Rene Descartes, the 17th century philosopher, takes you on an intellectual journey to rational realities with his meditation philosophy. Unlike traditionalists, he opted for a scientific approach to derive logic from doubt. After three centuries, he still remains relevant in an era where information is a search away and most of us are victims of believing its flawed versions.
Want to know more about this intellectual ride from skepticism to reliable truths? Let's dig deeper into René Descartes' meditation summary, so you are also better equipped to differentiate perceived and trusted realities.
In this article
Descartes' Meditations Explained | Summary & Examples
Meditation I - The Demon Argument: Root of Doubt
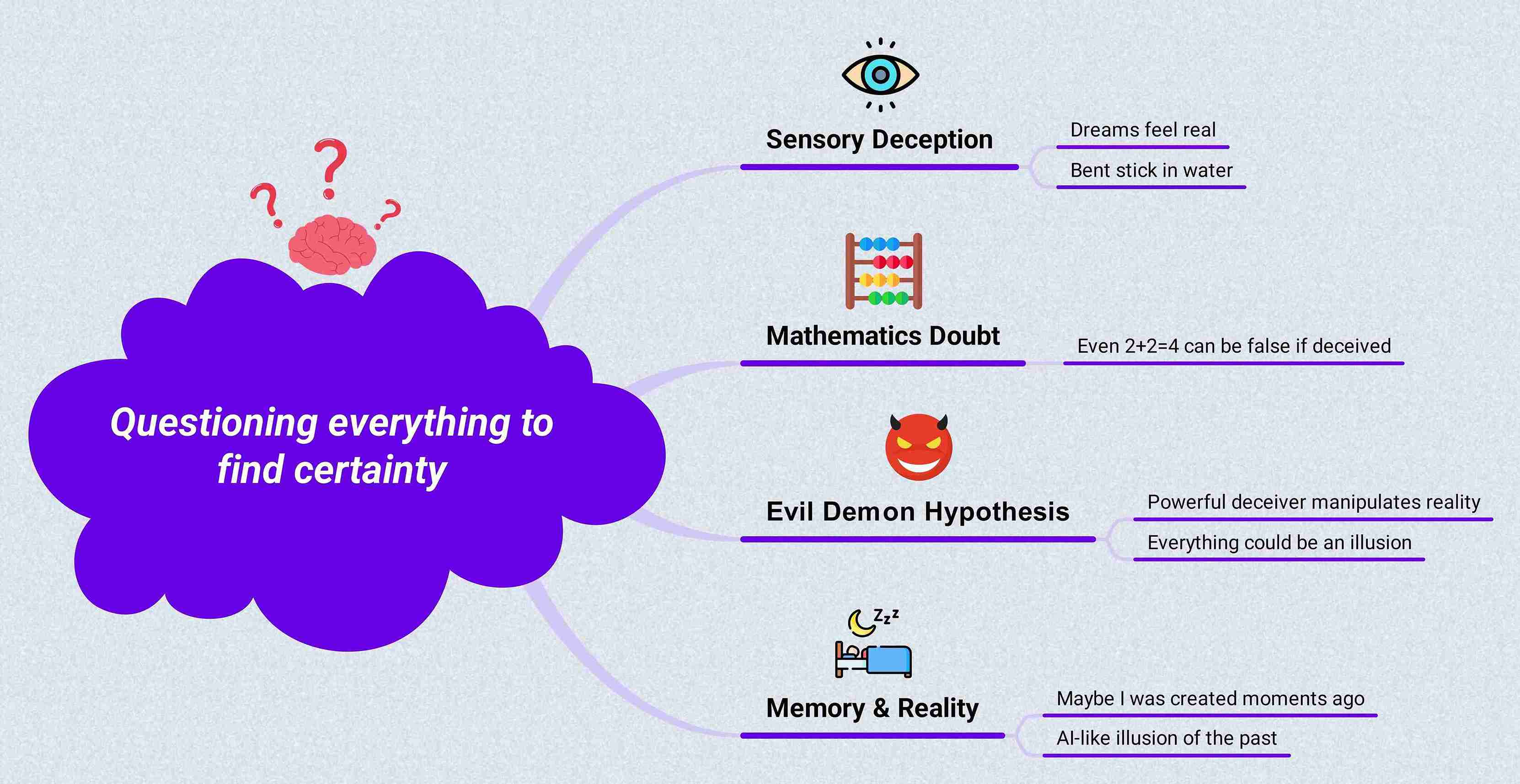
What if our reality is just an illusion and everything is a lie?
