When you’re analyzing a business, it’s easy to focus only on what happens inside the company. But what about the outside forces that can change everything?
You need to make a PESTLE analysis. It examines politics, economics, social issues, technology, legal issues, and the environment to provide a broader perspective.
By studying a PESTLE analysis example, you get a clearer sense of the challenges and opportunities shaping a brand’s future.
In this guide, you’ll explore examples from global companies and even entire countries, so you can see how this framework works in action.
In this article
What Is PESTLE Analysis?
The PESTLE analysis is a tool to identify macro (external) forces an organization faces in its business. More specifically, a PESTLE analysis examines the external challenges faced by a business. And guides to overcome them.
The external challenges encompass Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors. The word "PESTLE" is an acronym for these six factors.
PESTLE analysis is an important marketing tool. It helps every business identify significant changes in the broader business landscape, thereby enabling better strategic business planning.
There are many variants of the analysis to fulfill the needs of businesses with unique requirements. They can use variants as needed.
For example, if the technological factor is not relevant to an industry, they can choose a variant that excludes it. A few widely used variants of PESTLE analysis are STEEPLE, SLEPT, and PESEL.
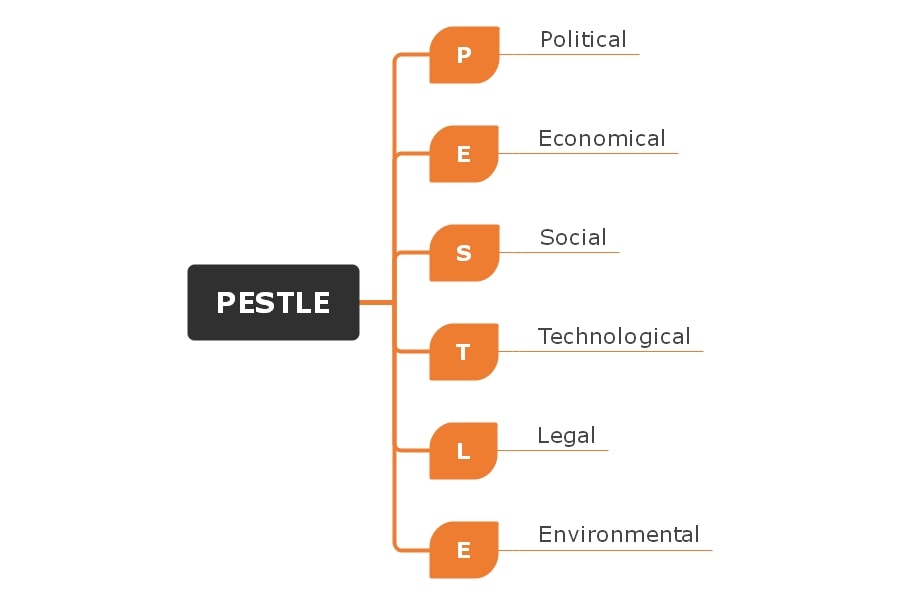
What Are the 6 PESTLE Factors? With Complete Lists
This section discusses each factor of the PESTLE analysis with examples and try to understand how they impact a business.
Political
The P stands for political, the first and an essential factor of the PESTLE analysis model. The political factor determines how the government and its policies may impact a business.
This part analyzes the government's policy-making patterns regarding business laws and regulations, like tax guidelines. It also examines business-to-political relations and their impact on the overall market.
The political stability or instability in a country, along with its potential outcomes. The government's behavior with businesses in general. The political factors deal with such and many other questions.
Summarization of the political sub-factors:
- Government stability
- Political policy
- Tax guideline
- Fiscal laws
- Trade regulation
- Safety regulation
- Employment laws
Economic
E stands for economic. The economy significantly affects a business's organizational operations. For example, equipment prices and maintenance costs increase with inflation and rising interest rates.
Additionally, with a rise in the currency exchange rate, the duty on imports of raw materials increases, ultimately leading to a corresponding rise in product prices. The economy directly impacts the growth and performance of the industry.
The end consumer's financial state is also essential. An affordable and high-quality production lays the foundation for a successful business; you can achieve this only when the economic factor is carefully analyzed.
Summarization of economic sub-factors:
- Inflation rates
- Interest rates
- Economic growth
- Employment or unemployment rates
- Currency exchange rates
- Raw material costs
Social
S is for social. This factor helps a business understand its end consumer needs. The focus remains on the social environment, public behavior, and identifying emerging trends among the people.
It deals with the customers' values, hopes, desires, and fears. It also discusses what motivates or disgusts the general masses and why. Careful analysis of social factors is essential for developing a robust business plan and strategy.
The social factor enables companies to conduct a thorough customer analysis, helping them address their customers' problems with their products or services.
Summarization of social sub-factors:
- Demographic characteristics
- Education levels
- Customs and values of the population
- Cultural trends
- Attitude changes
- Changes in lifestyles
Technological
Technological factors consider the rate of technological development and innovation that could affect a market or industry.
Technology is rapidly growing, and the industry should be able to acquire that technology as soon as possible to remain competitive before the competition overtakes the market.
Technology also poses threats. For example, it is also possible that a particular product could be replaced by a much cheaper and more advanced alternative from another company.
Therefore, keeping oneself updated on the new trends and advancements in an industry is necessary. Every organization must possess the latest technology required to develop and enhance its products or services.
Summarization of technological sub-factors:
- Changes in digital or mobile technology
- Automation
- Research
- Development
Legal
It is crucial for an organization to understand what is legal and allowed within the territories of the country in which it operates.
They must also be aware of any possible changes in laws or legislation in the country and their impact on industry operations.
Summarization of legal sub-factors:
- Employment legislation
- Consumer law
- Healthy and public safety
- Local trade regulation and restrictions
- International trade regulation and prohibitions
Environmental
A successful business model gives importance to the environment. Carbon footprint, climate change, and waste disposal are critical issues for it. Also, the environmental impacts are essential for the low-cost and good-quality production.
For example, a product suitable for a cold atmosphere should be prepared in a low-temperature area rather than investing in air conditioning. Also, proper environmental conditions ensure that the products remain fine for a longer period.
Summarization of environmental sub-factors:
- Climate
- Recycling procedures
- Carbon footprint
- Waste disposal
- Sustainability
When To Use PESTLE Analysis?
PESTLE analysis is used before a strategic business decision. The analysis effectively detects and understands broad, long-term trends in the business background. Therefore, it is extensively used in a range of business planning situations.
Strategic Business Planning
With a PESTLE analysis, you can obtain contextual information about the business direction, including whether the business is growing or not. Growth targets, brand positioning, and risks to productivity ratios.
Expansion of the Business
The PESTLE analysis may also help determine when and where a business should expand. It can be determined by considering labor costs, tax laws, and the need for the product in the industry's planned expansion area.
Workforce Planning
PESTLE analysis can help to plan the required workforce for an organization. For example, a technical workforce will be required for a technology-related business.
A PESTLE analysis helps choose the right workforce by considering factors such as labor availability, skilled labor availability, and cost.
Product Development
A PESTLE analysis helps determine if a product or service still fulfills the needs of consumers in the marketplace.
It may also indicate which product would best suit the current market conditions. Also, it reveals why a product fails or succeeds in similar business conditions.
Marketing Planning
A PESTLE analysis helps in effectively marketing a brand or product. It deals with the factors required to sell a product proficiently to the customers. Many major organizations use the PESTLE analysis for product promotion and marketing.
Organizational change is a PESTLE analysis example. It addresses the potential opportunities and threats associated with labor changes, including skills, increments or decrements in labor costs, shortages, or current workforce capabilities.
How To Do PESTLE Analysis?
Before doing a PESTLE analysis, it is better to arrange a team of experts for the task. A team could be organized based on six PESTLE factors. It is necessary to obtain information on each area of the PESTLE model.
Every element has its importance. If anything is left out, the analysis would not be very helpful. Therefore, field experts are required for this analysis, i.e., a technical team member could be hired to research the technological aspects.
Likewise, an environmentalist could be employed to study the environmental factors.
There are ten steps to conduct a successful PESTLE analysis.
- Identify the scope of research that encompasses both the present and potential future scenarios.
- Decide who will collect the information and how.
- Identify appropriate sources of information.
