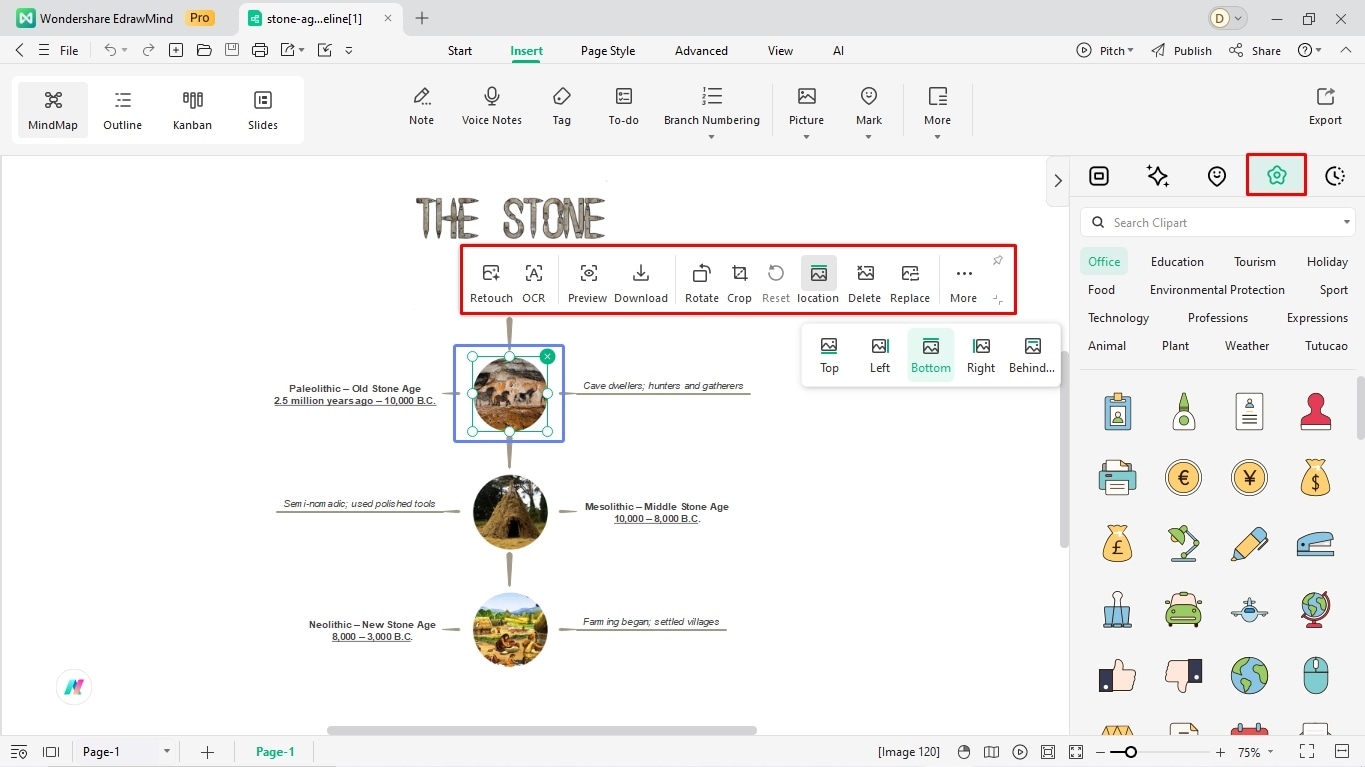
Step 6: Add Visual Cues
Adding visual cues in timelines is always a great idea. Be it pictures or symbols, visual elements better gauge your audience and help them register the events.
- Visit the right-side customization panel to access Clipart.
- You can resize them accordingly.
- Alternatively, copy and paste images directly onto the canvas.
- You are free to rotate, crop, and fine-tune them from the on-screen prompt.
