Indian history is long. We’re talking about one of the world’s oldest civilizations - the Indus Valley, which began around 3300 BCE. That’s over 5,000 years of ideas, empires, art, and revolution. From ancient trade routes to space missions, India has always been in motion.
This timeline covers it all. The rise of mighty dynasties like the Mauryas and Guptas, the arrival of the Mughals, British rule, and the 1947 freedom struggle. It’s a journey from stone tools to nuclear power. So, get ready, our journey begins where it all started - along the Indus River.
In this article
Part 1: Indian History Timeline
Across thousands of years, India has been a cradle of civilization, a center of learning, and a battleground for empires. It gave birth to major religions, revolutionary ideas, and timeless art. Each era brought change, challenge, and cultural growth. This isn't just India's history - it's world history in motion.
But to understand where we are now, we need to see where it all began. Let's explore the past through this timeline.
Indus Valley Civilization (3300 - 1700 BCE)
One of the world's oldest civilizations, known for its urban planning and advanced sanitation systems. The Indus Valley Civilization wasn't just old, it was smart. Cities like Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa had drainage systems, public baths, and streets laid out in grids. That's some serious urban planning, 5,000 years ago!
We still haven't cracked their script, but we know they were great traders, used standardized bricks, and kept things organized. They didn't leave behind grand palaces or massive weapons; just signs of a peaceful, well-planned life. Mysterious, impressive, and ahead of their time.
Vedic Period (1500 - 500 BCE)
Next came the Vedic Age. Indo-Aryans arrived. They brought Sanskrit with them and composed the Vedas - ancient hymns that became the foundation of Hinduism. Life revolved around fire rituals, cattle, rivers, and oral storytelling. It was a time of gods, nature worship, and philosophical beginnings.
Society was changing fast. The earliest forms of caste began forming. Kings and priests shared power. But beyond politics, the spiritual foundation of India was taking root. It was deep, lasting, and still relevant today.
Mahajanapadas & Age of Buddha (c. 600 - 322 BCE)
Before the Mauryas, India was divided into 16 powerful kingdoms, known as the Mahajanapadas. This was a time of political rivalries, urban growth, and deep philosophical shifts. It was during this time that Siddhartha Gautama (the Buddha) and Mahavira (founder of Jainism) were born.
Kingdoms like Magadha rose to power. Debates, councils, and reforms were common. And in some regions, there were even early republics! The political landscape was intense, but so was the spiritual awakening sweeping through ancient India.
Mauryan Empire (c. 322 - 185 BCE)
Then came the game-changer: Chandragupta Maurya. Guided by Chanakya, he founded the Mauryan Empire, India's first large-scale empire. It spread across most of the subcontinent. But the real star? His grandson, Ashoka.
Ashoka began as a fierce warrior, but after the bloody Kalinga war, he turned to Buddhism. He promoted peace, tolerance, and non-violence. His edicts, carved on rocks and pillars, are some of India's oldest written records. The Mauryan era brought governance, trade, and spiritual reform all in one shot.
Post-Mauryan Period: Shungas, Kushans & Satavahanas (185 BCE - 320 CE)
After the Mauryas, smaller kingdoms took over. The Shungas ruled in the north. The Satavahanas dominated the Deccan. And the Kushans- Central Asian rulers- brought new energy, especially to the northwest.
This period saw major artistic and religious developments:
- The rise of Gandhara art (a blend of Greek and Indian styles)
- Growth of Mahayana Buddhism
- A cultural melting pot thanks to the Silk Road trade
King Kanishka of the Kushans played a big role in spreading Buddhism far beyond India.
Gupta Empire (c. 320 - 550 CE)
The Gupta Empire was India's Golden Age. The Guptas brought stability, prosperity, and a love for learning. Under kings like Chandragupta I and Samudragupta, India saw a boom in:
- Mathematics (the concept of zero!)
- Astronomy
- Literature and Sanskrit poetry
Temples flourished, trade expanded, and scholars like Aryabhata and Kalidasa became legendary. It was a time of cultural brilliance, intellectual breakthroughs, and peace.
Post-Gupta & Regional Kingdoms (c. 550 - 750 CE)
After the Guptas fell, India didn't collapse, but it diversified. Regional kingdoms like the Vardhanas of Thanesar and early Chalukyas rose up. Power was more local now, but culture kept moving forward.
In the south, the Pallavas were innovating temple architecture. Each region had its own flavor; language, script, and art styles evolved. It wasn't one big empire, but many smaller ones that added layers to India's identity.
