Uber is one of the world’s biggest transportation and delivery companies. It started from a small idea in San Francisco and has grown to serve people in more than 70 countries.
Every day, millions of rides and deliveries happen through its app. To manage all this, Uber uses a smart structure that keeps teams connected and organized. Its organizational chart shows who leads the company, how decisions are made, and how different departments work together.
In this guide, we'll explain how Uber's structure works and why it helps the company stay successful. At the end, you’ll learn how to create an org chart for such a company.
In this article
Uber Organizational Chart
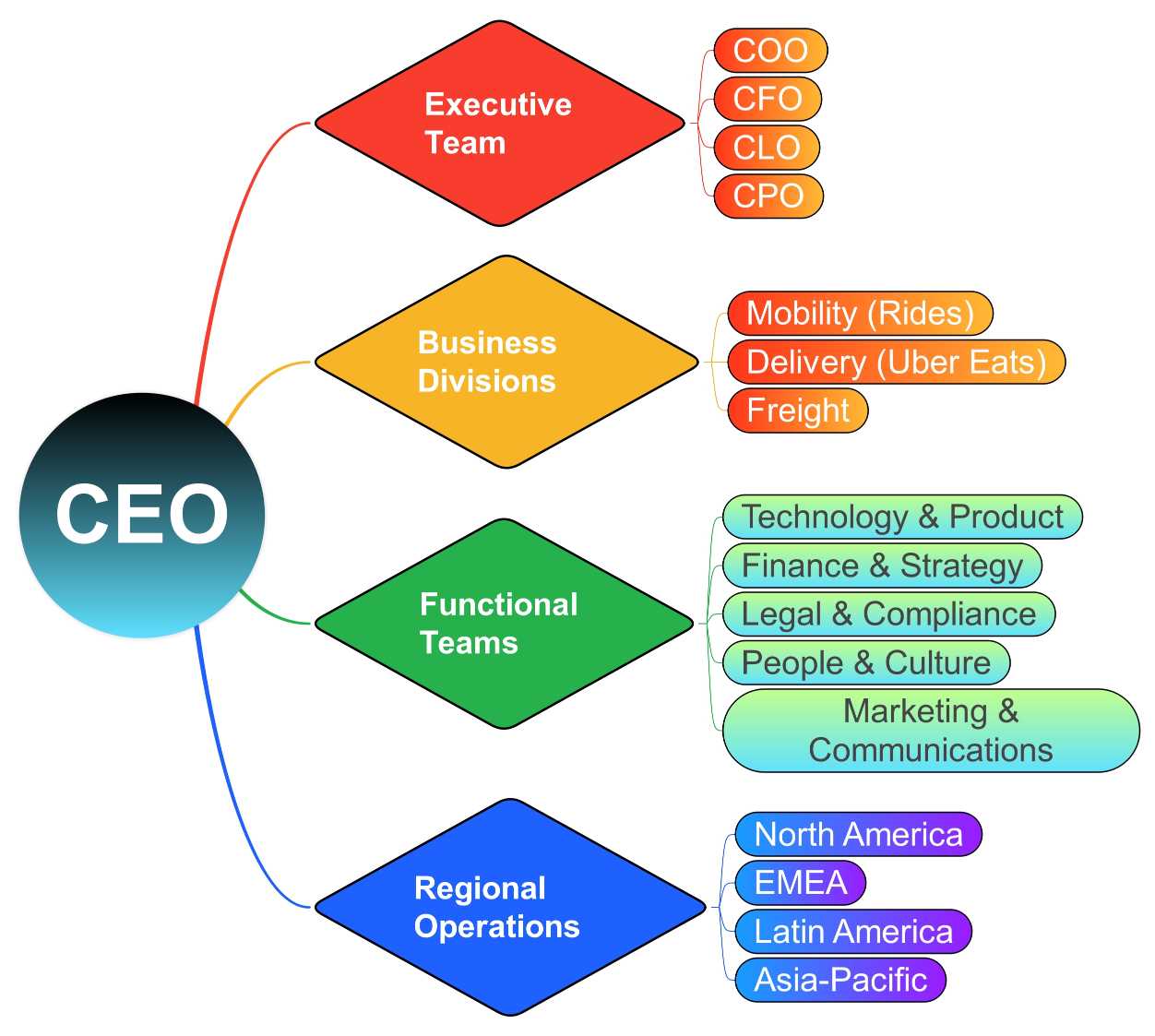
The organizational chart of Uber reveals the way it maintains everything in order. It describes the process of decision making and collaboration between various teams. It also demonstrates the role played by every section of the company in providing people around the world with reliable rides, food, and freight.
