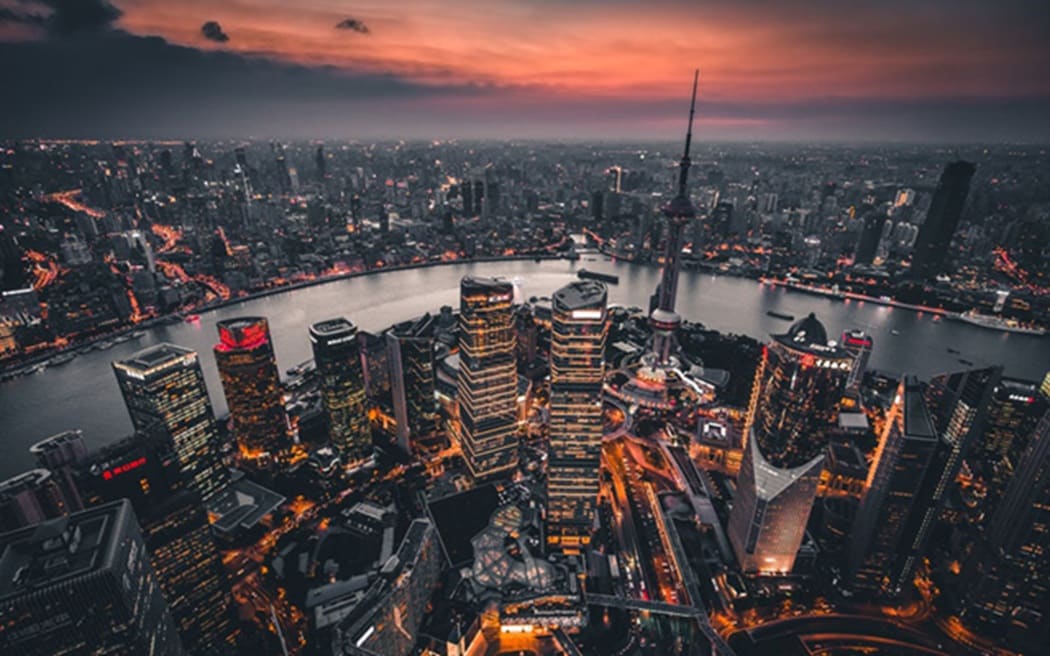
Shanghai is one of China’s most dynamic cities, blending ancient heritage with modern innovation. Its story stretches across thousands of years, evolving from quiet fishing villages into bustling trade hubs.
From the early settlements along the Huangpu River to its rise during the dynasties, Shanghai has always been shaped by movement, commerce, and cultural exchange. Each era added depth to its urban identity.
Today, Shanghai stands as a global powerhouse of finance, architecture, and culture. Its transformation reflects China’s rapid modernization while preserving the historical layers that continue to define this extraordinary city.
In this article
History of Shanghai
Shanghai today is one of the world's largest and thriving cities, with a population of 27 million. Below is a quick timeline made with Wondershare EdrawMind:
With an area of about 6,300 square kilometers, Shanghai is one of the largest metropolises and a world-famous financial center, divided into 16 districts.
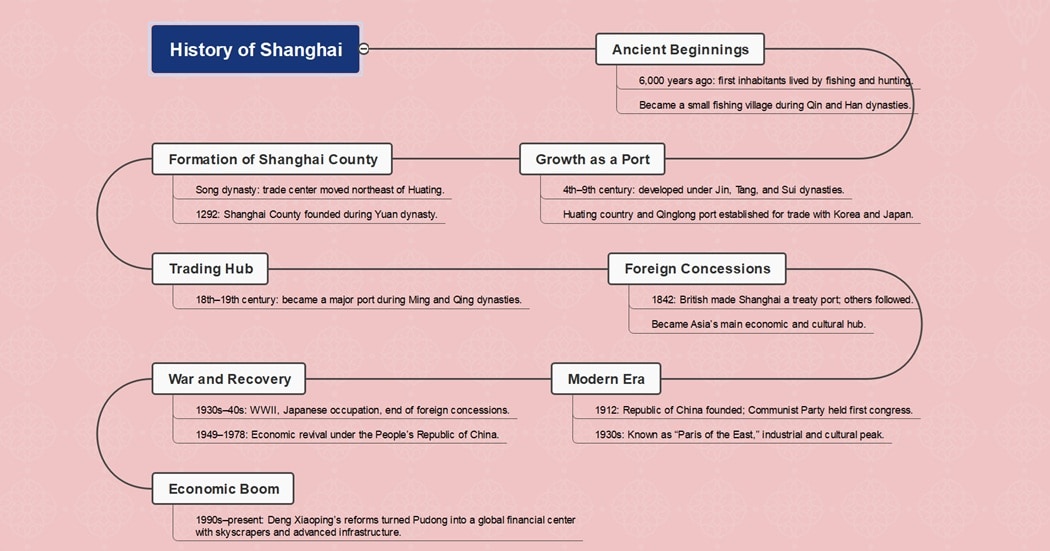
The history of Shanghai began around 6,000 years ago, when people started to live here.