Early Medieval India & Rise of the South (750 - 1200 CE)
This was the age of powerful southern dynasties. The Chalukyas, Rashtrakutas, and especially the Cholas took charge. The Cholas built grand temples, ruled strong naval fleets, and even reached Southeast Asia.
Meanwhile, in the north, dynasties like the Palas and Pratiharas held sway. Religion continued to evolve; Bhakti and Tantric traditions took root. This period was about regional pride, creativity, and the expansion of India's soft power.
Delhi Sultanate (1206 - 1526 CE)
Then came a wave of change - the Delhi Sultanate. It began when rulers from Central Asia established Islamic rule in Delhi. Over the next 300+ years, several dynasties ruled: Mamluks, Khiljis, Tughlaqs, Sayyids, and Lodis.
These Sultans brought:
- Persian influence in art and architecture
- New administrative styles
- Massive monuments like the Qutub Minar
It was also a time of cultural fusion - Hindu, Jain, and Muslim traditions interacting in new ways, sometimes tense, sometimes harmonious.
Mughal Empire (1526 - 1857 CE)
During this period came the Mughals, grand, powerful, and absolutely architectural. Babur kicked things off in 1526. But it was Akbar, Jahangir, and Shah Jahan who made it legendary.
They brought:
- A strong, centralized administration
- Religious tolerance (especially under Akbar)
- Stunning structures like the Taj Mahal and the Red Fort
Art, literature, and culture blended beautifully. But by the 1700s, the empire started weakening. Enter the British...
British Colonial Rule (1757 - 1947 CE)
It began with trade, then turned into full-blown control. The British East India Company took over after the Battle of Plassey (1757). Following the 1857 revolt, the British Crown ruled directly.
This period is famous for:
- Railways, English education, and new laws
- Famines, exploitation, and uprisings
- Reformers, rebels, and eventually - Gandhi
By 1947, after decades of struggle, India won independence. The British left, but not without deep scars and a divided subcontinent.
Post-Independence (1947 - Present)
Finally, India got independence in 1947, but had to rebuild from scratch. A new constitution. New leaders. New dreams. The country faced challenges, including partition trauma, wars, poverty, and many more. But also made progress in science, democracy, and global presence.
Today, India is:
- The world's largest democracy
- A rising economic power
- A nation of incredible diversity, history, and resilience