Descartes begins his first meditation with a daunting question: What if all our knowledge and experiences are deceptive? This questioning led him to take down everything he had believed so far by imagining that he was dreaming or that an evil demon was deceiving him.
- Reject the senses, as they are deceiving. For example, walking in the dream feels real, and a long stick in the water appears bent.
- Mathematics is just as unreal. What an evil genius has misled us into making sense of numbers (2+2=4).
- Past memories might be an illusion. How do I know I wasn't created AI, a little while ago, with fake recollections?
Understanding Descartes' Evil Genius Demon Hypothesis
Rene Descartes is radical in his approach, rejecting every sense he has felt so far to an extent that he is now tempted to give up on any knowledge altogether. This is his version of The Matrix. His hypothesis of an evil demon tricking us into a fake reality sparks a question: if nothing is real, how am I certain that I exist?
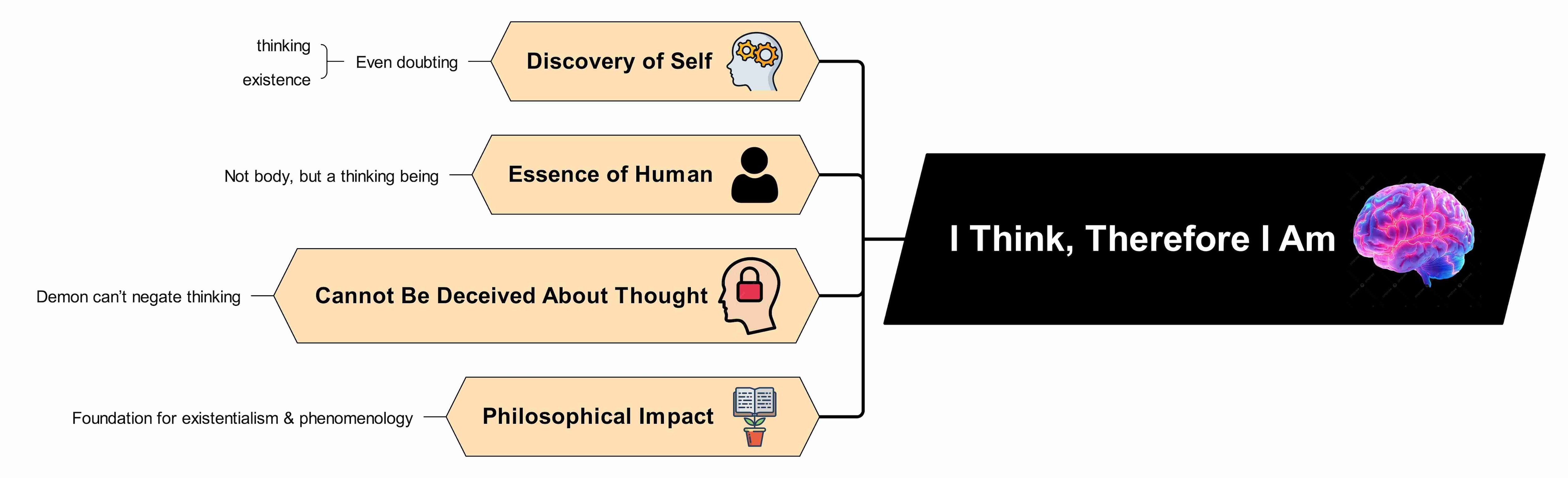
Meditation II - The Cogito, Ergo Sum: Essence of a Human Mind
"I think, therefore I am". This is the way out of the evil demon trap for Descartes.
After tearing down his entire world, Descartes comes across an inevitable fact - the realization of his mind. He now recognizes that his thinking makes him conscious and alive. Even if the evil demon is cunning, he cannot trick Descartes into negating his thoughts.
Now, he wonders what kind of being he is? He cannot live without his body or thoughts; so, he must be a thinking being.
- The one doubting everything? Thinking being.
- The one wrong? Thinking being.
- The one imagining and questioning? Still a thinking being.
Descartes' idea of "cogito, ergo sum" builds the foundation of modern philosophy of consciousness, deriving existence. This hypothesis later inspired the influential philosophers Sartre's Existentialism and Husserl's phenomenology.