- Gather the information. Ensure that the information is arranged correctly to be used easily again.
- What did you find? Analyze the information carefully.
- Create a list and categorize the items according to their importance. The most important things come first, and the less important things come last.
- Identify the options you have to address the issues.
- A discussion document for all stakeholders.
- Discuss the findings with stakeholders.
- Discuss the plan and decide on actions to take.
PESTLE Analysis Examples
A PESTLE analysis reveals how global giants respond to external forces and why their strategies take the form they do.
Here, you’ll find PESTLE analysis examples from well-known brands, industries, and even countries.
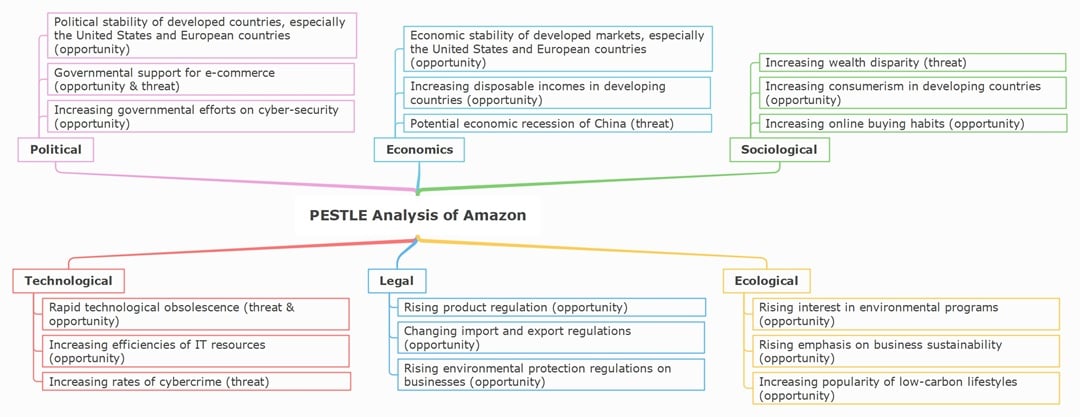
Amazon
In this PESTLE analysis example, Amazon looks strong in countries that support digital growth and stable trade. But it’s not all smooth sailing. Data privacy laws and cybersecurity issues require Amazon to remain vigilant.
You’ve probably noticed how Amazon’s global reach helps it survive economic dips. That’s true. Still, price-sensitive markets can hurt sales. Socially, more people prefer online shopping, but concerns about warehouse conditions or treatment of workers hurt trust.
Technology is where Amazon shines. AWS is powerful, and innovation moves fast. The catch? It has to keep up or risk falling behind.
Legal issues, like taxes and monopoly power, continue to follow the company. On the environmental side, Amazon faces pressure over packaging and fuel use, so it’s investing more in sustainability.
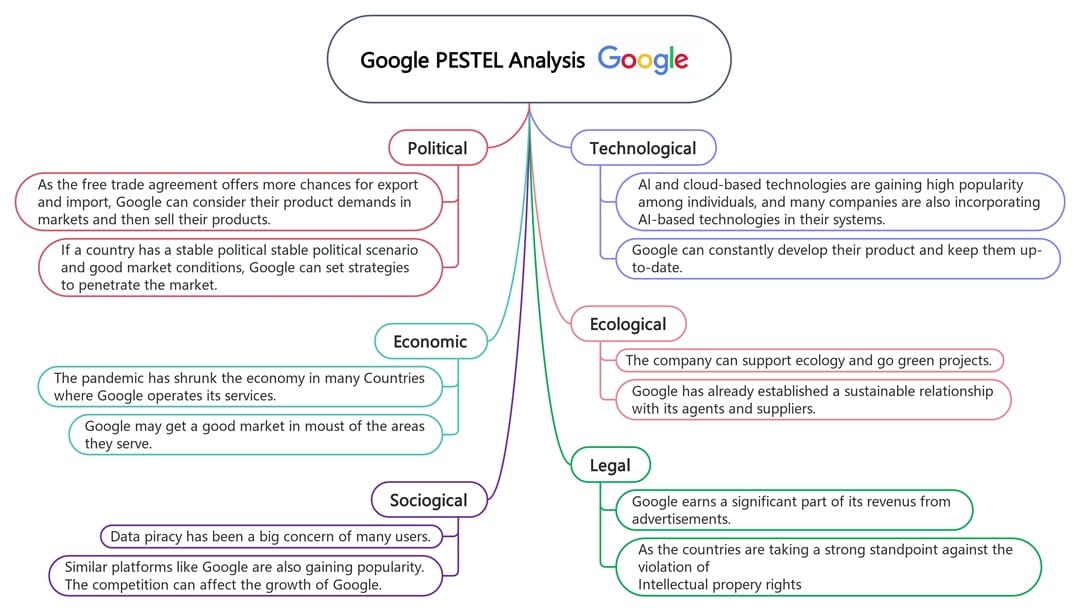
Google rides on global free trade, AI tools, and reliable cloud systems. However, this PESTLE analysis example of Google reveals cracks. Competition in tech spaces and ad regulation keeps the pressure high.
The pandemic affected ad spending, but demand rebounded fast. Even so, the economic climate affects advertisers' budgets. On the social front, users rely on Google products. Still, public trust is shaky due to concerns over data tracking and online monopolies.
Google is a leader in cloud, AI, and quantum computing. It stays ahead by investing money into research and development.
Legally, Google is under constant legal fire, from copyright disputes to anti-competitive behavior. Google’s eco-friendly push is real. It’s investing in renewables and encouraging green supply chains.
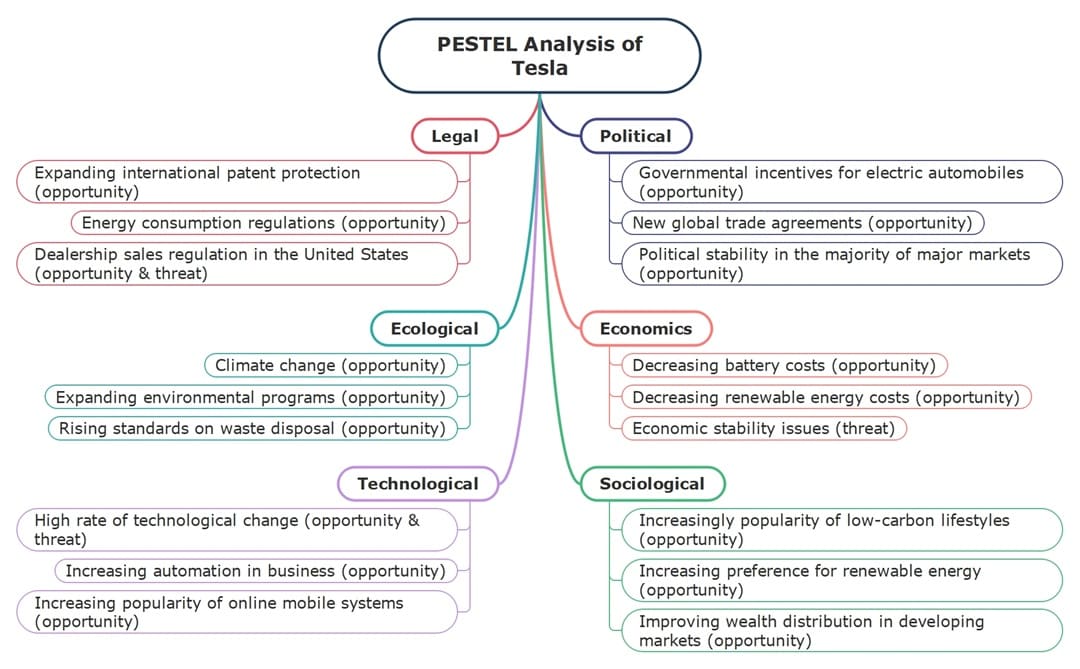
Tesla
Here’s a PESTLE analysis example where innovation drives everything. Tesla benefits from governments' backing of electric vehicles through incentives and policy support. Battery prices are dropping, and energy storage is improving, which helps increase affordability.
You might’ve noticed how EVs are becoming part of a low-carbon lifestyle. Tesla is riding that trend. Tech-wise, they lead in automation and self-driving features. But staying ahead means constant upgrades, which isn’t cheap.