From the Indus Valley to Mars missions, India's journey is long, complex, and still unfolding.
Part 2: How to Make an Indian History Timeline in EdrawMind?
India has a rich and long history, from ancient civilizations like the Indus Valley to modern-day India. Writing it all down in text can be hard to understand. But with EdrawMind, you can turn your notes into a colorful and easy-to-read timeline!
This tool lets you use ready-made templates, so even beginners can start quickly. Let's learn how to create an Indian History Timeline step by step.
Step 1: Log in and Open a New File
- Download and open EdrawMind on your computer.
- Or, you can use EdrawMind online in your browser.
- Log in using Google or any other social account. Or, make a new Wondershare account.
- Click New Mindmap to start.
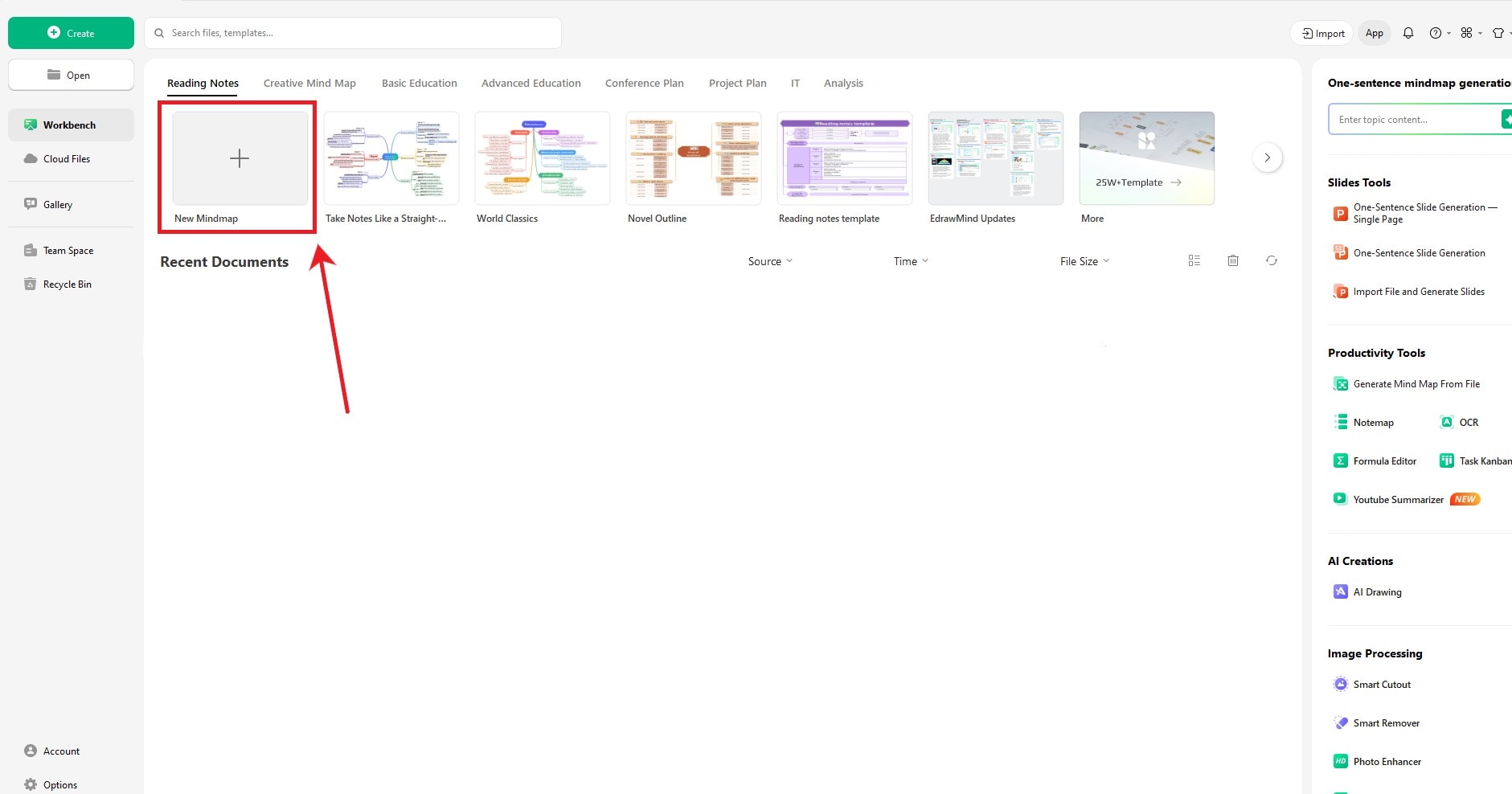
Step 2: Choose the Timeline Layout
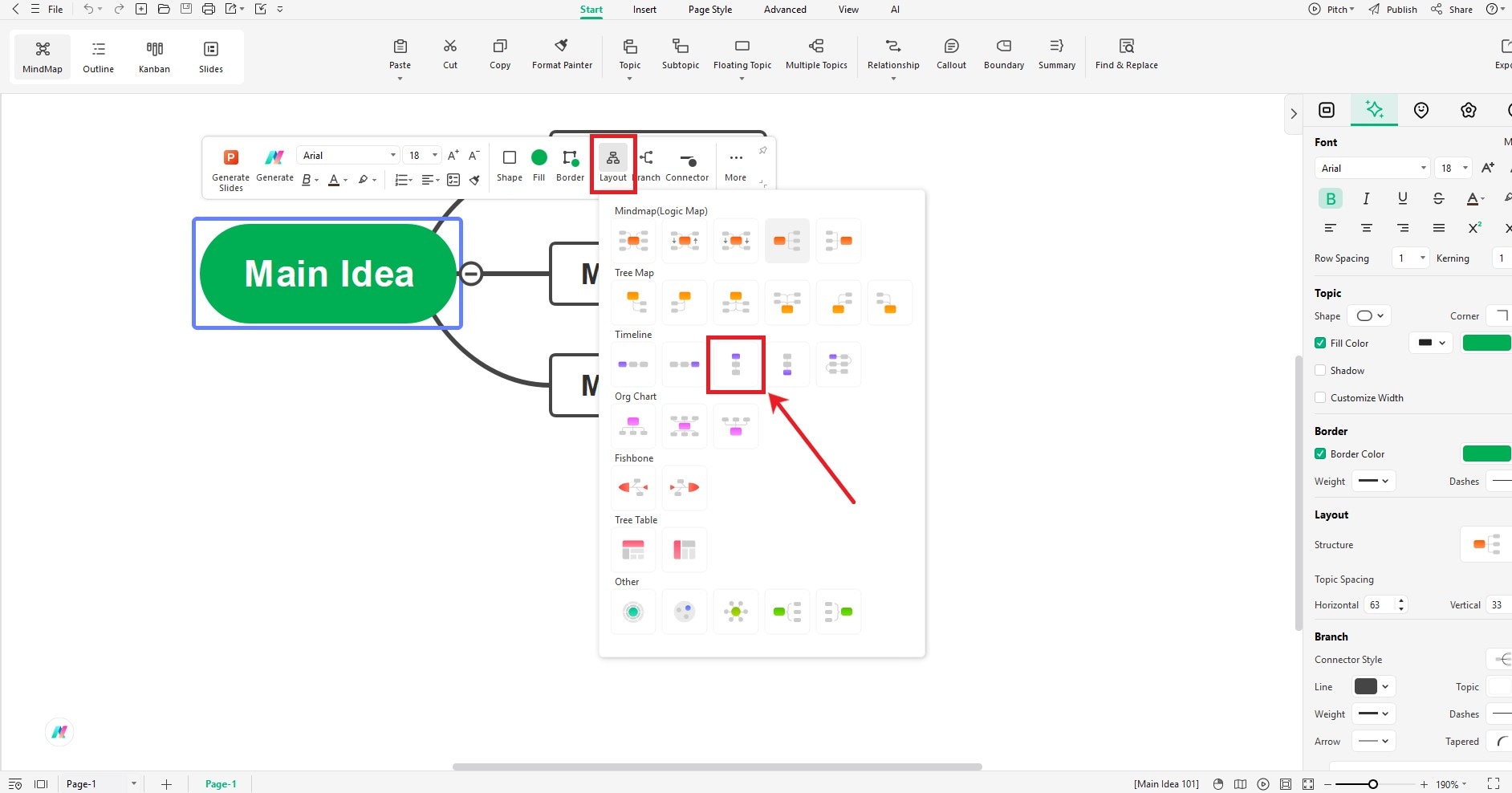
- Click on Main Idea in the center.
- Then, a small menu will appear, click Layout.
- From the layout list, select Timeline (Down). This makes your timeline go from top to bottom.
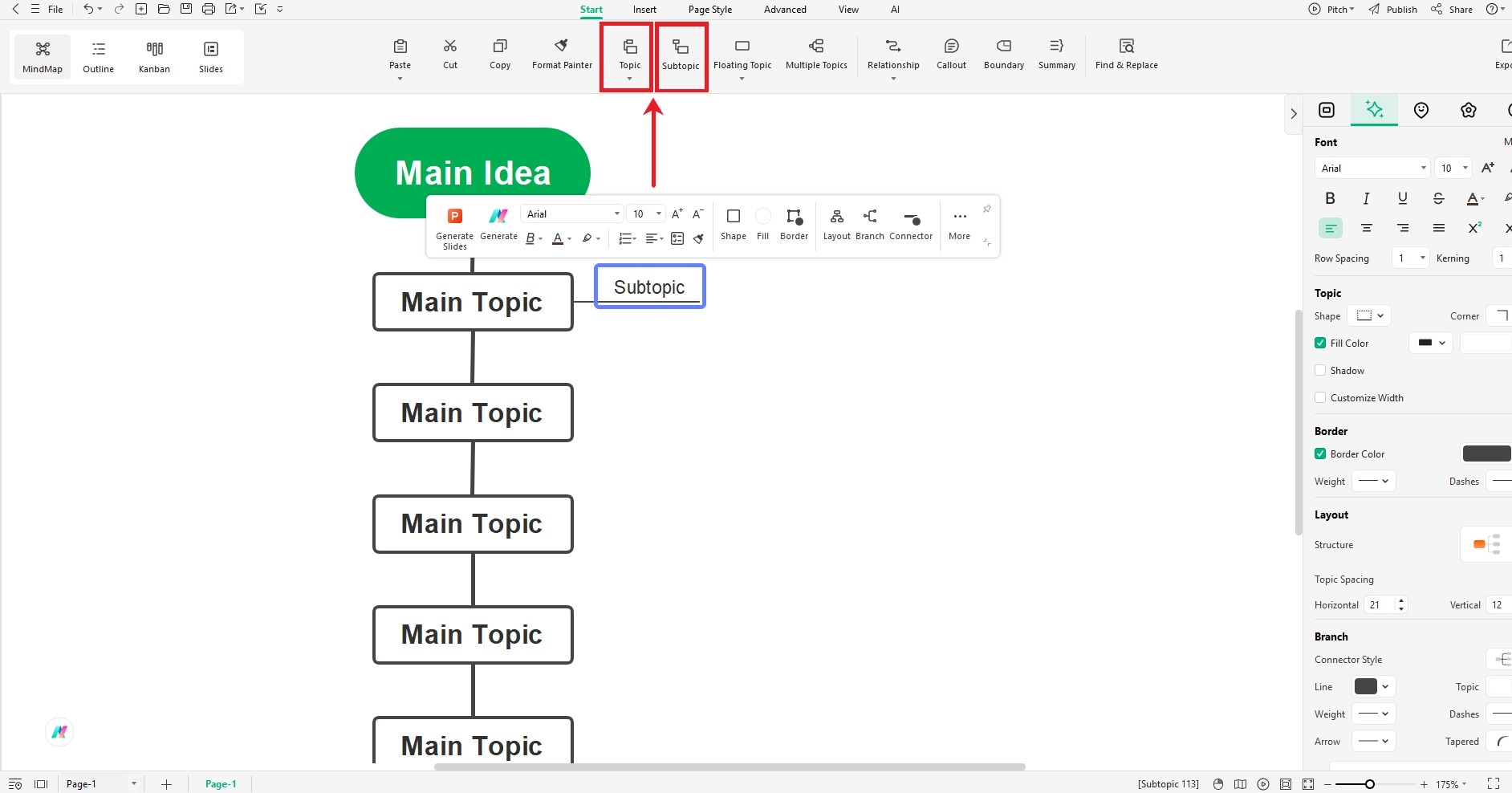
Step 3: Add Historical Events
- Click on Main Idea, then click Topic from the top menu. A new event (topic) will appear.