So, next time, if you put on virtual reality glasses and all your experiences seem fake, go back to Descartes. You are thinking, so you must be existing.
Meditation III: Existence of God
How do I know anything outside of my mind is real and not deceiving? He now proceeds to think, I exist, but who created me. This pops up the idea of God in his mind, and he wouldn't deceive men.
Perfection of God
Descartes concluded that the idea of God - all-knowing, all-powerful, infinite, eternal, and all-good - cannot be of any human, but rather God himself. Let's break this down.
- Descartes' idea of God was an infinite and perfect being.
- Since Descartes is finite and flawed, this idea of perfection cannot come from a human.
- Conclusion: Only a perfect being (God, the cause) could implant this idea (Perfect God, the effect).
Later, philosophers like Kant criticized Descartes' view of God. However, Descartes' entire point was that God is the perfection that can help us distinguish between reality and deception. Otherwise, wouldn't we think the reality "triangles have three sides" is a trick by the evil demon?
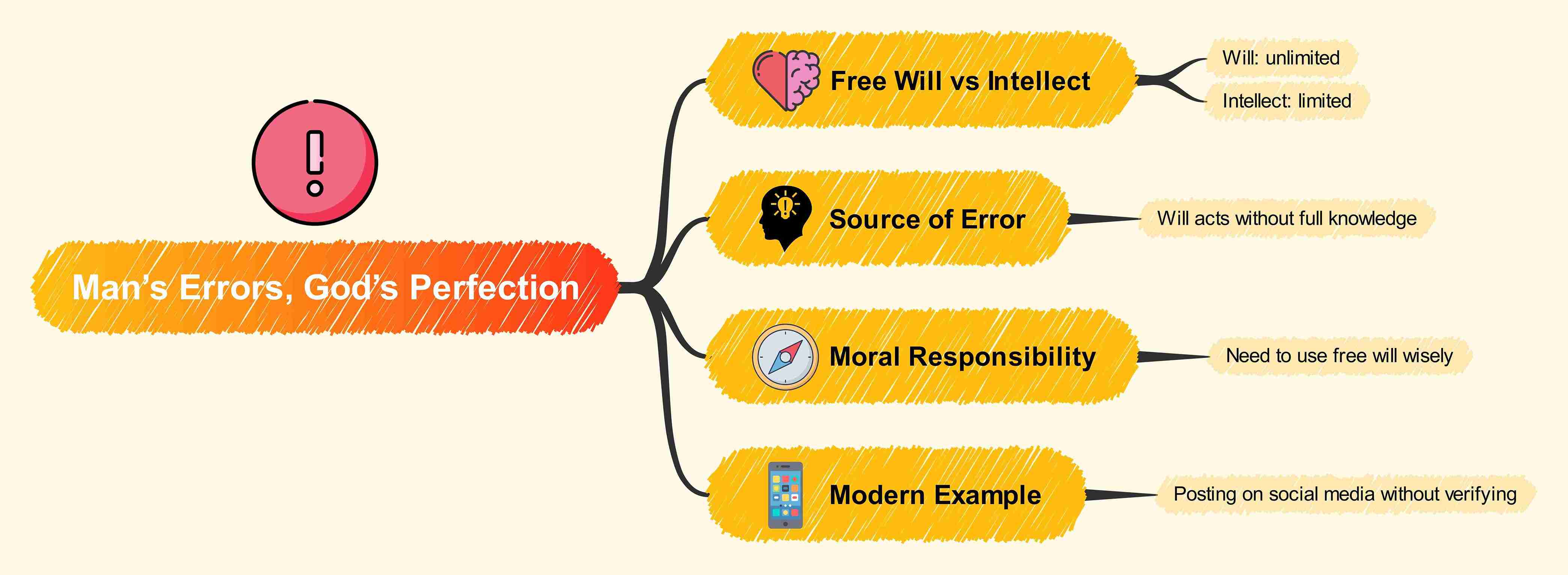
Meditation IV: Humans Making Errors
If Good is all-good, why do we still divert from the right path in this world?
Descartes' answer: The Universe is perfect, but man is not.
Let's apply Descartes' logic to this concept.
- Man has free will, which is stronger than his intellect (hence, he can desire everything).
- However, man does not have absolute knowledge about the world.
- Hence, he is subjected to frequent foolish decisions about things they are not aware of.