Over time, the area gradually developed into a trade center and a small port. Shanghai slowly evolved into the city that it is today, with a few rapid advancements in recent history.
First Inhabitants – 6,000 Years Ago
It goes back to around 6,000 years, when what is now popularly known as the western part of Shanghai had become inhabited. The indigenous people of this area used to survive on fishing and hunting.
Fishing Village – Before Christ
Beginning from the Qin dynasty (221 BC – 207 BC) onwards to the Han dynasty (206 BC – 220 BC), Shanghai started to develop as a fishing village, and slowly, with time, the economic relations with the inland cities strengthened.
Prospering Port – 4th And 5th Century
In the Jin dynasty (265 – 420 AD), Shanghai continued to flourish and enjoyed rapid advancement. The rapid growth and development continued in the Tang and Sui dynasties (581 AD – 907 AD).
With places abroad and at home, cultural and economic trade grew alongside the gathering of a large population. The city government took charge of the ancient area of Shanghai in the year 751.
The country of Huating was also established in the same year during the Tianbao years of the Tang dynasty. A new Qinglong port was established, allowing the ships to sail to coastal cities like Korea and Japan.
Establishment of Shanghai Town and County – 1292
In the initial period of the Song dynasty, from 960 to 1279 AD, the shift of the trade center to the northeast of Huating County gave birth to a small town.
In the year 1267, the town of Shanghai came into being and soon became one of the seven Bureaus for Foreign Shipping. In 1292, during the Yuan dynasty, the Shanghai County came into existence, which is today's Minhang district.
Trading Center – 18th and 19th Century
The Port of Shanghai became a significant trading center in the 18th and 19th centuries, which was the end of the Ming dynasty and the start of the Qing dynasty.
Till then, the Shanghai county developed into a popular city in southeast China.
Beginning of The Foreign Concession – 1842
After the First Opium War in 1840, the British made Shanghai a treaty port in 1843. Numerous other countries also established concessions there. Some of them opened factories, whereas others pursued industrial raw materials.
With developments and advancements, including the setting up of enterprises in banking, shipping, printing, public utilities, pharmacy, and architecture, the city flourished into a prosperous port and a center for culture and economy.
Shanghai at that time was the only metropolis in Asia with international status.
Early 20th Century
The Republic of China was established in 1912. At that time, the area of Shanghai was under Jiangsu Province, which included ten suburbs. In 1912, the Communist Party of China held its first National Congress in Shanghai.
Paris of The East – the 1930s
In the 1930s, Shanghai's modern industry grew rapidly and was known as the Paris of the East. It became a hub for some large enterprises and advanced equipment and techniques.
Additionally, various foreign goods entered the city. Meanwhile, both foreign and local people started to establish their businesses here, and popular industries came into existence.
During World War II, From the 1930s to the 1940s
After a period of success and prosperity, the city went through the phase of World War II. In the 1930s, Shanghai became a shelter for Jewish refugees, but it was seized by Japan.
The 1940s were the time when countries slowly started to give up their foreign concessions in Shanghai. And later in 1945, the Republic of China officially took over those concessions, ending the foreign presence.
The Revival of the Economy – 1949 to 1978
In 1949, the People's Republic of China was founded, following which Shanghai managed to recover its economy. During this period, a boost in the industry was observed.
Deng's Rule – 1978 to Present
More critically, in 1990, Deng Xiaoping assigned Shanghai to lead China's economic development, with the Pudong New Area on the east side of the Huangpu River scheduled for improvement into Shanghai's new economic focus.
Overnight, this former farmland transformed into the home of some of China's greatest structures, including the first and largest stock exchange center, the tallest TV tower in Asia, the tallest hotel in China, and the second-largest retail chain on the planet.
The structure trend proceeded through the 1990s and into the 21st century, with the establishment of new buildings and structures.
Fun Facts About Shanghai
Shanghai, widely known as the Paris of the East and Pearl of Asia, is a city of commerce, youth, and an international beat that permeates every side river walk and street.
The city is China's bustling metropolis, and here are a few interesting facts about it.
- Shanghai is a transportation powerhouse.
- The population of Shanghai is around 27 million, making it one of the largest cities in the world.