Legally, safety recalls and labor concerns grab headlines. On the environmental front, Tesla is both a hero and a target. While it helps reduce fuel emissions, battery waste, and factory emissions bring their own set of problems.
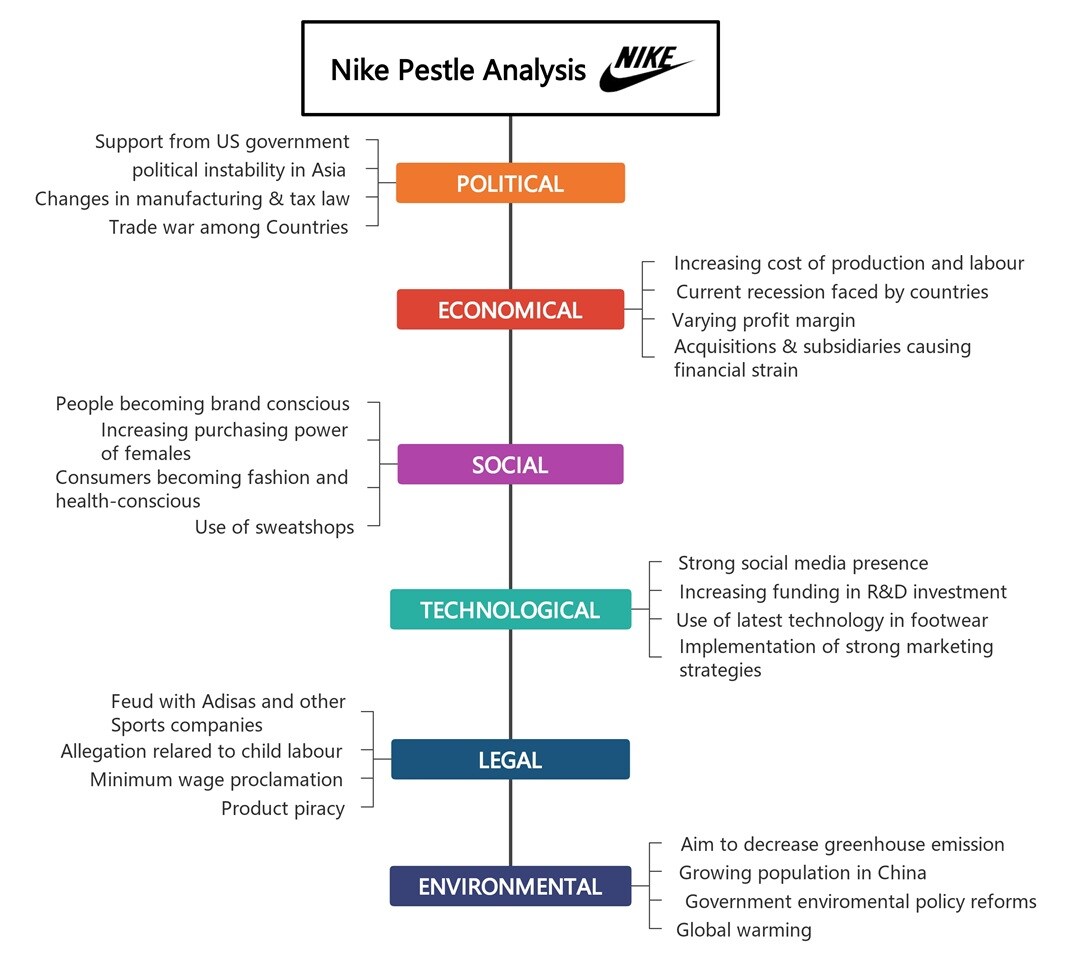
Nike
Nike gains support from favorable trade policies, yet global tensions and tariffs can hit margins. The PESTLE analysis example illustrates how social shifts, such as the demand for ethical fashion, impact Nike’s brand image.
Tech and e-commerce help it stay connected, but labor laws and environmental scrutiny raise the stakes.
Legally, counterfeit products and labor law violations are challenges. Nike has cracked down on both but can't escape the spotlight. Environmentally, it's investing in sustainable materials and reducing packaging waste.
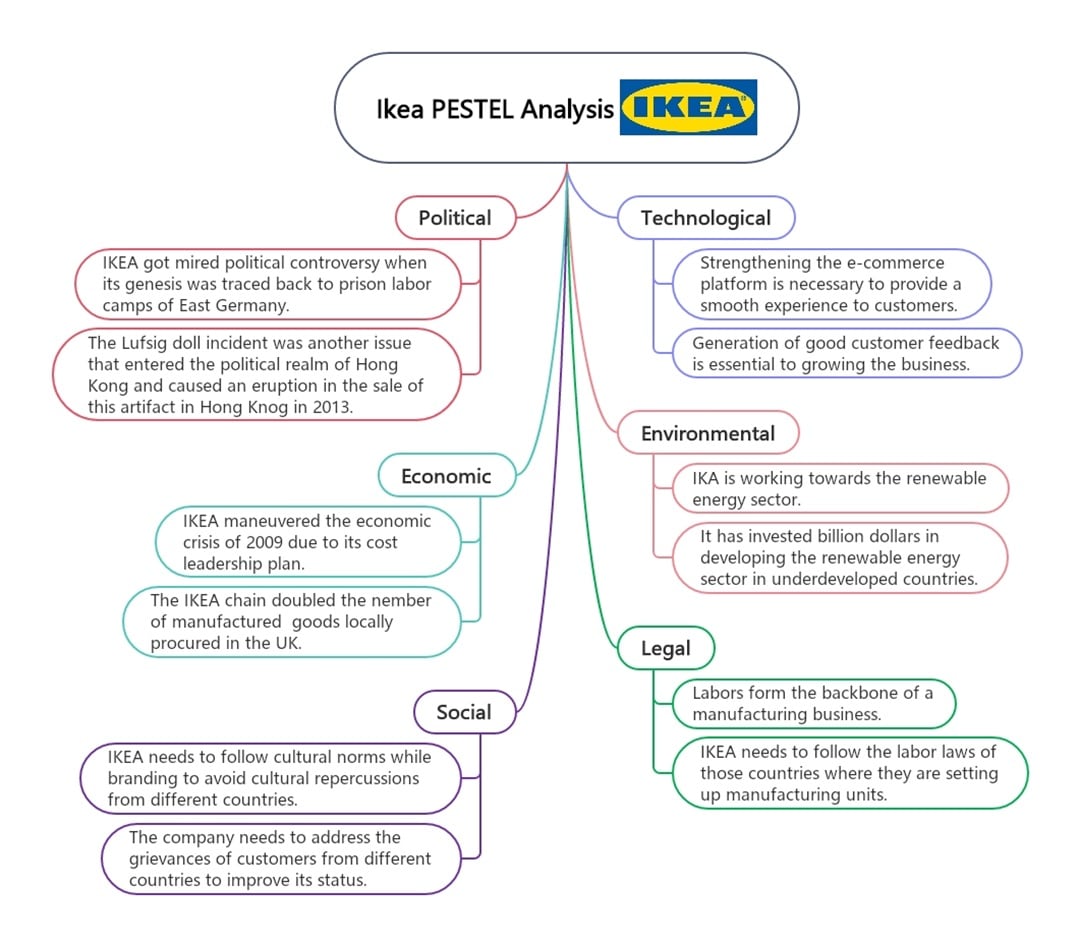
IKEA
IKEA's PESTLE analysis example illustrates how the company addresses political backlash and cultural sensitivities. It adapts to local preferences and effectively leverages digital sales. However, it must meet global labor standards and manage its carbon footprint as its scale grows.