Are you not tempted to share a new Instagram story without confirming it further? This is exactly what Descartes is talking about.
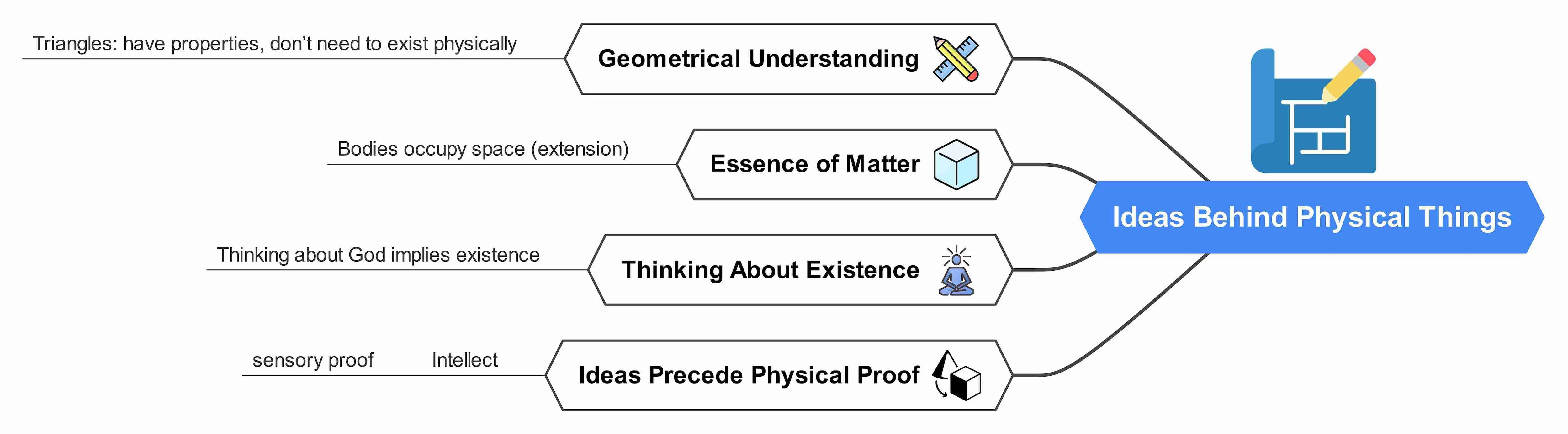
Meditation V: Material Things and Their Essence
How to discover the truth behind things, irrespective of whether they exist or not?
Descartes then inquires into the ideas of the material things rather than the things themselves. For this, he uses abstract geometrical objects to understand things that do not exist physically but are not nothing.
A triangle is one such thing. It does not exist in the world, yet it has some essence. He then uses its shape to derive its properties
The essence of matter is Geometry. For example, bodies are extended things with a certain magnitude (they occupy space). So, whenever you are thinking of God's perfection, you are automatically thinking of his existence.
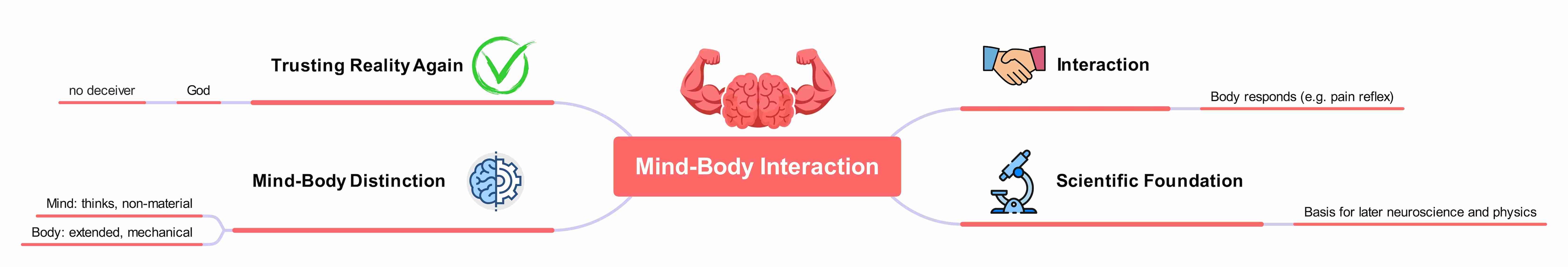
Meditation VI: Rebuilding the World Realities
Descartes goes back to the routine things he was doubtful of in the first meditation. Now that he is certain that God is all-good and no deceiver, Descartes becomes aware of the physical things like his body.