- Repeat to add more important events.
- To add small details under any event, click Subtopic.
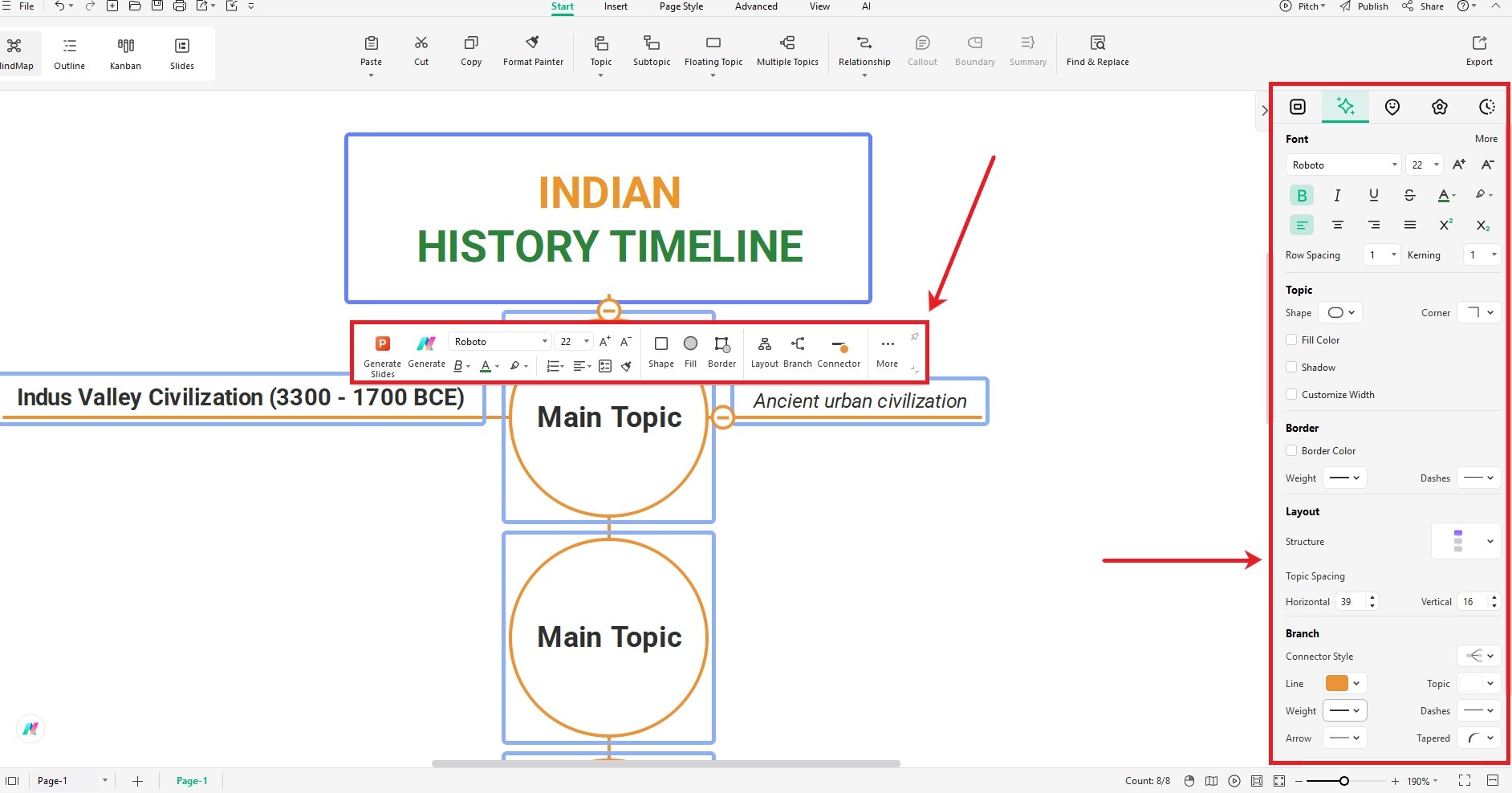
Step 4: Customize Your Timeline
- Click on any event box to see a floating menu for customization.