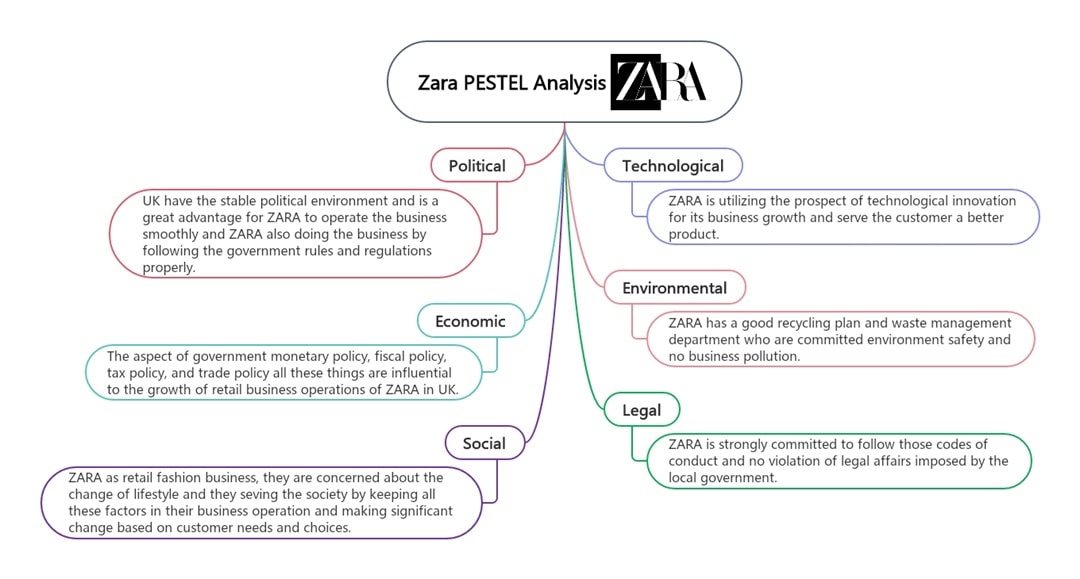
Zara
In this PESTLE analysis example, Zara’s strengths are also its risks. The brand is quick to turn fashion trends into in-store products. That speed gives it an edge, especially in markets with strong trade infrastructure.
Zara thrives because it reads lifestyle shifts well. But fast fashion creates waste and relies on low-cost labor, which can backfire socially and legally.
You’ve probably seen how they push online sales hard; tech helps a lot with forecasting and logistics. On the legal front, the brand’s focus on ethical supply chains has improved.
Still, critics push for more. Environmental impact remains one of the brand’s biggest challenges, despite recycling efforts.
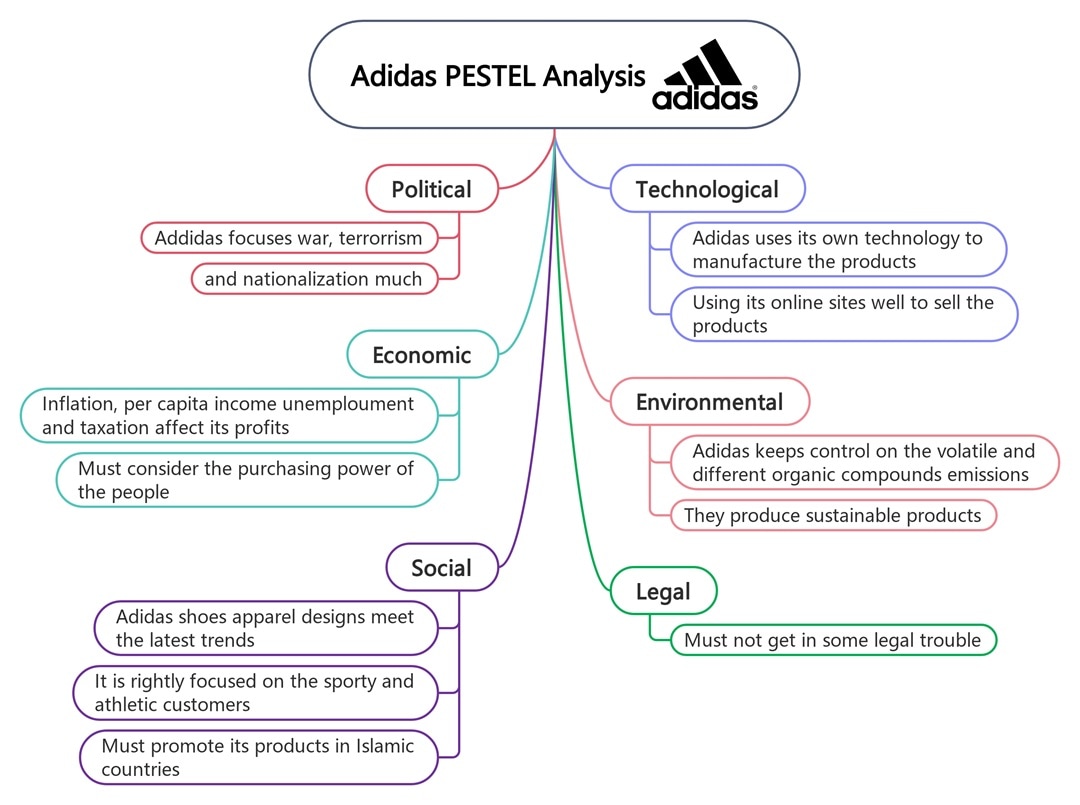
Adidas
Adidas keeps evolving. This PESTLE analysis example shows that it benefits from stable political environments and fair trade. However, inflation and fluctuating currencies remain risks.
Health trends and the rise of wellness culture have given Adidas a significant social boost. You’ve probably seen its campaigns shift toward a lifestyle focus, not just athletics. Technology helps, from better shoe design to seamless online shopping.
Legally, the brand protects its identity while complying with international labor laws. On the green side, Adidas works with ocean plastics and sustainable materials. That said, fast-moving consumer expectations force it to keep improving.
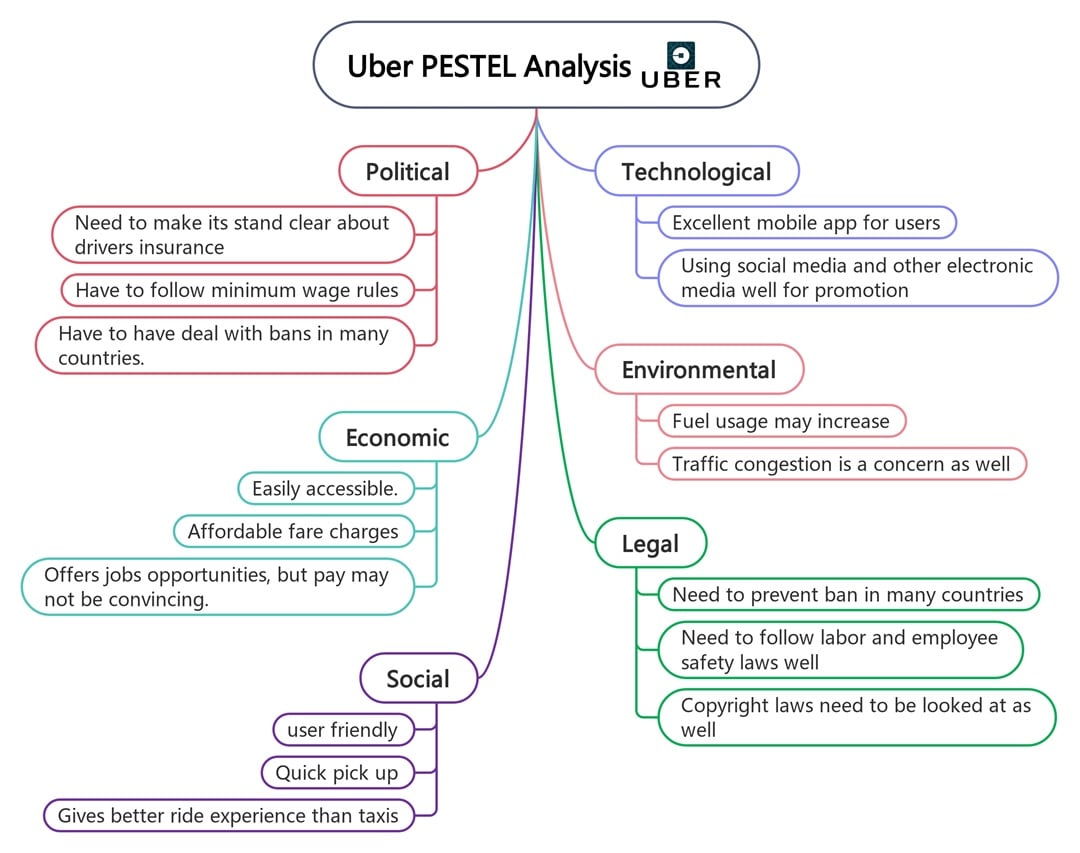
Uber
This PESTLE analysis example illustrates how legal hurdles and political obstacles mark Uber’s journey. From driver protests to regulatory bans, politics can make or break operations in certain countries.