He then goes on to distinguish between the body and mind, as the body requires the mind's guidance to operate. When our senses and perceptions are accompanied by our cognition and intellect, we are safe to trust them.
Let's break this down.
- Mind = thinking element (does not take space)
- Body = extended (takes considerable space and is mechanical)
This mind-body dualism (interaction of the mechanical body with our intellect) makes us realities we can trust.
This conception of body-mind interaction paved the way for modern physics. Don't you feel pain and pull away your hand after touching something hot? This is a typical example of Descartes' mind-body dualism.
Why We Relate to Descartes' Meditations Today?
Fundamentals of Modern Philosophy
Traditional philosophy relied heavily on statecraft and governance. Descartes became the source of transition to modern philosophy, making the individual the center of focus.
Deepfakes, VRs, AI, and Consciousness: The Test of Your Mind's Existence
Descartes' framework of doubt and reason is crucial for today's machine consciousness. Imagine putting on the Virtual Reality set and experiencing an entirely different arena. You will, at one point, begin to doubt if any of it is real. Is your brain conscious of the surroundings?
Such is the impact of deepfakes and modern technology as well. On one hand, Descartes' cogito "I think, therefore I am" has augmented debates on machine consciousness. On the other hand, applying his logic of intellect being a safe reality, you still cannot doubt your thoughts.