- Use the right-side toolbar to change colors, fonts, and shapes.
- Double-click any box to edit the text and type your event.
Step 5: Add Pictures
- Download or copy any history-related picture (like a photo of the Taj Mahal or Mahatma Gandhi).
- Paste it into the timeline space.
- Drag it to the event you want.
- Use the menu bar and toolbar to adjust the picture.
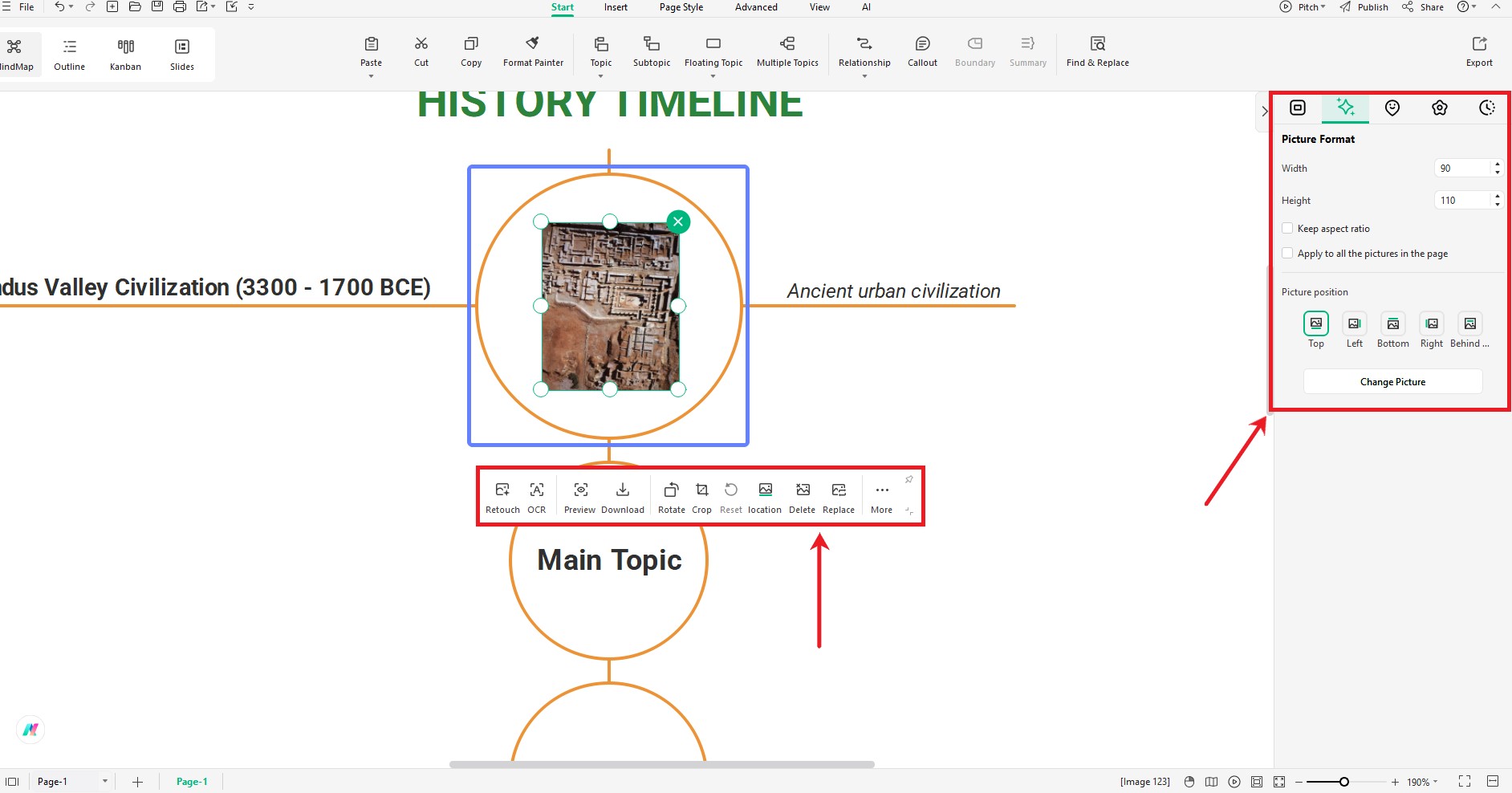
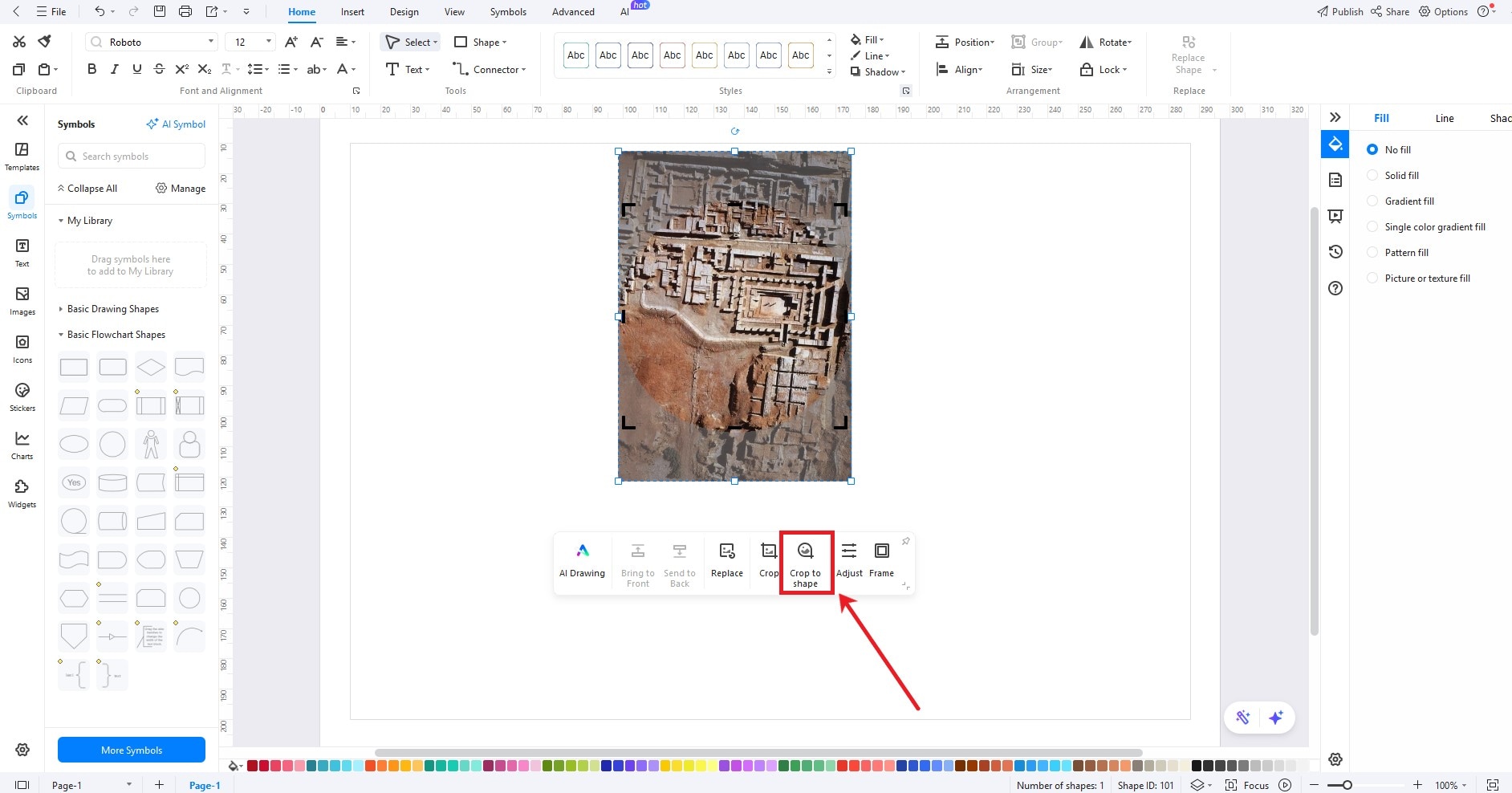
Pro Tip: Crop and Resize Pictures
- Sometimes, pictures don't fit well.
- Copy and paste the picture in EdrawMax.
- Click Crop to Shape.
- Adjust the image and copy-paste it back into EdrawMind.