It succeeds economically because of accessibility and competitive fares. But when drivers earn less than minimum wage, public perception takes a hit. Socially, riders love convenience, but safety and fairness are always under review.
Uber’s success depends on tech, including GPS, in-app payments, and data matching. Still, environmental concerns, including traffic and emissions, remain issues. Legally, it must play nice with labor laws while still defending its gig economy model.
Starbucks
Starbucks rides on habits, and this PESTLE analysis example shows how strong its roots are in urban life. Politically, food regulations and tax laws affect how it prices and serves products.
Economic shifts impact what people can afford, especially with rising coffee bean and labor costs. Socially, it benefits from lifestyle trends that favor cafe culture. Nonetheless, affordability, competition, and the ethical sourcing of products have been constant worries.
Starbucks uses technology through the customer programs, store app, and food delivery apps. Expectations from them also include co-efforts such as recyclable packaging. Legally, food safety, employment contracts, and store franchising are also monitored.
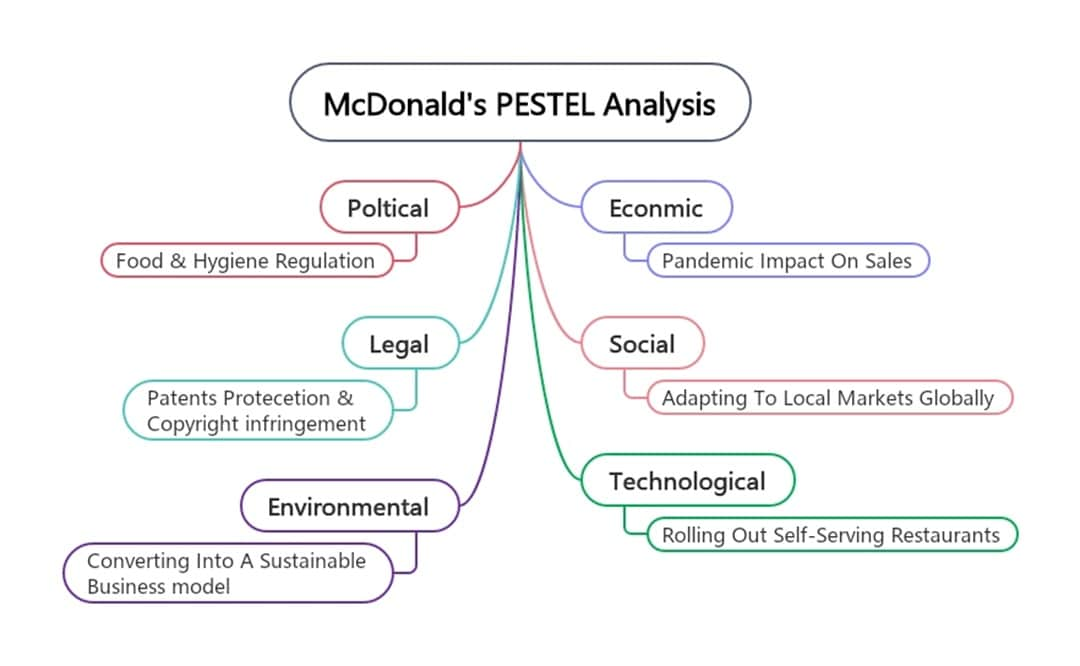
McDonald’s
This PESTLE analysis example captures a brand that adjusts quickly. It faces strict food laws, and countries expect top-notch hygiene. When COVID hit, sales dropped sharply, but delivery apps and drive-thru options helped cushion the blow.
McDonald’s reshapes its menu to fit local markets. Tech investments in self-service and mobile orders speed things up. But legal pressure remains, from franchising rights to health compliance.
Environmentally, the brand is cutting waste and aiming for a greener supply chain. It’s a work in progress, but it’s happening.
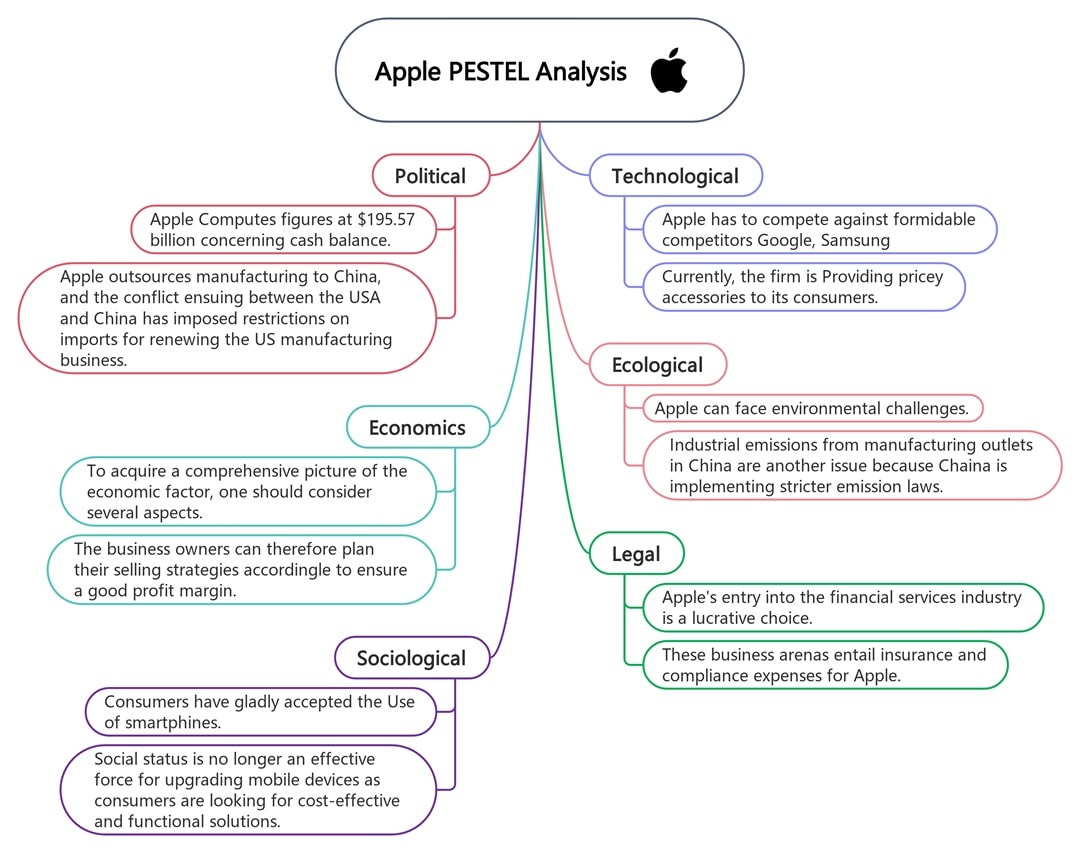
Apple
Apple’s brand power remains strong, but this PESTLE analysis example reveals challenges. Politically, US-China tensions affect manufacturing and export costs. Economically, Apple’s pricing model relies on high margins, so inflation matters.
The social acceptance of smartphones remains high. Its cash reserves help, but tech rivals and public sentiment around device pricing shift the balance. Environmentally, it involves investing in closed-loop systems and utilizing greener materials.