Let's have a closer look at the way Uber is organized and the way this structure contributes to the effectiveness of the company working globally.
Structure Type
The organizational structure of Uber is hybrid, which includes the functional departments, business units, and geographic regions. It is a strategy that enables the company to run its international business efficiently and at the same time be flexible in the local markets.
Leadership
At the top of the list is CEO Dara Khosrowshahi. He manages the global vision, strategy and performance of Uber. Reporting to him are:
- Heads of some of its core business units: Mobility (Rides), Delivery (Uber Eats) and Freight.
- Global functional leaders: Technology and Product, Finance and Strategy, Legal and Compliance. People, Culture, and Marketing as well as Communications.
Functional Divisions
These divisions offer strategic supervision and operational assistance throughout all the regions and business units:
- Technology & product: Innovates and sustains the Uber platform, mobile application, and information systems.
- Finance strategy: Budgeting, forecasting and investor relations.
- Legal + compliance: Makes sure that the activities of Uber do not contradict the laws.
- People & culture: Concerns the development of talent, inclusion, and well-being of employees.
- Marketing/ communications: Talks about the Uber brand and handles customer interaction on a global scale.
Business Divisions
The attention of P&L lies with the following core business units of Uber:
- Mobility (Rides): Unites riders with drivers by providing ride-hailing.
- Delivery (Uber Eats): Food, grocery, and retail delivery.
- Freight: Provides freight and trucking solutions to companies.
Regional Structure
Uber plans their operations by branching into regional hubs so as to localize the global strategies to the local markets:
- North America
- EMEA (Europe, Middle East, Africa)
- Latin America
- Asia-Pacific
The leadership team in each region is responsible for implementing strategies. They make decisions that fit their local market. They also follow regional regulations. The teams work closely with functional departments and business units. This helps ensure global goals match local needs.
Number of Employees
The latest filings of the company show that there are approximately 31,000 full-time workers of Uber globally as of 2025. This figure doesn't include millions of independent drivers and delivery partners who are using the Uber platform on a daily basis.
The main offices of Uber are in San Francisco (headquarters) and Amsterdam, Singapore, Hyderabad, and Sao Paulo, and they fulfill the role of major coordination centers of the organization's operations.
The overall Uber internal employee base looks like this:
- Technology & Engineering (approximately 40 percent): Software, data science and infrastructure.
- Operations & support (about 25%): City work, drivers and logistics.
- Corporate & administration (approximately 20%): Finance, Hr, and legal.
- Marketing & partnerships (approximately 15 percent): Brand expansion and regional advertising.
Uber maintains a lean employee base. AI-driven tools, data analytics, and automation will decrease manual work so that Uber can grow rapidly without increasing the cost base. This is one of the reasons why it is an efficient company.
Key Executives
The leadership team at Uber combines expertise in public policy, operations, finance, and technology. Every executive is essential in directing the performance and strategy of the business.
- Dara Khosrowshahi (CEO): The CEO of Uber, Dara Khosrowshahi, is in charge of the company's global strategy and innovation plan. Dara has pushed for profitability and growth into delivery, freight, and autonomous technologies since assuming control in 2017
- Andrew Macdonald - President & Chief Operating Officer (COO): Andrew Macdonald. Andrew was appointed in 2025. He is in charge of Uber's daily operations. In addition to cross-platform operations like membership, security, and customer service, he oversees Mobility, Delivery, and Freight.
- Prashanth Mahendra-Rajah - Chief Financial Officer (CFO): He is in charge of Uber's planning, finances, and investor relations. Prashanth concentrates on using effective capital management to promote long-term profitability and responsible growth
- Tony West - Chief Legal Officer & Corporate Secretary: Uber's global legal department is led by Tony West. He ensures compliance with complex international transportation and labor laws.
- Nikki Krishnamurthy - Chief People Officer (CPO): Nikki is in charge of talent development, human resources, and cultural initiatives. She encourages inclusivity and diversity among Uber's employees worldwide.