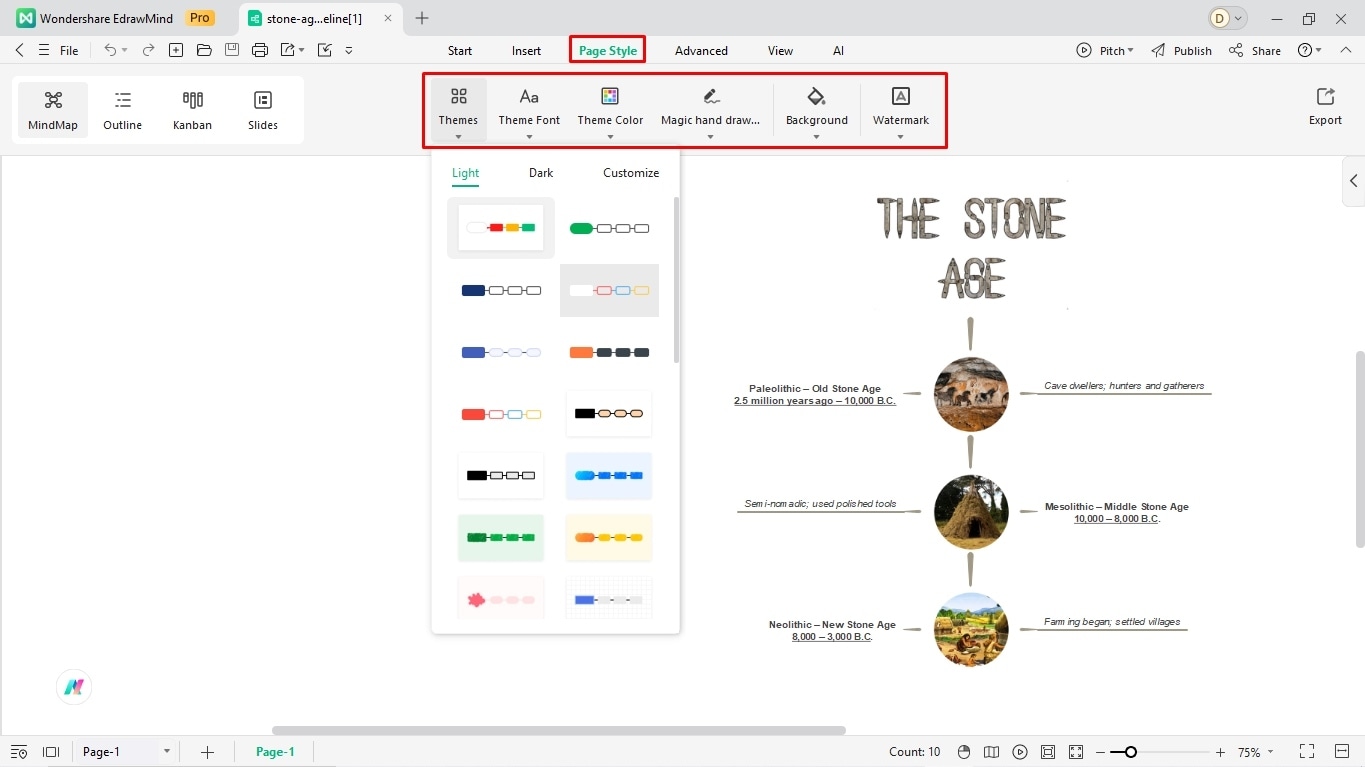
Step 7: Modify Design Details
You are almost there. Just a few final design finishes.
- Locate the Page Layout tab at the top.
- Adjust the theme, color scheme, background image, and orientation of the diagram accordingly.
- It is better to choose a color batch that best reflects your timeline theme.