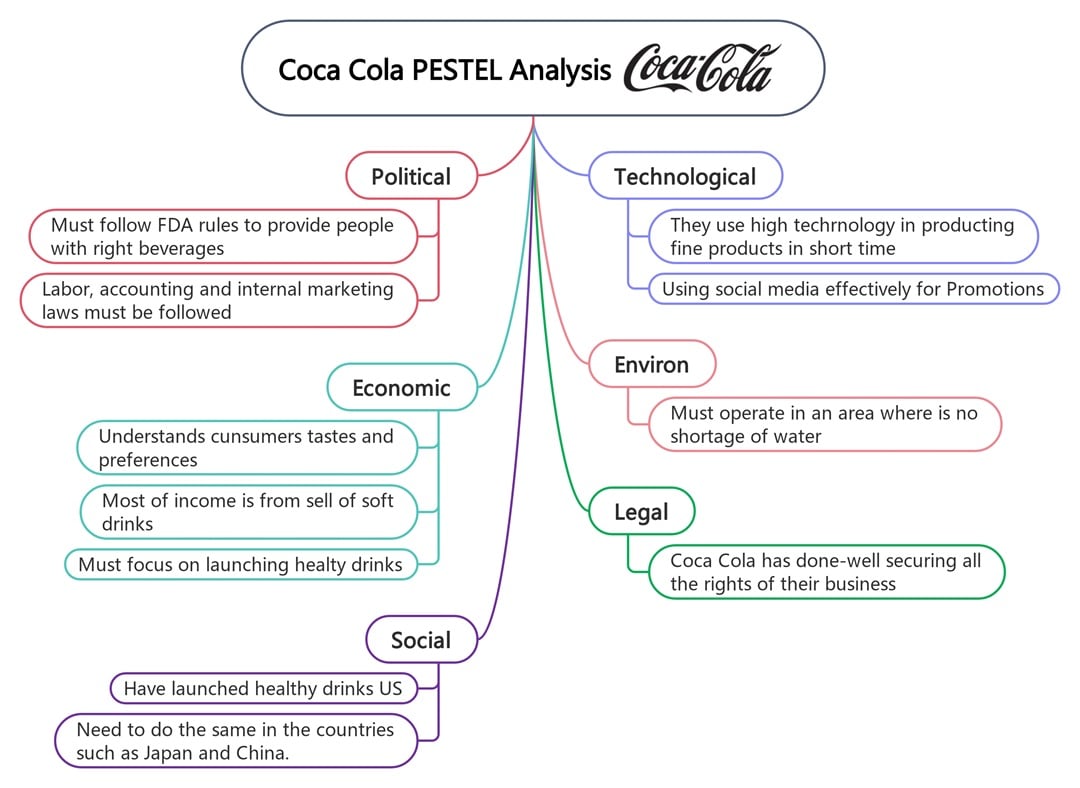
Coca-Cola
Show how Coca-Cola faces sugar taxes and health-conscious consumers in this PESTLE analysis example. Inflation drives up costs, but its global reach helps mitigate that impact. Regulations on marketing and plastics are also growing fast.
Health trends are reshaping what people want to drink, and as a result, Coca-Cola has begun offering low-sugar and functional options. Tech helps optimize distribution, forecast trends, and monitor quality.
Legally, labeling, advertising, and safety laws keep the company accountable. On the environmental front, it’s investing in circular packaging and cleaner water use.
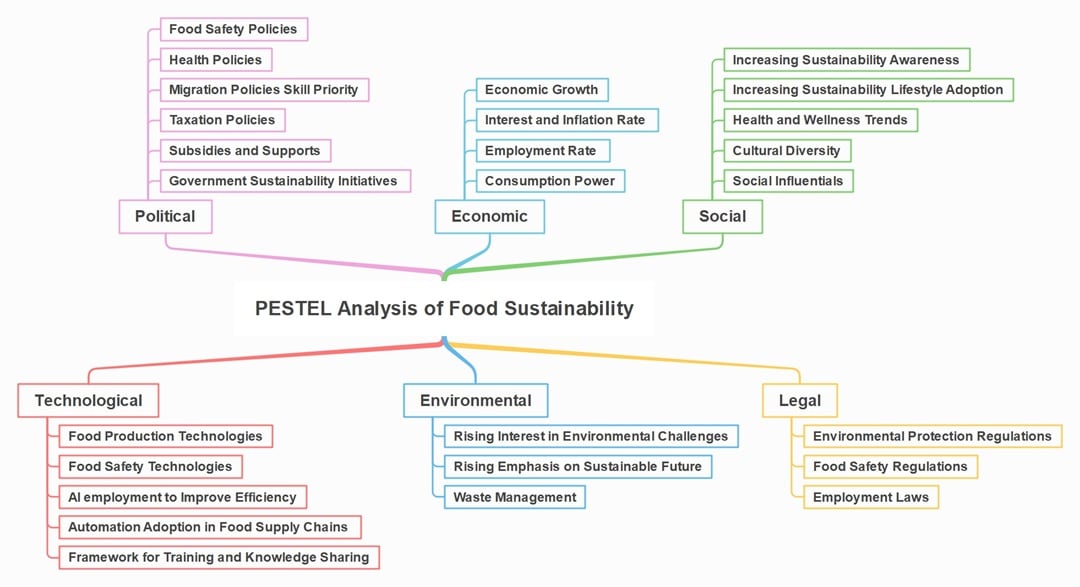
Food Sustainability
This PESTLE analysis example expands beyond a single brand. It zooms in on how food systems evolve. Policies focus on health and safety, while inflation affects affordability.
Public demand is shifting to ethical choices. Innovation in farming and distribution matters more than ever. Environmental and legal factors drive tighter food safety rules.
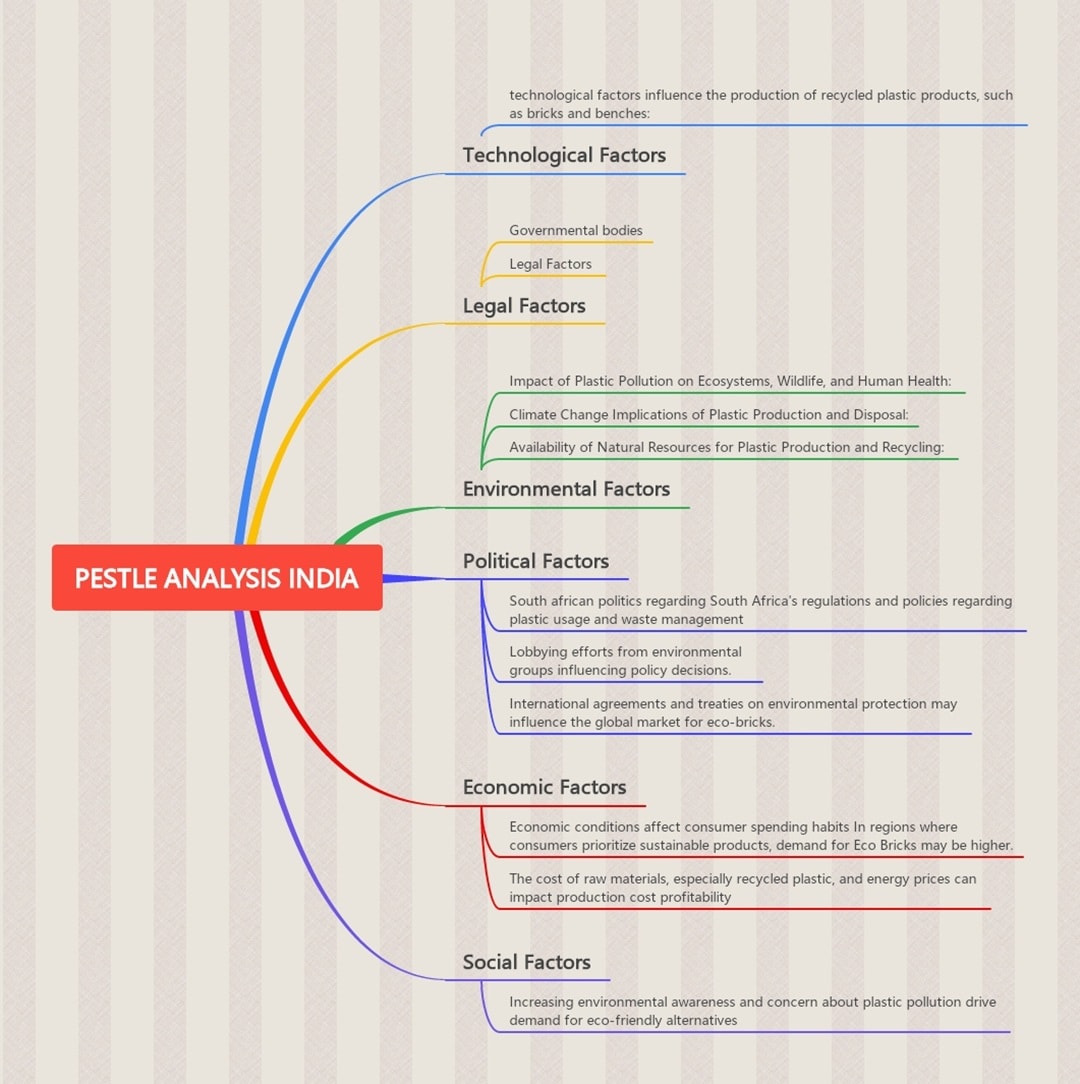
India
India’s PESTLE analysis example shows momentum around plastic recycling. Global agreements and domestic rules shape the landscape. Technological innovations drive new methods for reusing waste. But economic hurdles and social behaviors still slow progress. Government enforcement remains crucial.