- Pradeep Parameswaran - Global Head of Mobility: Pradeep Parameswaran oversees Uber's main ride-hailing operations worldwide. He concentrates on enhancing user experience, cost, and safety in all areas
- Susan Anderson - Regional General Manager, Delivery (Uber Eats): Susan oversees international delivery operations and grows Uber Eats into the retail and grocery industries. She concentrates on enhancing customer satisfaction and merchant relationships.
These executives work together to make sure Uber functions as a single, integrated company. They aim to balance local agility with global strategy.
Adaptivity of the Structure
Uber's greatest benefit is its adaptability. Because of its organizational structure, the company can react swiftly to changes in the market, advancements in technology, and emerging regulatory issues.
Uber has established cross-functional project teams when it introduces a new service or enters a new market. These teams integrate experts from marketing, operations, engineering, and law to expedite the transition from testing to deployment. For example, when growing programs for electric vehicles, teams include specialists in infrastructure partnerships, logistics, and sustainability.
Additionally, regional teams are free to adjust their plans to suit local circumstances. Uber gives local leaders the ability to modify pricing, promotions, and partnerships to accommodate cultural and economic differences. A campaign that is successful in London might not be appropriate in Tokyo.
Technology maintains the structure's connectivity. Uber can track performance, optimize routes, and spot opportunities more quickly than traditional transportation companies. This is possible thanks to real-time data and analytics.
Why Does Uber Org Structure Work?
Uber's organizational structure works because it keeps the right balance between global coordination and local flexibility. The company can make big strategic moves at the top while still allowing each region to adapt to local markets, regulations, and customer needs.
Here's why the system is so effective:
- Hybrid design: Uber combines functional, geographic, and product-based structures. This lets experts from different departments collaborate while regional leaders handle local operations.
- Clear leadership chain: The CEO and COO provide unified direction, while divisional heads (Mobility, Delivery, and Freight) keep each business line focused and accountable.
- Fast decision-making: With smaller, cross-functional teams, Uber can launch, test, and scale new ideas quickly. This ability to move fast is essential in a fast-changing mobility industry.
- Regional autonomy: Local managers have the authority to make market-specific adjustments in pricing, partnerships, and strategy without waiting for headquarters' approval.
- Technology-driven integration: Real-time data and analytics connect every department. This allows quick responses to customer feedback and operational issues.
- Scalable and efficient: Uber keeps its team small and uses a lot of automation. This lowers costs and makes it easier to grow the company.
To conclude, Uber's structure keeps innovation alive while maintaining order. It helps the company stay fast, focused, and ready for the future.
How to Make Such an Org Chart?
Want to make your own Uber-style organizational chart? It’s easier than you might think. Uber’s structure looks complex, but once you understand how it works, you can build something similar for your own company. The key is to keep it simple, clear, and accurate. Here’s how you can do it step by step:
- Know the purpose: First, think about why you are making the chart. Is it for training, presentations, or to understand your company better? Knowing this helps you decide how detailed the chart should be.
- Collect information: Find out who reports to whom, what each department does, and who leads them. Make sure all names, roles, and responsibilities are correct.
- Identify levels: Draw the main categories from the board or top leaders to department heads and team leaders. Show who reports to whom so it is easy to follow.
- Choose a style: Choose a layout that fits your company. Uber uses a hybrid style, mixing top-down hierarchy with regions and project teams.
- Build the chart: Use tools like EdrawMind, Lucidchart, or Visio. Make main branches for departments like Technology, Marketing, Operations, and Finance. Add smaller teams under each.
- Check and update: Look over the chart to make sure it is clear and accurate. Update it whenever people or roles change.
Steps to Create the Org Chart
After gathering your data and choosing your design, it’s time to build your chart. Here’s how to make a clear, modern Uber-style org chart using Wondershare EdrawMind.
Step1 Start a New File & Add the CEO
- Open Wondershare EdrawMind and start a blank mind map.
- Choose org layout and make the CEO the central node or main topic.
Step2 Add Executive Team
- Below the CEO, add boxes for key leaders: COO, CFO, CLO, CPO
- They are the key executive members under the CEO.
Step3 Add Business Divisions
- Create three new branches: Mobility (Rides), Delivery (Uber Eats), and Freight
- These are Uber’s main services.