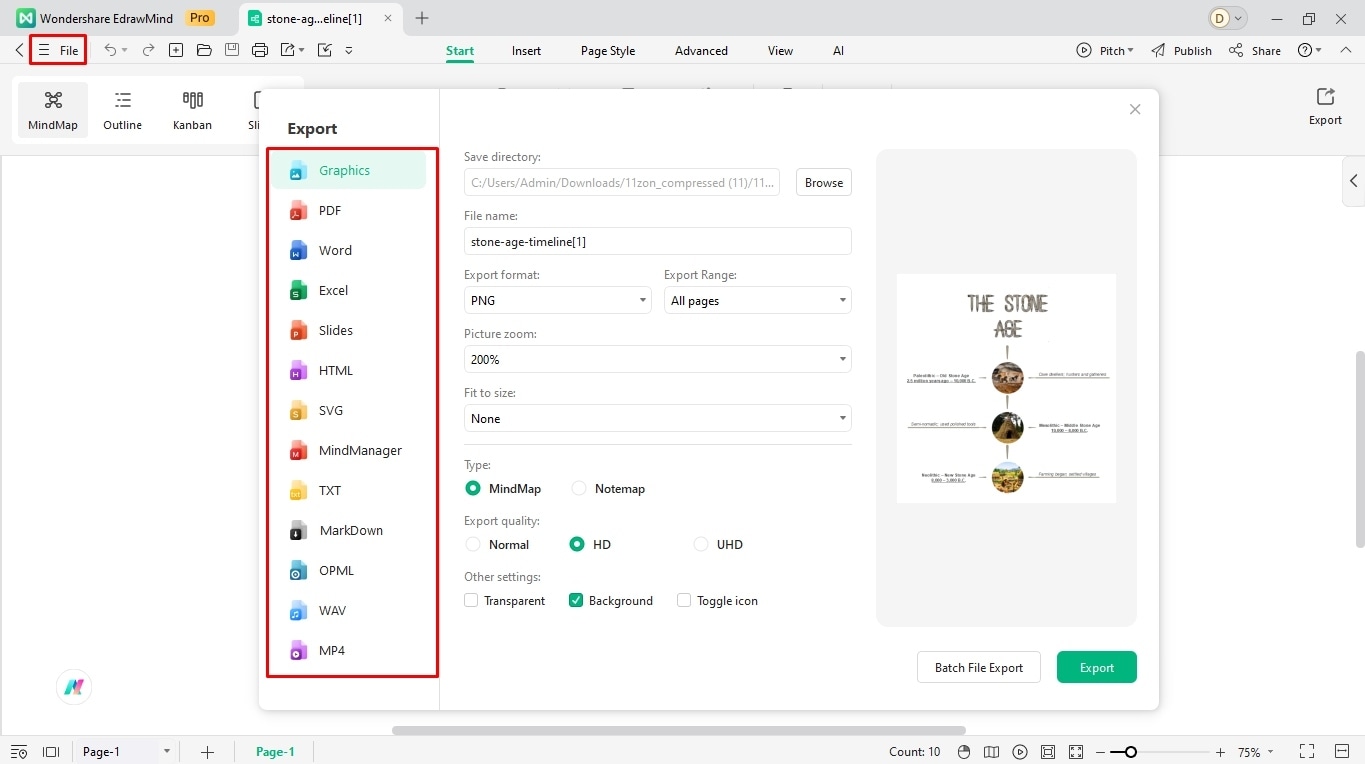
Step 8: Download Your Work
Finally, you can download your work in over ten formats, including Graphics (JPG, PNG, JPEG, etc), MS Office, and PDF.
- Visit the File menu from the top-left corner.
- Click Export and select the desired format.
Conclusion
There you have it - the longest prehistoric age explained in seconds. The Stone Age timeline gives you a quick glance at human development through the three eras, with minimal effort. You can also explain similar complex historical episodes using timelines.
It is easier with an advanced toolkit like EdrawMind. Its preset structures and ample canvas space give you freedom to expand your timeline. Give it a try for free and see if it works for you.