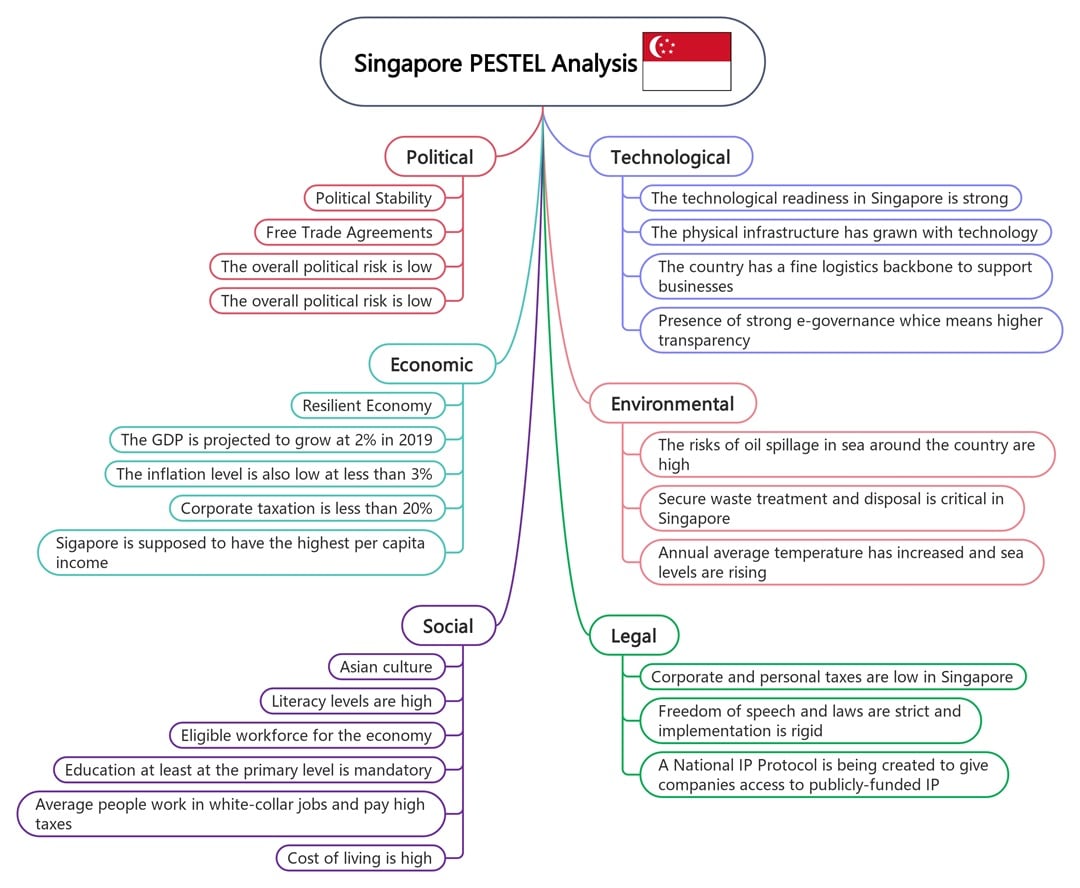
Singapore
Singapore’s political stability and good governance give it an edge. This PESTLE analysis example highlights low corporate tax, strong education, and tight IP laws.
Socially, a literate workforce supports growth. Tech-wise, it’s a global leader in logistics and automation. Singapore is now doubling down on waste management and climate resilience.
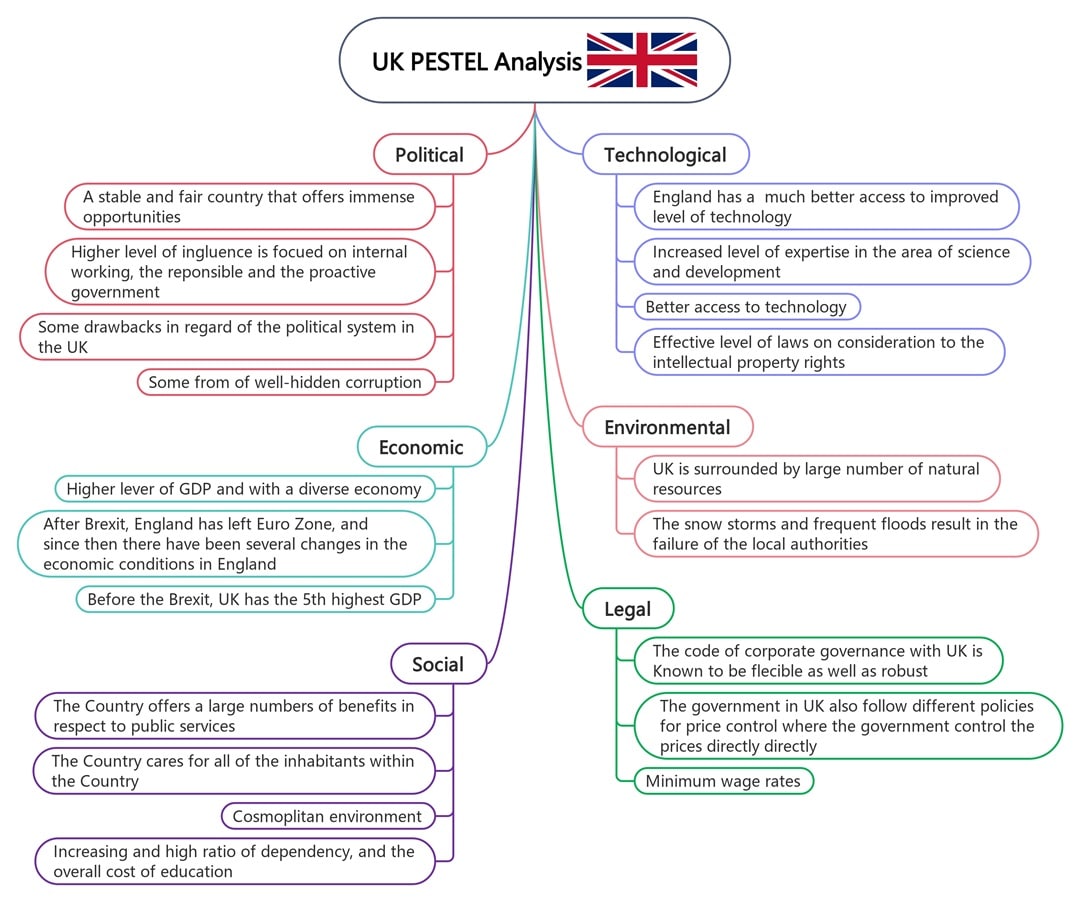
UK
In this PESTLE analysis example, the UK remains an economic heavyweight, but it’s also facing changes. Politically, Brexit caused ripple effects. Economically, inflation and housing are pain points, even with a strong service sector.
Socially, the UK blends tradition with modern diversity. Tech and research remain strengths. Environmental risks, especially flooding, keep policymakers on alert. Legal systems offer flexibility and stability for businesses.
Now that you’ve seen how each PESTLE analysis example works in real scenarios, you might be wondering how to create one for your own project. The good news is you don’t need complicated tools to do it.
You can make one for free using Wondershare EdrawMind. It’s easy to use, beginner-friendly, and comes with templates to help you get started quickly, even if this is your first time.
