You know math lives in every field, but the path from ancient counting to modern computing is not clear. That gap slows study and weakens insight.
A history of math timeline reveals why ideas rose when they did and what they unlocked next. With order, the story makes sense.
In this guide, I'll outline a decade-spanning math history timeline that you can scan in just minutes. You will explore key turns and how they link. I'll also share a hands-on method to build your own timeline.
In This Article
Why Knowing Math’s Past Helps You Understand the Future
Born from Human Needs
Farmers once counted crops. Builders divided land and shaped geometry. Traders used algebra to manage goods. Every new challenge pushed people to invent better tools.
Math in Everyday Life
Your phone’s GPS uses geometry first mapped by the Greeks. Credit cards depend on prime numbers from the 1600s. Video streaming works because calculus and Fourier analysis enable the compression of data.
The Modern Continuation
Today, that same pattern continues. Hospitals rely on linear algebra. Weather models use Newton’s equations. Music apps process sound using math once used to study heat.
People Behind the Formulas
Behind each formula is a problem someone tried to solve. Archimedes measured curved shapes. Newton studied planetary motion. Indian mathematicians built the number system we use daily.
A Chain of Ideas
Math builds like a staircase, each step supports the next. Arithmetic led to algebra, which in turn led to calculus. And every culture added a piece, from Arabic algebra to Chinese counting.
The Shared Human Story
Learning math means tracing this shared story of progress. You’re joining a long human journey of discovery.
Math Timeline: Key Milestones Through History
Before Zero Existed
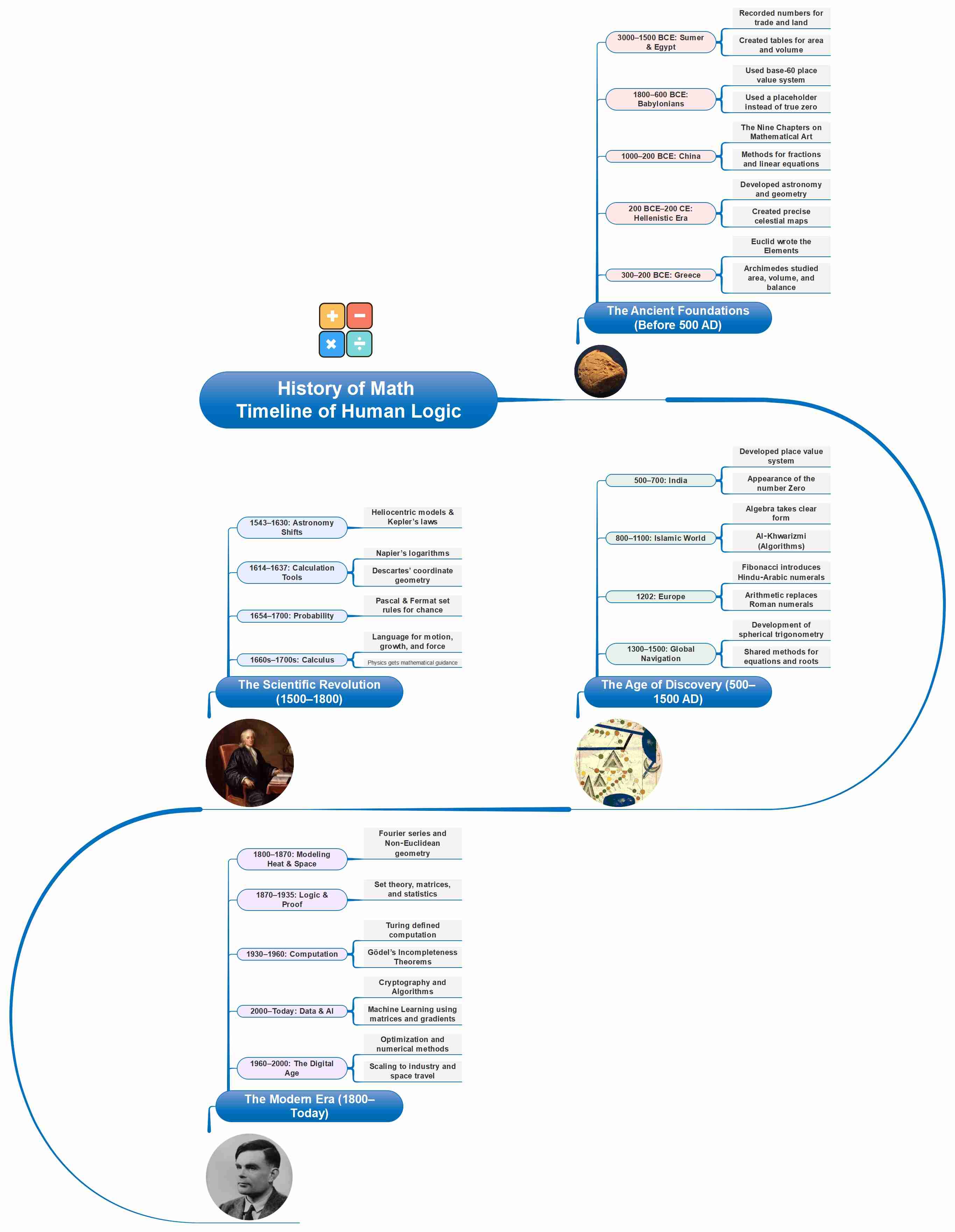
The Ancient Foundations (Before 500 AD)
- 3000–1500 BCE: Sumer and Egypt developed systems for recording numbers for trade and land transactions. They created tables for area and volume.
- 1800–600 BCE: The Babylonians used a base-60 place value system. Rather than the true zero, they used a placeholder.
- 1000–200 BCE: The Nine Chapters of China showed methods for working with fractions and solving linear equations using counting rods.
- 300–200 BCE: Greek work shaped proof. Euclid wrote the Elements. Archimedes studied area, volume, and balance.