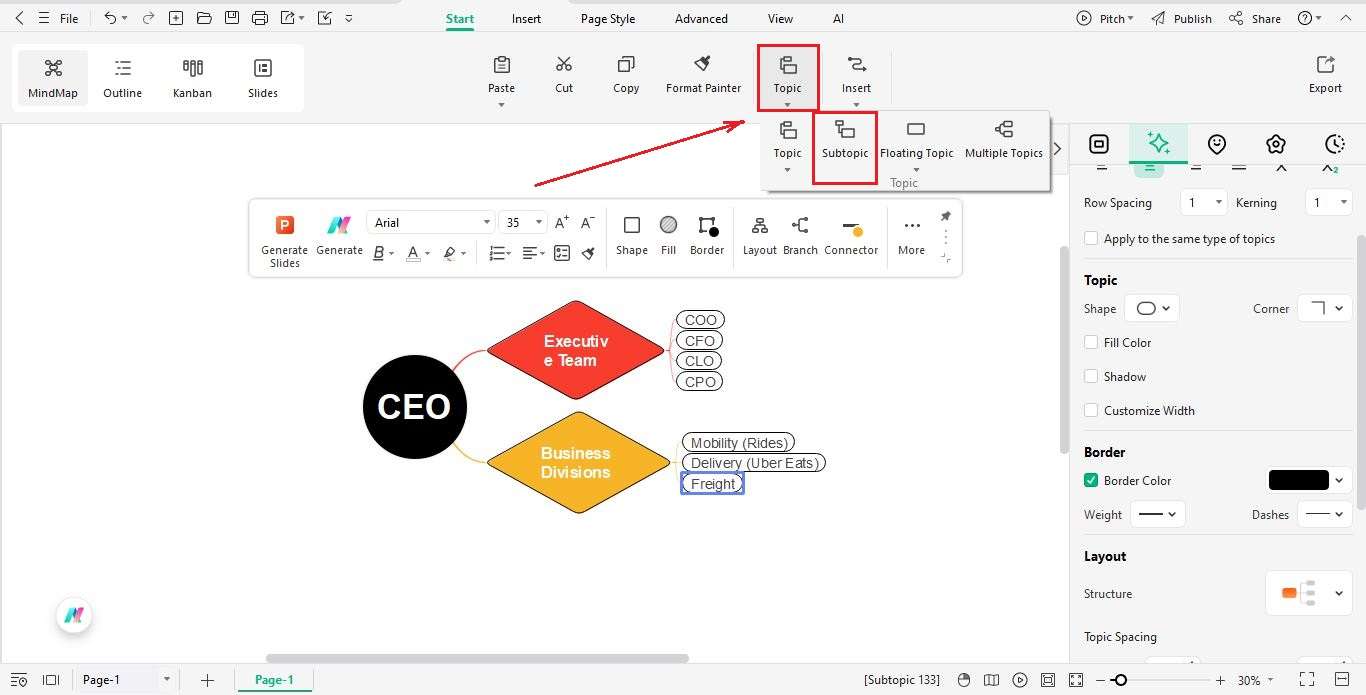
Step4 Add Functional Teams
- Make another layer for departments like:
- Technology & Product
- Finance & Strategy
- Legal & Compliance
- People & Culture
- Marketing & Communications
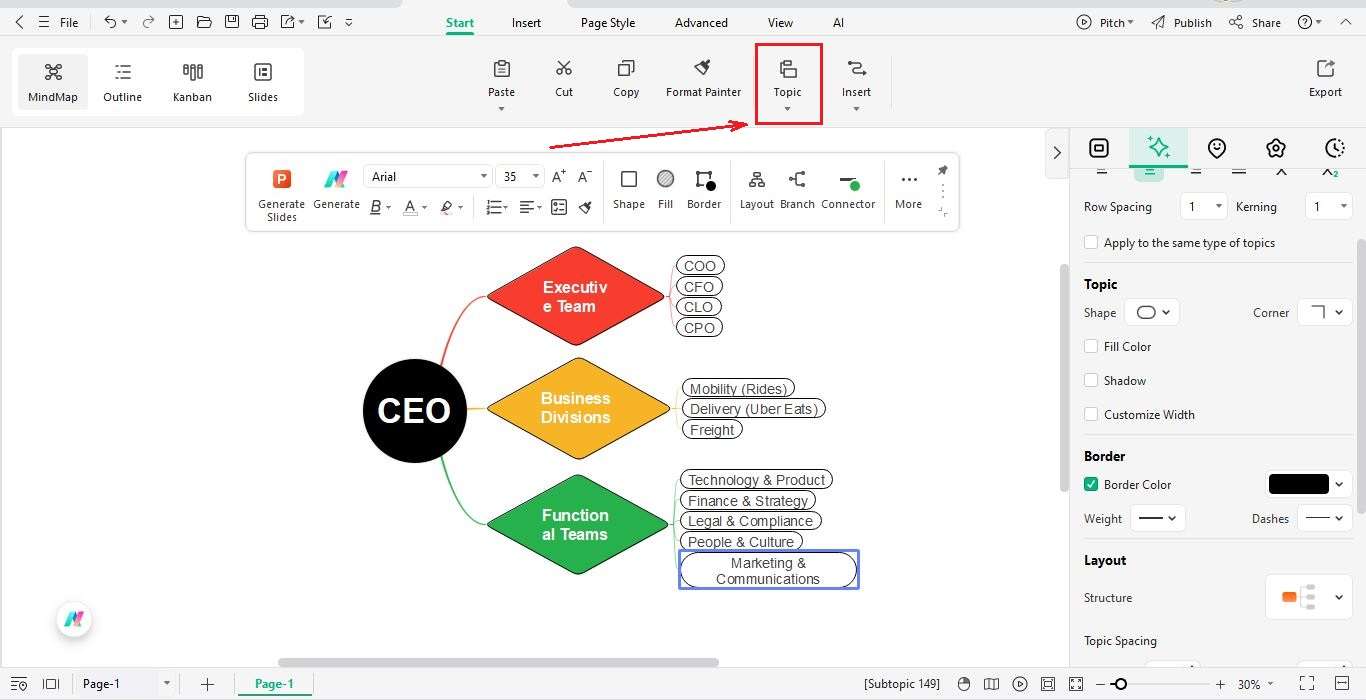
Step5 Add Regional Operations
- Add a branch named Regional Operations and include:
- North America
- EMEA
- Latin America
- Asia-Pacific
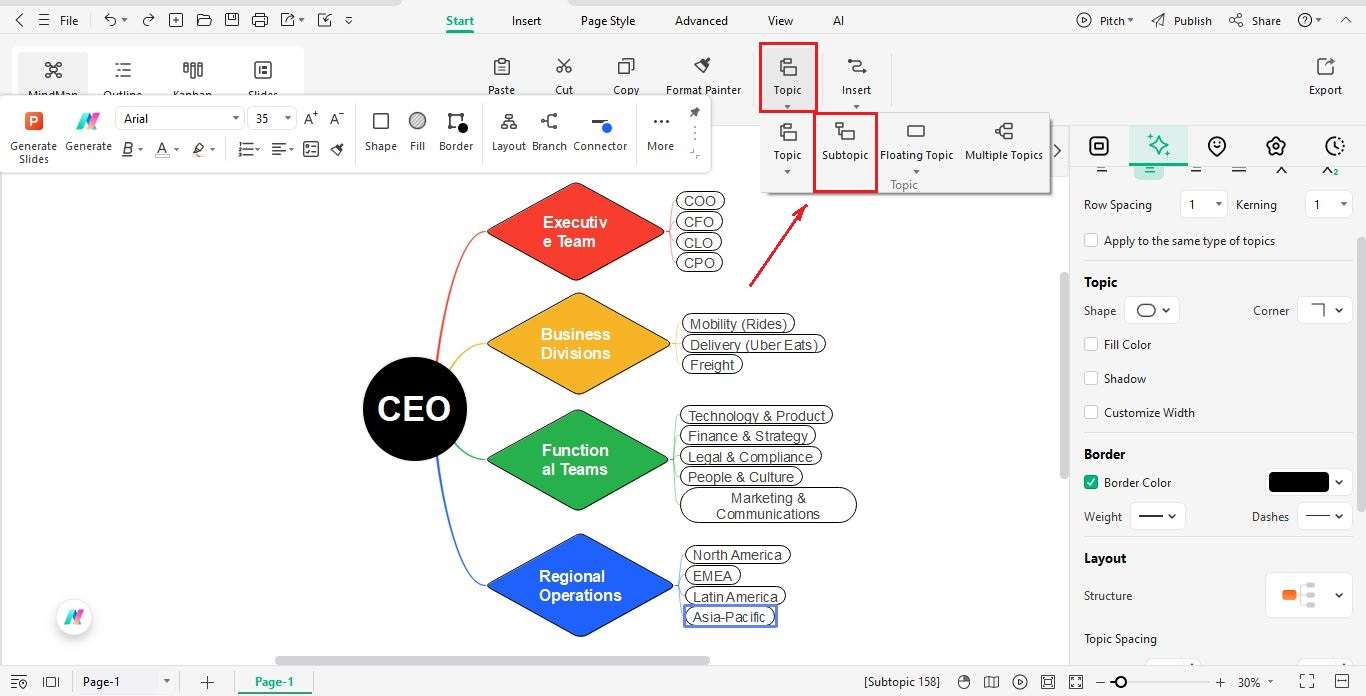
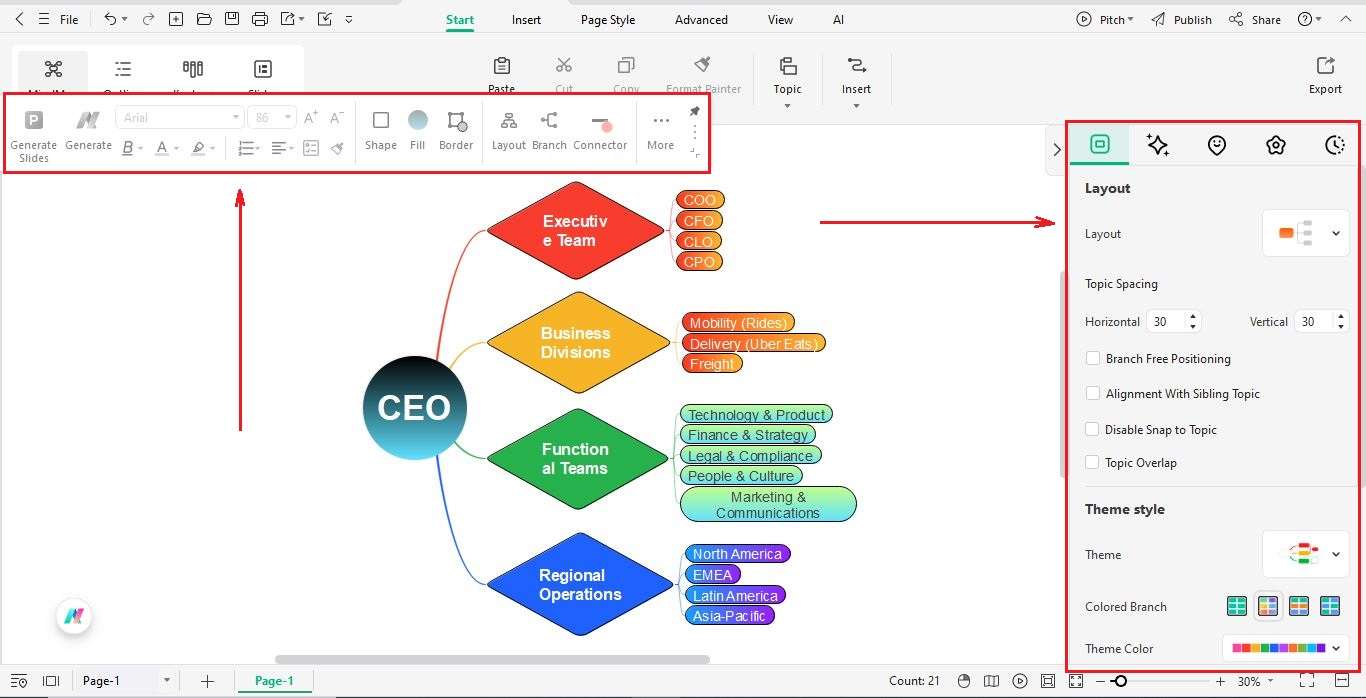
Step6 Customize the Chart
- To customize the chart, use the floating toolbar or the panel on the right.
- You can change shapes, colors, and fonts to make it look nice.
- Make the CEO stand out with a bigger shape, and use bright colors for executives and managers.
Step7 Review and Share
- Look at the chart to make sure all roles are linked correctly.
- Save or export the chart as a PDF, PNG, or PowerPoint file.
- You can also share the chart with your teammates directly via a link.