How To Make a PESTLE Analysis for Free Online
Follow these steps to create a PESTLE analysis for free with EdrawMind online:
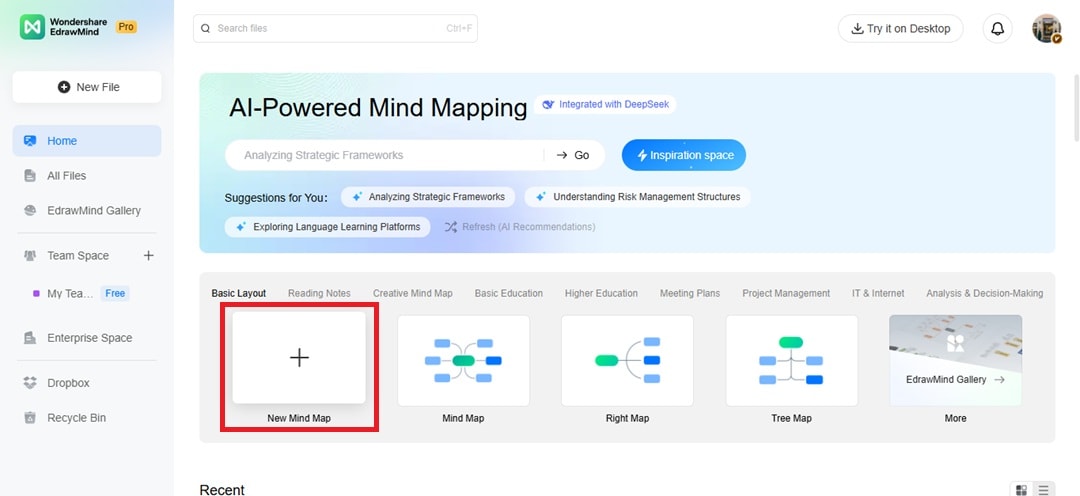
Step 1 Start Your Workspace
Click New Mind Map on the Basic Layout tab from Home.
Alternatively, go to the EdrawMind Gallery on the left side menu and search “PESTLE” to use a template.
Rename the Main Idea to your company or project.
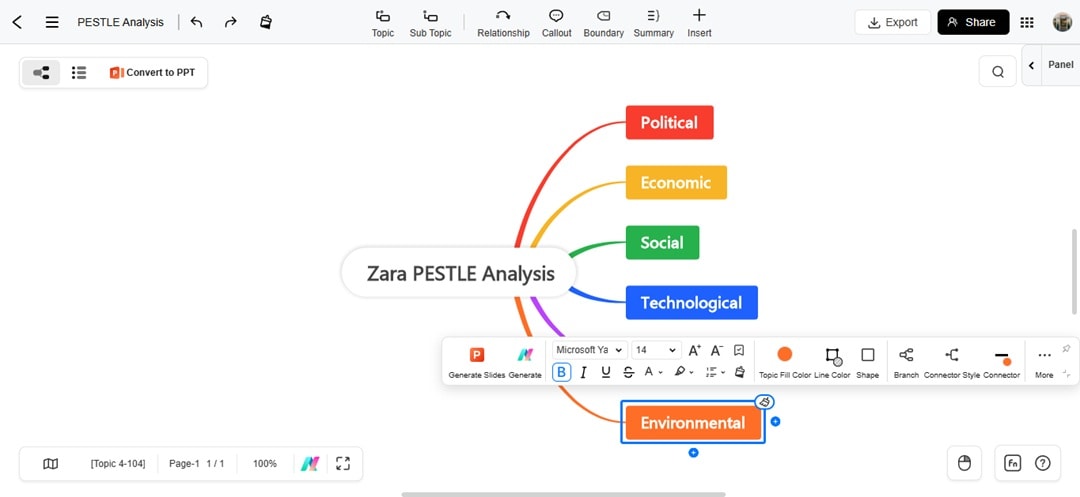
Step 2 Create the PESTLE Analysis
Add six first‑level branches: Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental.
On your keyboard, use the Tab key to add sub-branches and the Enter key to add siblings for quick outlining.
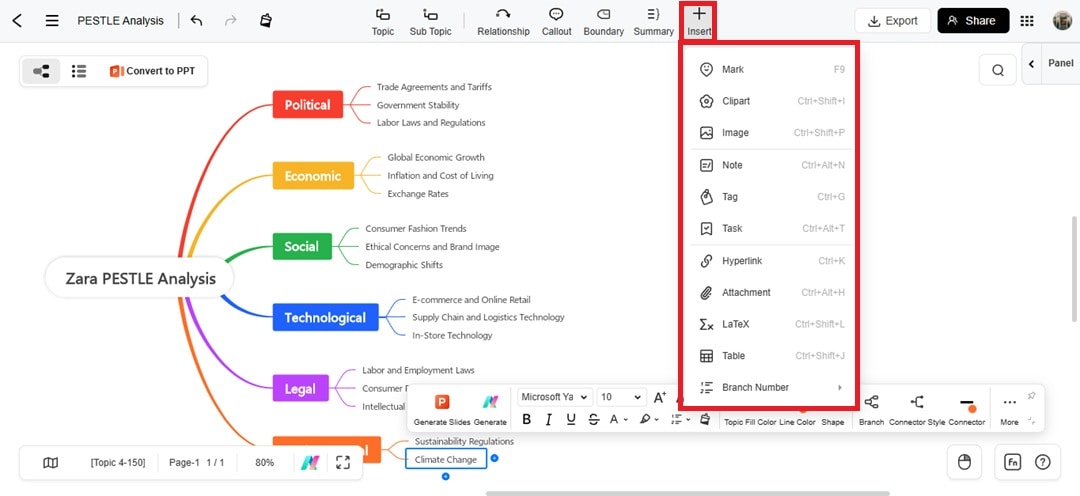
Step 3 Add Research and Proof
Add content to the subtopics in the mind map.
Link sources in Notes or add URLs to nodes for quick checks. To do so, select a topic, go to Insert from the top menu, and choose Note or Hyperlink.
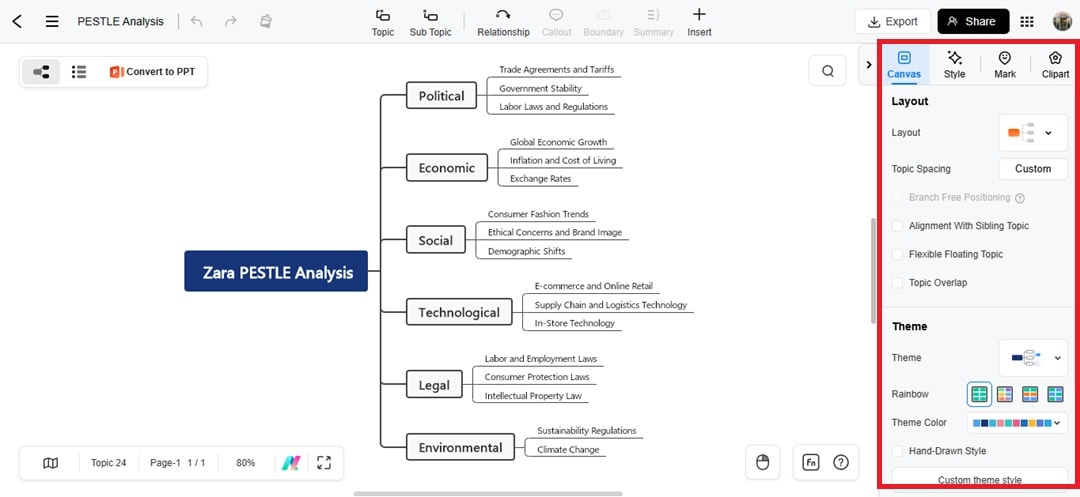
Customize the mind map from the right panel.
Step 4 Share and Export
Click "Share" to create a link for your teammates.
Export to PNG, PDF, or Word for reports.
Use Presentation mode to walk stakeholders through each branch.
Pros and Cons of PESTLE Analysis
- It encourages critical thinking.
- It helps to prepare the business for the future.
- It helps to manage business risks and threats.
- It helps businesses capitalize on new opportunities.
- It is a straightforward approach with a simple framework.
- It takes a lot of time to process.
- It involves many steps.
- It needs to be done at regular intervals.
- External factors can change quickly, making it challenging to present and analyze up-to-date information.
Final Thought
PESTLE analysis helps in the development and growth of businesses and organizations. It helps to analyze the strengths and weaknesses of industries. A proper PESTLE analysis report may help you grow your business.
With EdrawMind, you can create eye-appealing PESTLE analysis graphs and reports for your business with a few clicks and easily share them with your team members.
You can also select from 100s of already present templates and customize them according to your needs.