- 200 BCE–200 CE: Hellenistic astronomy and geometry developed, using precise triangles and circles for celestial maps.
When Scholars Connected the Dots
The Age of Discovery (500–1500 AD)
- 500–700: India developed a place value system. Brahmi numerals spread. The number zero appeared in texts later in this era.
- 800–1100: In the Islamic world, algebra took a clear form. The word algorithm came from al‑Khwarizmi. Sine, cosine, and tangent tables improved.
- 1202: Fibonacci’s book helped bring Hindu‑Arabic numerals to Europe. Written arithmetic replaced many Roman numeral methods.
- 1300–1500: Navigation and mapmaking work led to the development of spherical trigonometry. Chinese and Islamic texts shared methods for equations and roots.
When Math Became a Tool for Science
The Scientific Revolution (1500–1800)
- 1543–1630: Astronomy shifted with heliocentric models and Kepler’s laws. Data needed stronger numerical tools.
- 1614–1637: Napier’s logarithms and Descartes’ coordinate geometry speed calculation and linked algebra to geometry.
- 1654–1700: Probability began with games of chance and risk. Pascal, Fermat, and others set rules for chance.
- 1660s–1700s: Calculus appeared in Europe. It gave a language for motion, growth, and force, which guided physics.
The Math Behind Every Modern Innovation
The Modern Era (1800–Today)
- 1800–1870: Fourier series modeled heat and waves. Non‑Euclidean geometry showed new spaces. Group theory began.
- 1870–1935: Set theory and logic formalized proof. Vectors and matrices grew. Statistics gained tests and models.
- 1930–1960: Turing defined computation. Gödel showed the limits of formal systems. Probability meets information theory.
- 1960–2000: Control, optimization, and numerical methods scaled to industry, climate, and space.
- 2000–Today: Cryptography, algorithms, and data science used number theory, linear algebra, and calculus at scale. Machine learning uses matrices, gradients, and optimization algorithms.
Great Mathematicians and Their Impact
Ancient Thinkers Who Defined Logic
Pythagoras
His triangle rule checked right angles. It allows builders to confirm frames and designers to compute distances without drawing a curve.
Archimedes
His principle explained floating and sinking. His area tricks previewed the idea of adding tiny slices that later grew into new methods.