The Era of Fake News
In an era of misinformation, from social media stories to deepfakes, AI systems, and access to quick data, Descartes' method is to question everything. Verification is the only way to survive this world.
Neuroscience's Hard Problem
Descartes' mind-body dualism was picked up in modern-day neuroscience. Currently, the hot debate is understanding how the physical brain generates a person's subjective reality.
Key Takeaways from Descartes' Meditations that Changed How We Perceive the World
- Survival guide for your cognition: Descartes believes in skepticism. Daring to doubt can help you unravel the necessary knowledge to solve the complexities of the world.
- Journey of doubt to reality is for every citizen: Whether you are a student, scientist, philosopher, or a skeptic, the theory of doubt-to-reality applies to all. It is the journey of reaching your maximum intellect.
- Truth lies in your mind: The Truth and essence of material things lie in their existence. Your body and mind's synergy can help you build a trusted reality.
- Humans making errors is inherent: The Universe is perfect, but it is in man's nature to make mistakes. This is because he is not aware of absolute knowledge about his surroundings.
- Philosophy is for every era: Distinguishing truth from deception is extremely relevant in today's time of AI revolution. Understanding the basis of intellect and adopting skepticism is the only way to survive it.
How to Make Reading Meditations Easier?
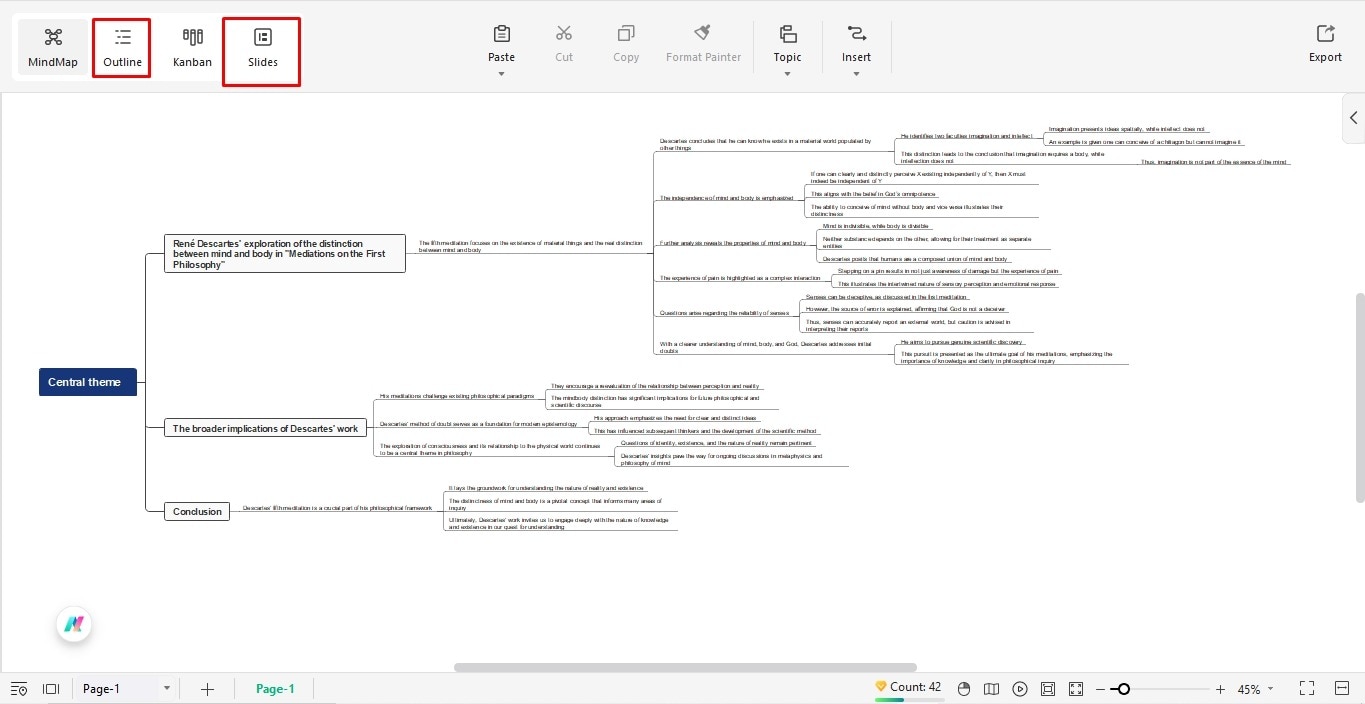
Going through a philosophy can take you days and even weeks, if you struggle with the pace. To avoid this time and effort consumption, there is a solution in EdrawMind. It has various AI functions for summarization, mind mapping, and presentations.
Let's see how this tool can help you easily grasp extensive philosophies.
Step 1: Summarize a Document
An excellent way to break down complex and extensive philosophies is a quality summary. EdrawMind further simplifies it with its AI file analysis tool. It uses advanced algorithms to extract meaningful insights from documents and structure it in a mind map. Here is how it goes.
- Explore the dashboard and click Intelligent File Analysis under the Create tab.
- Upload your desired document (Word, PDF, PPT, Excel, etc).
- Click Generate Mind Map, and the AI will automatically extract key points in a mind map infographic.

Step 2: Summarize a Portion of the Text
Want to summarize only a portion (chapter, concept, paragraph) of your philosophy? It's easier.
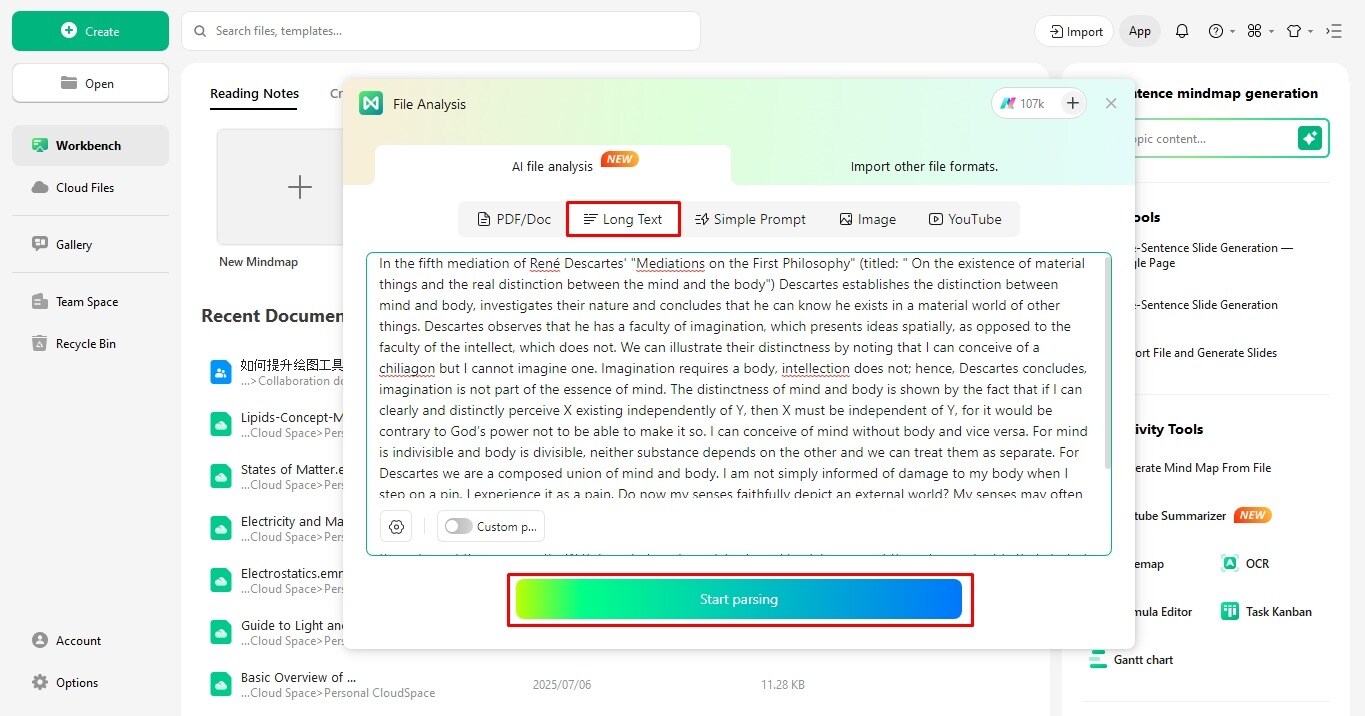
- Select the Long Text option from the Intelligent File Analysis tab.
- Paste your text in the search box.
- Click Start Parsing to view the summary of key points on the screen.
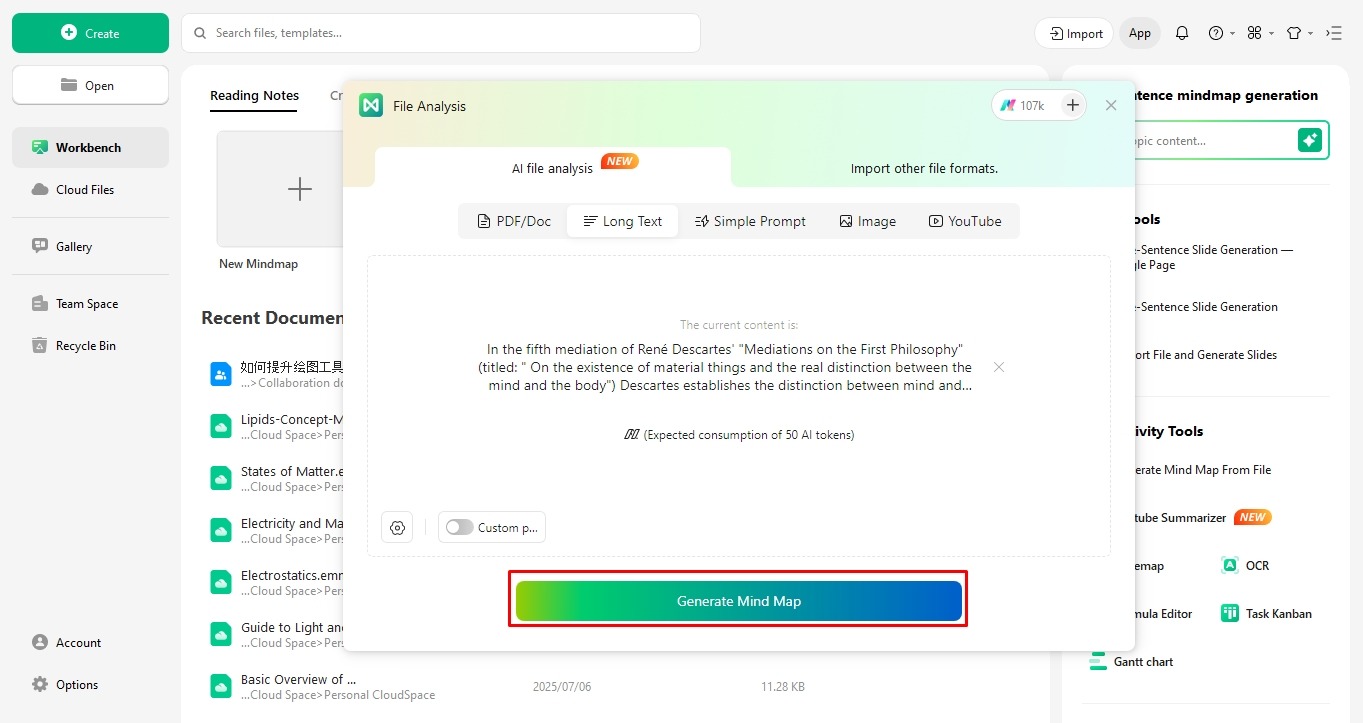
Step 3: Create Your Mind Maps
You can go a step further and convert these summarized insights into visually appealing mind maps.