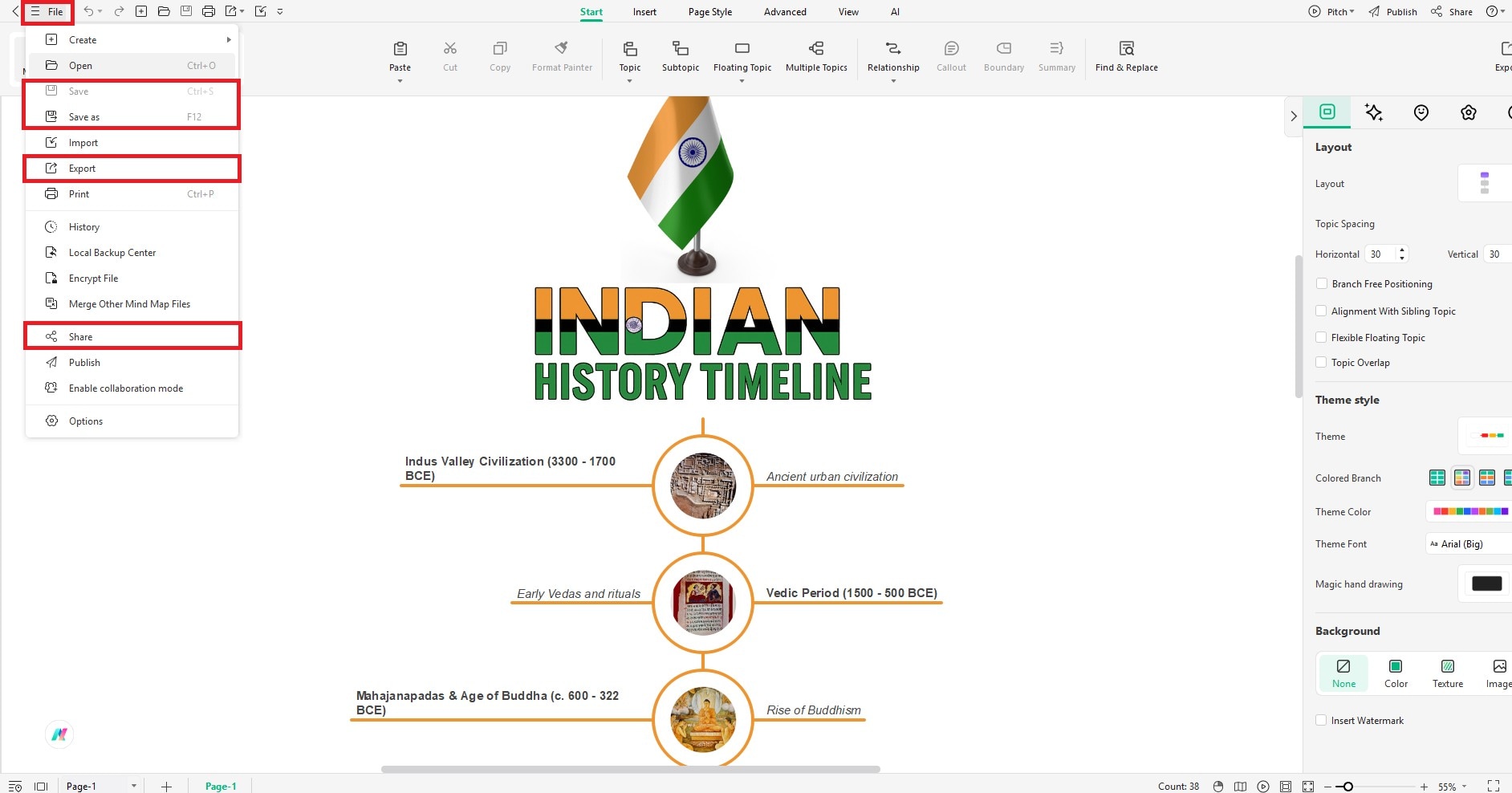
Step 6: Save or Share Your Timeline
- Click the File menu (3-line icon at top left).
- Click Save to download the file.
- Or Share to send it via email or get a shareable link.
- Click Export to get more format options like JPG, PNG, PPT, PDF, and many more.
Final Thoughts
India's journey from the Indus Valley to the digital age is nothing short of incredible. With its history as a guide and innovation as its compass, the future holds limitless potential. Science, technology, culture, and resilience continue to shape a rising global leader.
So, do you want to see how far India has come - and where it's going? Use EdrawMind to map the milestones, visualize change, and build connections. It's free and easy to use for making timelines in no time.