- Shanghai is the world's economic and cultural center.
- Shanghai is close to several ancient water towns.
- The people of Shanghai are mostly sweet-toothed.
Create a Timeline To Understand History Better
Studying the past can be overwhelming without a clear visual path. A timeline turns complex history into something you can easily see and understand.
It gives structure to years of progress, helping you track how cities like Shanghai grew from small settlements to world powers.
Benefits of Creating a Timeline
Making a timeline has many learning benefits:
- Simplifies complex history: It breaks long periods into smaller, clearer parts. Students can see what happened first and what followed.
- Shows cause and effect: Timelines reveal how early decisions or events influence later outcomes, such as trade leading to economic growth.
- Improves memory: Visual cues like icons, photos, or color-coded erasers help learners recall events faster.
- Encourages analysis: Comparing different periods helps you find trends, progress, or recurring challenges in history.
- Supports project planning: Students and researchers can organize sources by date and build reports that flow naturally through time.
By visualizing history in sequence, timelines make learning more engaging and accurate. They transform information into a story you can follow with ease.
How To Make a Timeline
Creating a timeline is an exciting way to organize historical events. It helps you see the order of progress, key turning points, and lasting influences. With the right method, you can turn facts into a clear story of growth.
Follow these steps to make an effective history timeline:
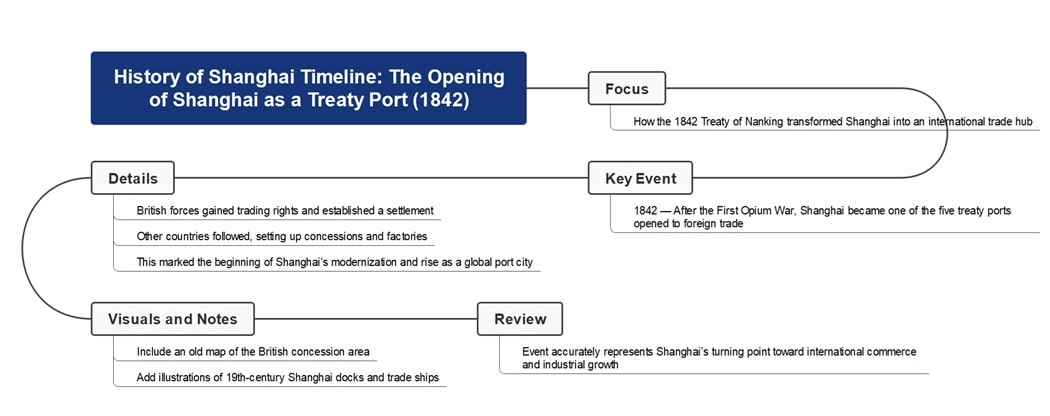
Choose Your Focus
Decide what topic to highlight, such as Shanghai’s rise as a trading hub or its cultural expansion. A clear focus keeps your research organized and prevents unnecessary details.
Collect Key Events
Research major milestones, political changes, and social developments that shaped the city’s identity. Use reliable sources like archives, books, and verified online materials to ensure accuracy.
Arrange by Time
Place the events in order, starting from the earliest known settlement up to modern developments. Grouping related events can also help show progress and cause-and-effect relationships.
Add Visuals and Notes
Include photos, maps, and short explanations to make the timeline engaging and informative. Visuals enhance understanding and help readers remember important historical points.
Review for Accuracy
Check that each event has the correct date and a brief, factual description. Proofreading also helps ensure your timeline tells a smooth and logical story.
The timeline highlights Shanghai’s transformation in 1842, when the Treaty of Nanking opened the city to international trade. This moment marked the beginning of Shanghai’s global connection and laid the foundation for its rapid modernization.
Foreign powers established settlements and trading posts along the Huangpu River, turning Shanghai into a bustling commercial hub. The city’s economy grew quickly as goods, culture, and ideas flowed between China and the West.
This event reshaped Shanghai’s identity from a regional town to a global metropolis. The opening as a treaty port ignited industrial progress, urban expansion, and lasting cultural exchange that still define the city today.
Tool Recommendation
There are many tools for creating visual timelines, but EdrawMind offers an intuitive way to organize historical data. It provides clear layouts and templates, which you can use to design the Shanghai timeline above.
Conclusion
Since 1978, when China's reforms and opening-up were observed, Shanghai has significantly profited from its own perks and favorable national policies.
With the restructuring of the financial system, the city strengthened its native economy and improved living standards for its people.
These days, the international metropolis is an influential global monetary force and undoubtedly a trade, economic, financial, technological, scientific, and cultural center of China.