- Click Generate Mind Map once the summary is generated.
Step 4: Edit Your Summary Mind Map
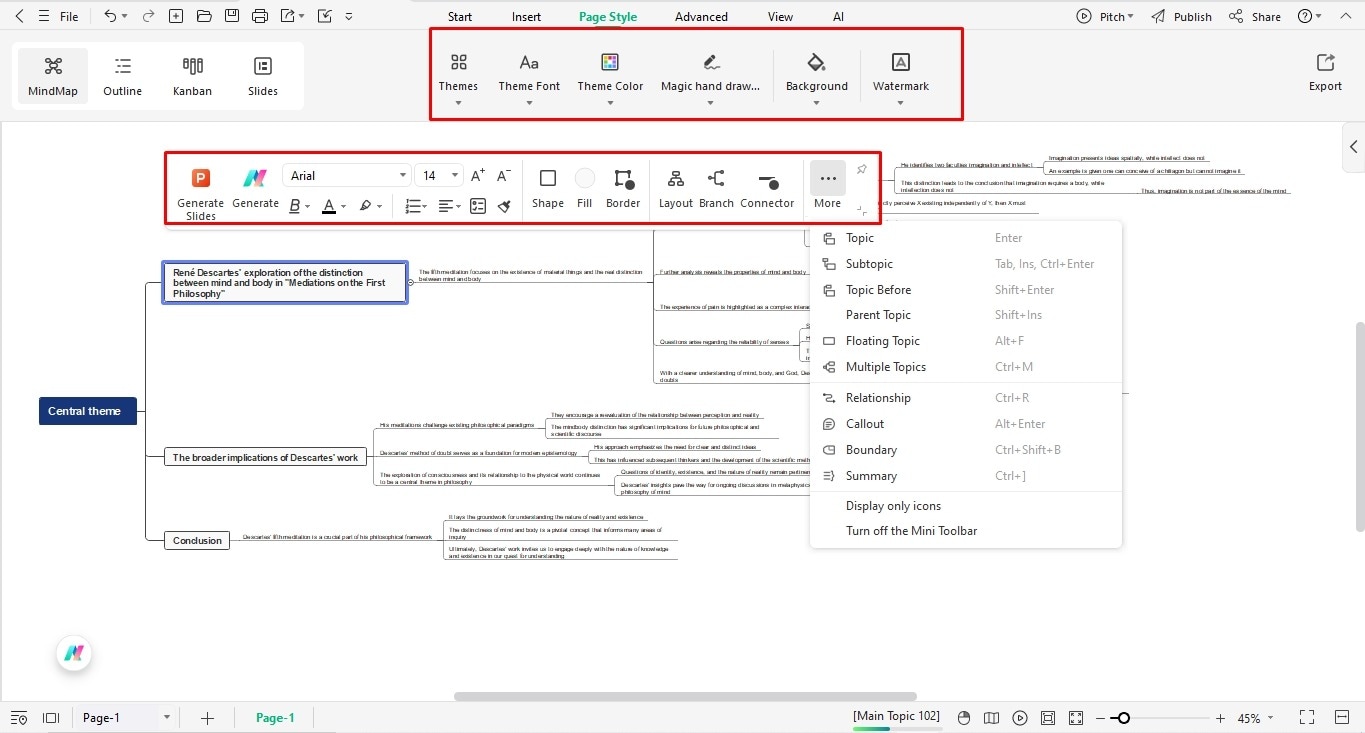
Once on the editing panel, proceed to edit your mind map.
- Select any node to add text labels.
- Expand branches by clicking More from the on-screen prompt.
- Moreover, visit the Page Layout tab to change the colors, themes, and background image of the diagram.
Step 5: Convert Mind Maps into Slides/Outlines
EdrawMind also gives you the freedom to convert this generated mind map into outlines and slides for writing essays or presentations.
- Switch to Outline or Slide mode from the left side of the canvas and change the diagram accordingly.