Aryabhata
He gave accurate values for π and established trigonometric tables. These helped refine calendar cycles and align observations with calculations.
Revolutionaries Who Changed the Rules
Isaac Newton
He linked forces to measured change and created tools to sum tiny effects. Later, Physics and engineering started relying on this to predict motion and load.
Carl Friedrich Gauss
He led work in numbers, shapes, and data. The normal curve, least squares, and modular arithmetic began to support risk models and map control.
Leonhard Euler
He established clear symbols and found results that connect the discrete and continuous worlds. Graph ideas he started to support path planning and network flow.
Modern Minds Who Shaped Technology
Alan Turing
He set the idea of a simple device that can run any precise instruction list. That idea fits under today’s software stack.
Kurt Gödel
He proved there are true statements that no rule set can prove within itself. It set a boundary for what math and machines can decide.
Srinivasa Ramanujan
He wrote identities that still unlock hard sums and number patterns. Many active areas have built on his notes and later proofs.
How to Create a History of Math Timeline in EdrawMind
Building a math history timeline in EdrawMind is quick once you know the steps. Here’s how I do it:
Step 1 Start from a Clean Timeline Template
- I open the Templates Gallery in EdrawMind, search for “historical timeline,” and pick a simple, suitable history layout.
- Then, I click Duplicate to start my own version.
Step 2 Enter Consistent Entries and Notes
- I start by renaming the primary node to “History of Math Timeline” and inserting decade subtopics.
- For every node, I follow the format “Year - Name - Result” and keep it short and uniform.
- Then, I add a one-line note to make it easier to recall later.
- If needed, you can attach a hyperlink to the source page to check details when preparing lessons.
Step 3 Make It Scannable with Theme and Tags
- Next, I select a theme with high contrast and assign one color per era to make the timeline easy to scan.
- For a more personal color scheme, you can click on all the entries, choose one color, and then repeat this process for each era.
- You can customize the layout from the right-side panel.
- Select any node to modify branch style, connectors, text, style, color, etc.
Step 4 Present, Share, or Export Your Handouts
- When I’m ready, I click Slides to rehearse the timeline order and fix any crowded nodes.
- Finally, I export the timeline as a PDF for handouts and as a PPT for lecture slides.
- If you need, use the Share button to generate a view link and keep an editable copy for staff.
Why Use EdrawMind for Historical Timelines
EdrawMind helps you focus and prevent clutter while creating diagrams.
- Traverse Mode shows one topic at a time for clean teaching.
- Topic numbering keeps eras and decades in order.
- Work efficiently with keyboard shortcuts: press Tab to add subtopics and Enter for siblings.
- Export to SVG or HD images for print, and to Word for a text handout that mirrors your map.
Tips for Creating a Meaningful Timeline
- Decide which discoveries to include. Pick first finds, rediscoveries, or both. Choose pure math, applied math, or both. Write these rules at the top to stay focused.
- Check everything with at least two sources. Note conflicts and keep links for later verification.
- Cover all major eras, but focus on two or three key discoveries per century. Depth beats quantity.
- Separate practical use from theory. Show when solutions came before formal frameworks.
- Highlight simultaneous discoveries and disputes. Mark independent achievements and credit conflicts.
- Use symbols to identify types of discoveries. For example, triangles for theory, circles for applications.
- Include failures and dead ends. Record problems that took centuries to solve.
- Group-related discoveries. Cluster topics to show evolving systems.
- Adjust the detail by era. Ancient times can get broad strokes; modern times can be more specific to a particular decade.
- Measure impact, not novelty. Prioritize discoveries that influenced later work the most.
- Work backward from modern tech. Trace today’s tools to their historical math roots.
Wrap-Up
From counting crops to AI, math has evolved over 5,000 years. Zero altered arithmetic, calculus explained motion, and Turing’s insights helped humans create computers. Every discovery is built on the last.
That illustrates the importance of math history timelines.
So, start EdrawMind, select a timeline template, and add milestones that interest you. Turn math history into visible patterns the way you want it.